- MD5CRK
-
In cryptography, MD5CRK was a distributed effort (similar to distributed.net) launched by Jean-Luc Cooke and his company, CertainKey Cryptosystems, to demonstrate that the MD5 message digest algorithm is insecure by finding a collision — two messages that produce the same MD5 hash. The project went live on March 1, 2004. The project ended on August 24, 2004 after researchers independently demonstrated a technique for generating collisions in MD5 using analytical methods by Xiaoyun Wang, Feng, Xuejia Lai, and Yu[1]. CertainKey awarded a 10,000 Canadian Dollar prize to Wang, Feng, Lai and Yu for their discovery.
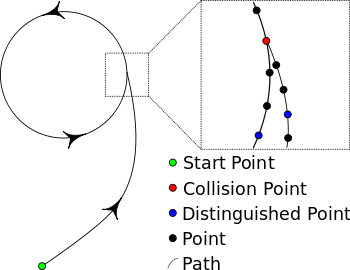
A technique called Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm was used to try to find a collision for MD5. The algorithm can be described by analogy with a random walk. Using the principle that any function with a finite number of possible outputs placed in a feedback loop will cycle, one can use a relatively small amount of memory to store outputs with particular structures and use them as "markers" to better detect when a marker has been "passed" before. These markers are called distinguished points, the point where two inputs produce the same output is called a collision point. MD5CRK considered any point whose first 32 bits were zeroes to be a distinguished point.
Complexity
The expected time to find a collision is not equal to 2N where N is the number of bits in the digest output. It is in fact
 , where K is the number of function outputs collected.
, where K is the number of function outputs collected.For this project, the probability of success after K MD5 computations can be approximated by:
 .
.The expected number of computations required to produce a collision in the 128-bit MD5 message digest function is thus:

To give some perspective to this, using Virginia Tech's System X with a max performance of 12.25 Teraflops, it would take approximately
 seconds or about 3 weeks. Or for commodity processors at 2 gigaflops it would take 6,000 machines approximately the same amount of time.
seconds or about 3 weeks. Or for commodity processors at 2 gigaflops it would take 6,000 machines approximately the same amount of time.See also
References
- Paul C. van Oorschot, Michael J. Wiener: Parallel Collision Search with Application to Hash Functions and Discrete Logarithms. ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security 1994: pp210–218 Online version (PDF format).
Categories:- Cryptographic attacks
- Distributed computing projects
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.