- Vampire Squid
Taxobox
name = Vampire Squid
regnum =Animal ia
phylum = Mollusca
classis =Cephalopod a
subclassis =Coleoidea
superordo =Octopodiformes
ordo =Vampyromorphida
subordo =Vampyromorphina
familia =Vampyroteuthidae
genus = "Vampyroteuthis"
genus_authority = Chun, 1903
species = "V. infernalis"
binomial = "Vampyroteuthis infernalis"
binomial_authority = Chun, 1903
synonyms =
*"Cirroteuthis macrope"
Berry, 1911
*"Vampyroteuthis macrope"
(Berry, 1911)
*"Melanoteuthis lucens"
Joubin, 1912
*"Watasella nigra"
Sasaki, 1920
*"Danateuthis schmidti"
Joubin, 1929
*"Hansenoteuthis lucens"
Joubin, 1929
*"Melanoteuthis schmidti"
Joubin, 1929
*"Melanoteuthis beebei"
Robson, 1929
*"Retroteuthis pacifica"
Joubin, 1929
*"Melanoteuthis anderseni"
Joubin, 1931The Vampire Squid ("Vampyroteuthis infernalis", lit. "
vampire squid fromhell ") is a small, deep-sea cirratecephalopod found throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world. Unique retractile sensory filaments justify the Vampire Squid's placement in its own order:Vampyromorphida (formerly Vampyromorpha), though it shares similarities with both squid andoctopus es. As a phylogeneticrelict it is the only known surviving member of its order, first described and mistakenly identified as an octopus in 1903 by German teuthologistCarl Chun .Physical description
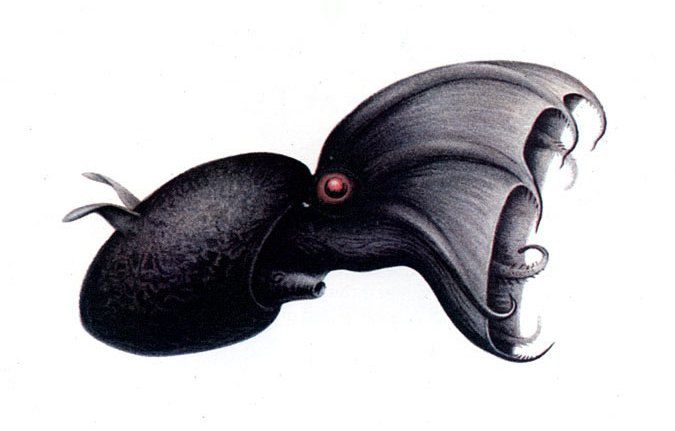
At a maximum 30 cm (1 ft) in total length, the Vampire Squid is no threat to humans. Its 15 cm (6 inch) gelatinous body varies in color between velvety jet-black and pale reddish, depending on location and lighting conditions. A webbing of skin connects its eight arms, each lined with rows of fleshy spines or "cirri"; the inside of this "cloak" is black. Only the distal half (farthest from the body) of the arms have suckers. Its limpid, globular eyes—which appear red or blue, also depending on lighting—are proportionately the largest in the animal kingdom at 2.5 cm (1 inch) in diameter.Fact|date=March 2008
Mature adults have a pair of ear-like fins projecting from the lateral sides of the mantle. These fins serve as the adult's primary means of propulsion: Vampire Squid are said to "fly" through the water by flapping their fins. Their powerful beak-like jaws are as white as ivory. Within the webbing are two pouches wherein the tactile "velar filaments" are concealed. The filaments are analogous to a true squid's tentacles, extending well past the arms; however, they are a different arm pair than the squid's tentacles. Instead, the filaments are the same pair that were lost by the ancestral octopuses.
