- Drain (surgery)
-
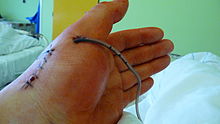
A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound. Drains inserted after surgery do not result in faster wound healing or prevent infection but are sometimes necessary to drain body fluid which may accumulate and in itself become a focus of infection. The routine use of drains for surgical procedures is diminishing as better radiological investigation and confidence in surgical technique have reduced their necessity. It is felt now that drains may hinder recovery by acting as an 'anchor' limiting mobility post surgery and the drain itself may allow infection into the wound. In certain situations their use is unavoidable. Drains have a tendency to become occluded or clogged, resulting in retained fluid that can contribute to infection or other complications. Thus efforts must be made to maintain and assess patency when they are in use. Once a drain becomes clogged or occluded, it is usually removed as it is no longer providing any benefit.
Drains may be hooked to wall suction, a portable suction device, or they may be left to drain naturally. Accurate recording of the volume of drainage as well as the contents is vital to ensure proper healing and monitor for excessive bleeding. Depending on the amount of drainage, a patient may have the drain in place one day to weeks. Signs of new infection or copious amounts of drainage should be reported to the health care provider immediately. Drains will have protective dressings that will need to be changed daily/as needed.
Types of drains
Surgical drains can be broadly classified into:
- Tube drains
- Corrugated drains
Some types of surgical drains are:
- Jackson-Pratt drain - consists of a tube connected to a see-through collection bulb. The bulb has a drainage port which can be opened to remove fluid or air so that the bulb can be squeezed to create suction. The drain is placed below the area of the wound.
- Penrose drain
- Negative pressure wound therapy - Involves the use of enclosed foam and a suction device attached; this is one of the newer types of wound healing/drain devices which promotes faster tissue granulation, often used for large surgical/trauma/non-healing wounds.
- Redivac drain
- Pigtail drain - has an exterior screw to release the internal "pigtail" before it can be removed
- Davol
- Chest tube
- Wound manager
See also
Categories:- Medical equipment stubs
- Surgical instruments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.