- Desmoulin's whorl snail
-
Desmoulin's whorl snail 
Vertigo moulinsiana Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda (unranked): clade Heterobranchia
clade Euthyneura
clade Panpulmonata
clade Eupulmonata
clade Stylommatophora
clade OrthurethraSuperfamily: Pupilloidea Family: Vertiginidae Subfamily: Vertigininae Tribe: Vertiginini Genus: Vertigo Subgenus: Vertigo Species: V. moulinsiana Binomial name Vertigo moulinsiana
(Dupuy, 1849)[2]Synonyms - Pupa moulinsiana Dupuy, 1849
- Pupa laevigata Kokeil, in Gallenstein, 1852
- Pupa charpentieri Shuttleworth, in Küster, 1852
- Pupa moulinsiana var. personata Moquin-Tandon, 1855
- Vertigo ventrosa Heynemann, 1862
- Pupa küsteriana Westerlund, 1875
- Pupa mulinsania var. octodentata Westerlund, 1878
- Vertigo limbata Moquin-Tandon, 1855
- Pupa desmoulinsi Germain, 1913
Desmoulin's whorl snail, scientific name Vertigo moulinsiana, is a species of minute air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc or micromollusc in the family Vertiginidae, the vertigo snails.
This species was named after the early 19th century French naturalist, Charles des Moulins.
Contents
Habitat
This species lives in marshes and swamps.
Desmoulin's whorl snail lives in calcareous wetlands, where there are tall sedges, saw-sedge (Cladium mariscus), reed-grass (Glyceria maxima) or the reed Phragmites australis.[3]
Distribution
The distribution of this species is Atlantic (the part of the Palearctic area which is under the direct climatic influence of the Atlantic Ocean), and southern-European.[4]
This small snail occurs across Europe as far north as southern Sweden.[5]
Within Western Europe, only the populations in England (Great Britain) and Ireland are considered to be viable,[5] although further populations exist in the Czech Republic (critically endangered, occupying White Carpathians Biospehere Reserve, Kokořínsko Landscape Protected Area and Southern Moravia),[6][7][8] in Poland (critically endangered)[9] and elsewhere in Europe (for example: Netherlands,[10] France).[11] Its conservation status in the Czech Republic in 2004-2006 is favourable (FV) in the report for the European Commission in accordance with the Habitats Directive.[12] Its conservation status in Spain is endangered and it occurs in two localities only: near Estañá lake and near Lake of Banyoles.[13]
Distribution of other European countries include Belgium, Switzerland, Italy, Germany, Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Denmark, Norway, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Belarus, Ukraine, Russia, Georgia and Azerbaijan.[1] Its distribution also include Algeria and Morocco.[1]
This species is mentioned in Annex II of the European Union's Habitats Directive.[14]
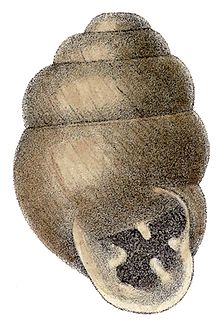
Shell description
The shell is dextral, minute, ovate, ventricose, obtuse at apex, smoothish, subperforate. Aperture is semiovate, 4-toothed: 1 tooth on the parietal wall, another on the columella, and two palatals, the lower one longer. The shell has 4 whorls, parted by a distinct suture, the last doubly larger than all the others together. Rather solid, glossy, subpellucid and of a uniform fulvous color.[15]
The shell of this species reaches about 3 mm tall. The shell is yellowish or brownish and translucent.[16]
Status in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, Desmoulin's whorl snail is listed as endangered, although it occurs in a number of areas in a band from Norfolk to Dorset, with outlying populations in Kent and the Llŷn Peninsula in North Wales[5] and has probably been under-reported in the past because of its minute size. Its presence on the site of the planned Newbury bypass caused the building of that road to be postponed; the building works were able to go ahead once the snails had been moved to a new habitat nearby. It is reported to have since died out at the new site,[17][18] but the same report states "Desmoulin's whorl snail is now considered less scarce than it was 10 years ago".
