- Masking threshold
-
The masking threshold is the sound pressure level of a sound needed to make the sound perceptible in the presence of another noice, called a "masker". This threshold depends upon the frequency, the kind of masker, and the kind of sound being masked. The effect is strongest between two sounds close in frequency.
In the context of audio transmission, there are some advantages to being unable to perceive a sound. In audio encoding, for example, better compression can be achieved by omitting the imperceptible tones, thus requiring fewer bits to encode the sound and reducing the size of the final file.
Applications in audio compression
It is uncommon to work with only one tone; most sounds are composed of multiple tones. There may be many possible maskers at the same frequency. In this situation, it is necessary to compute the global masking threshold using a high resolution Fast Fourier transform via 512 or 1024 points to determine the frequencies that comprise the sound. Because there are bands that humans are not able to hear, it is necessary to know the signal level, masker type, and the frequency band before computing the individual thresholds. To avoid having the masking threshold under the threshold in quiet, one adds the last one to the computation of partial thresholds.[clarification needed] This allows computation of the signal-to-mask ratio (SMR).
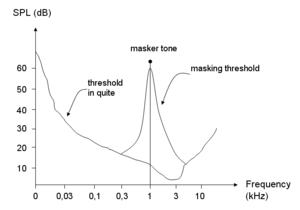 The spectrum of a 1 kHz tone. A sound will not be heard if it is under the threshold in quiet. This limit changes around the masker frequency, making it more difficult to hear a nearby tone. The slope of the masking threshold is steeper toward lower frequencies than toward higher frequencies, which means it is easier to mask with higher frequency tones.
The spectrum of a 1 kHz tone. A sound will not be heard if it is under the threshold in quiet. This limit changes around the masker frequency, making it more difficult to hear a nearby tone. The slope of the masking threshold is steeper toward lower frequencies than toward higher frequencies, which means it is easier to mask with higher frequency tones.
The psychoacoustic model
The MPEG audio encoding process leverages the masking threshold. In this process, there is a block called "Psychoacoustic model". This is communicated with the band filter and the quantify block. The psychoacoustic model analyzes the samples sent to it by the filter band, computing the masking threshold in each frequency band using a Fast Fourier transform. The number of points used depends upon the MPEG layer. Using these thresholds, the signal-to-mask ratio is determined and sent to the quantifier. The quantifier assigns more or less bits in each block based upon the SMR. The block with the highest SMR will encode with the maximum number of bits.
Categories:- Hearing
- MPEG
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
