- Dental arches
-
Dental arches 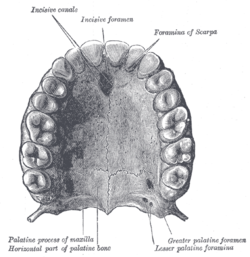
Permanent teeth of upper dental arch, seen from below. 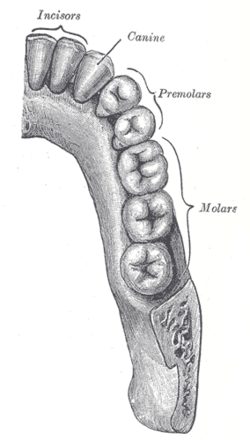
Permanent teeth of right half of lower dental arch, seen from above. Latin arcus dentalis mandibularis, arcus dentalis maxillaris Gray's subject #242 1114 The superior dental arch is larger than the inferior, so that in the normal condition the teeth in the maxillae slightly overlap those of the mandible both in front and at the sides.
Since the upper central incisors are wider than the lower, the other teeth in the upper arch are thrown somewhat distally, and the two sets do not quite correspond to each other when the mouth is closed: thus the upper canine tooth rests partly on the lower canine and partly on the first premolar, and the cusps of the upper molar teeth lie behind the corresponding cusps of the lower molar teeth.
The two series, however, end at nearly the same point behind; this is mainly because the molars in the upper arch are the smaller.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Categories:- Dentistry stubs
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
- Mouth
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
