- Overton window
-
For the novel by Glenn Beck, see The Overton Window.
The Overton window, in political theory, describes a "window" in the range of public reactions to ideas in public discourse, in a spectrum of all possible options on a particular issue. It is named after its originator, Joseph P. Overton,[1] former vice president of the Mackinac Center for Public Policy.[2]
Contents
Overview
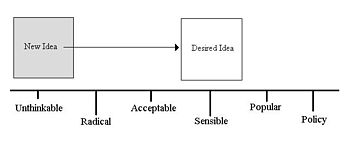
At any given moment, the “window” includes a range of policies considered to be politically acceptable in the current climate of public opinion, which a politician can recommend without being considered too “extreme” or outside the mainstream to gain or keep public office. Overton arranged the spectrum on a vertical axis of “more free” and “less free” in regard to government intervention. When the window moves or expands, ideas can accordingly become more or less politically acceptable. The degrees of acceptance[3] of public ideas can be described roughly as:
- Unthinkable
- Radical
- Acceptable
- Sensible
- Popular
- Policy
The Overton Window is a means of visualizing which ideas define that range of acceptance by where they fall in it. Proponents of policies outside the window seek to persuade or educate the public so that the window either “moves” or expands to encompass them. Opponents of current policies, or similar ones currently within the window, likewise seek to convince people that these should be considered unacceptable.
Other formulations of the process created after Overton's death add the concept of moving the window, such as deliberately promoting ideas even less acceptable than the previous "outer fringe" ideas, with the intention of making the current fringe ideas acceptable by comparison.[4] The "door-in-the-face" technique of persuasion is a similar concept.
In media
The novel Boomsday applies the Overton Window to the subject of Social Security reform in the United States. The technique used was to agitate for "voluntary transitioning," that is, suicide at a certain age in exchange for benefits, as a method of reducing the cost of Social Security. Ultimately, the goal was a more modest form of reducing the burden on younger people for the costs of Social Security.
Conservative talk show host and columnist Glenn Beck has written a novel titled The Overton Window, published June 15, 2010.[5]
A similar idea is expressed in the novel Phineas Finn:
"Many who before regarded legislation on the subject as chimerical, will now fancy that it is only dangerous, or perhaps not more than difficult. And so in time it will come to be looked on as among the things possible, then among the things probable;–and so at last it will be ranged in the list of those few measures which the country requires as being absolutely needed. That is the way in which public opinion is made.”
“It is no loss of time,” said Phineas, “to have taken the first great step in making it.”
“The first great step was taken long ago,” said Mr. Monk,–”taken by men who were looked upon as revolutionary demagogues, almost as traitors, because they took it. But it is a great thing to take any step that leads us onwards.”
— Anthony Trollope, Phineas Finn
See also
References
- ^ NNDB “intelligence aggregator” Web site, "Joseph P. Overton"
- ^ Mackinac - Joseph Overton biography and article index
- ^ Daily Kos story, "Why the Right-Wing Gets It--and Why Dems Don't"
- ^ Daily Kos diary, "Morning Feature: Crazy Like a Fox?"
- ^ Glenn Beck Web site, Books, "The Overton Window"
External links
- Mark Pilgrim (23 August 2006). "W3C and the Overton window - includes a clear explanation"]. Dive into Mark. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. http://web.archive.org/web/20110718035511/http://diveintomark.org/archives/2006/08/23/overton-window.
Categories:- Social psychology
- Public opinion
- Policy
- Politics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.