On a stamp
Deutsche Post featured V. moulinsiana on a 2002 German €0.51 postage stamp as part of a series on endangered species of animals.[19]
References
This article incorporates public domain text from reference [15].
- ^ a b c Steffek J. (1996). "Vertigo moulinsiana". 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. http://www.iucnredlist.org/search/details.php/22939/summ. Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- ^ Dupuy D. (1849). Catalogus extramarinorum Galliae testaceorum brevioribus specierum nondum descriptorum diagnosibus. pp. 1-4, p. 4, No. 248, Paris.
- ^ "Action plan for Vertigo moulinsiana". Joint Nature Conservation Committee. 2001–2007. http://www.ukbap.org.uk/UKPlans.aspx?ID=629. Retrieved 2007-06-19.
- ^ (Slovak) Lisický M. J. (1991). Mollusca Slovenska [The Slovak molluscs]. VEDA vydavateľstvo Slovenskej akadémie vied, Bratislava, 344 pp.
- ^ a b c "SAC selection species account: Desmoulin's whorl snail". http://www.jncc.gov.uk/ProtectedSites/SACselection/species.asp?FeatureIntCode=S1016.
- ^ (Czech) "Evropsky významné lokality v České republice". 2003. http://stanoviste.natura2000.cz/index.php?page=zivocich_detail&ZivocichID=132.
- ^ "Red List of the molluscs (Mollusca) of the Czech Republic". 2006-07-14. http://mollusca.sav.sk/malacology/redlist.htm.
- ^ Beran L. (2006). "New records of Vertigo moulinsiana (Gastropoda: Vertiginidae) and notes on its distribution and habitats in the Czech Republic". Malacologica Bohemoslovaca 5: 14–17. http://mollusca.sav.sk/pdf/5/5.Beran2.pdf.
- ^ Pokryszko B. M.. "Vertigo moulinsiana (Dupuy, 1849)". Instytut Ochrony Przyrody Polskiej Akademii Nauk. http://www.iop.krakow.pl/pckz/opis.asp?id=237&je=en.
- ^ (Dutch) "Vertigo moulinsiana". Stichting Anemoon. 2005. http://www.anemoon.org/anm/voorlopige-kaarten/landmollusken/wetenschappelijk/vertigo-moulinsiana.
- ^ (French) "Recherche de sites par espèce : Invertébrés : Vertigo moulinsiana (Vertigo moulinsiana)". Ministère de l’écologie et du développement durable. 2007. http://natura2000.environnement.gouv.fr/especes/1016.html.
- ^ (Czech) Dušek J., Hošek M. & Kolářová J. (2007). "Hodnotící zpráva o stavu z hlediska ochrany evropsky významných druhů a typů přírodních stanovišť v České republice za rok 2004-2006". Ochrana přírody 62(5): appendix 5:I-IV.
- ^ Ramos M. A. (1998). "Implementing the habitats directive for mollusc species in Spain". Journal of Conchology, Molluscan Conservation: A Strategy for the 21st Century, Special Publication 2: 125-132.
- ^ "Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora". Official Journal of the European Union (European Union) L 206: 0007–0050. 1992-07-22. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:31992L0043:EN:HTML.
- ^ a b Pilsbry H. A. & Cooke C. M. (1918-1920). Manual of Conchology. Second series: Pulmonata. Volume 25. Pupillidae (Gastrocoptinae, Vertigininae). Philadelphia. page 178.
- ^ "Vertigo moulinsiana". ARKive. http://www.arkive.org/species/ARK/invertebrates_terrestrial_and_freshwater/Vertigo_moulinsiana/more_info.html. Retrieved 2007-06-19.
- ^ "Concern for Newbury bypass snail". BBC News. 2006-07-27. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/5217558.stm.
- ^ Weaver M. (2006-07-27). "End of the road for protected snail". The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/conservation/story/0,,1831682,00.html.
- ^ (German) Bartl A.. "Bauchige Windelschnecke". http://www.briefmarken-archiv.de/brd/01/2002/a020602.htm. Retrieved 2007-05-14.
External links
Categories:- IUCN Red List conservation dependent species
- Vertigo
- Animals described in 1849
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.