The Vampire Squid is covered entirely in light-producing organs called
photophore s. The animal has great control over the organs, capable of producing disorienting flashes of light for fractions of a second to several minutes in duration. The intensity and size of the photophores can also be modulated. Appearing as small white discs, the photophores are larger and more complex at the tips of the arms and at the base of the two fins, but are absent from the underside of the caped arms. Two larger white areas on top of the head were initially believed to be photophores too, but have turned out to bephotoreceptor s.The
chromatophore s (pigment organs) common to most cephalopods are poorly developed in Vampire Squid. While this means the animal is not capable of changing its skin colour in the dramatic fashion of shallow-dwellingcephalopods , such trickery is not needed at the pitch-black depths in which it lives.Habitat and adaptations
The Vampire Squid is an extreme example of a deep-sea cephalopod, thought to reside at
aphotic (lightless) depths from 600-900 metres (2,000-3,000 feet) or more. Within this region of the world's oceans is a discrete habitat known as theoxygen minimum zone (OMZ). Within the OMZoxygen saturation is too low to support aerobicmetabolism in most higher organisms. Nonetheless, the Vampire Squid is able to live and breathe normally in the OMZ at oxygen saturations as low as 3%; a feat no other cephalopod, and few other animals, can claim.In order to cope with life in the suffocating depths, vampire squid have developed several radical adaptations. Of all deep-sea cephalopods, their
mass-specific metabolic rate is the lowest. Their blue blood'shemocyanin binds and transports oxygen more efficiently than in other cephalopods (Seibel "et al." 1999), aided bygill s with especially large surface area. The animals have weak musculature but maintain agility and buoyancy with little effort thanks to sophisticatedstatocyst s (balancing organs akin to a human's innerear ) andammonium -rich gelatinous tissues closely matching thedensity of the surrounding seawater.At the shallower end of the Vampire Squid's vertical range, the view from below is like the sky at twilight: The highly sensitive eyes of deepwater denizens are able to distinguish the silhouettes of other animals moving overhead. To combat this, the vampire squid generates its own bluish light (
bioluminescence ) in a strategy calledcounterillumination : The light diffuses the animal's silhouette, effectively "cloaking" its presence from the watchful eyes below. Its own large eyes detect even the faintest of gleams. A pair of photoreceptors are located on top of its head, perhaps alerting the animal to movements above.Like many deep-sea cephalopods, Vampire Squid lack
ink sacs. If threatened, instead of ink, a sticky cloud of bioluminescent mucus containing innumerable orbs of blue light is ejected from the arm tips. This luminous barrage, which may last nearly 10 minutes, is presumably meant to daze would-be predators and allow the Vampire Squid to disappear into the blackness without the need to swim far. The display is made only if the animal is very agitated; regenerating the mucus is costly from a metabolic point of view.Development
Few specifics are known regarding the
ontogeny of the Vampire Squid. Their development progresses through three morphologic forms: the very young animals have a single pair of fins, an intermediate form has two pairs, and the mature form again has one. At their earliest and intermediate phases of development, there is a pair of fins located near the eyes; as the animal develops, this pair gradually disappears as the other pair develops (Pickford 1949). As the animals grow and their surface area to volume ratio drops, the fins are resized and repositioned in order to maximize gait efficiency. Whereas the young propel themselves primarily by jet propulsion, mature adults find flapping their fins to be the most efficient means (Seibel et al. 1998). This unique ontogeny caused confusion in the past, with the varying forms identified as several species in distinct families (Young 2002).If hypotheses may be drawn from knowledge of other deep-sea cephalopods, the Vampire Squid likely reproduces slowly by way of a small number of large eggs. Growth is slow as nutrients are not abundant at depths frequented by the animals. The vastness of their habitat and its sparse population make procreative encounters a fortuitous event. The female may store a male's hydraulically implanted
spermatophore (a sort of tapered, cylindrical satchel ofsperm ) for long periods before she is ready to fertilize her eggs. Once she does, she may need to brood over them for up to 400 days before they hatch. The female will not eat towards this culmination and dies shortly thereafter.Hatchlings are c. 8 mm in length and are well-developed miniatures of the adults, with some differences. Their arms lack webbing, their eyes are smaller and their velar filaments are not fully formed. The hatchlings are transparent and survive on a generous internal
yolk for an unknown period before they begin to actively feed. The smaller animals frequent much deeper waters, perhaps feeding onmarine snow (falling organic detritus).Behaviour
What behavioural data known has been gleaned from ephemeral encounters with
ROV s; animals are often damaged during capture and survive for no more than about two months in aquaria. An artificial environment makes reliable observation of non-defensive behaviour difficult.With their long velar filaments deployed, Vampire Squid have been observed drifting along in the deep, black ocean currents. If the filaments contact an entity, or if vibrations impinge upon them, the animals investigate with rapid acrobatic movements. They are capable of swimming at speeds equivalent to two body lengths per second, with an acceleration time of five seconds. However, their weak muscles limit stamina considerably.
Unlike their relatives living in more hospitable climes, deep-sea cephalopods cannot afford to expend energy in protracted flight. Given their low metabolic rate and the low density of prey at such depths, Vampire Squid must use innovative predator avoidance tactics in order to conserve energy. Their aforementioned bioluminescent "fireworks" are combined with the writhing of glowing arms, erratic movements and escape trajectories, making it difficult for a predator to home in.
In a threat response called "pumpkin" or "pineapple posture", the Vampire Squid inverts its caped arms back over the body, presenting an ostensibly larger form covered in fearsome-looking though harmless spines (called cirri). The underside of the cape is heavily pigmented, masking most of the body's photophores. The glowing arm tips are clustered together far above the animal's head, diverting attack away from critical areas. If a predator were to bite off an arm tip, the Vampire Squid can regenerate it.
Copepod s,prawn s andcnidarian s have all been reported as prey of Vampire Squid. Little else is known regarding their feeding habits, but considering their environment, a fussy palate is unlikely. Vampire Squid have been found among the stomach contents of large deepwater fish, deep divingwhale s andpinniped s such assea lion s.Relationships
The Vampyromorphida are characterized by such
apomorph ies as the possession of photophores, a peculiar type of uncalcifiedendoskeleton called "gladius", 8 webbed arms and the 2 velar filaments. Until fairly recently known only from the modern species and somefossil remains tentatively allocated to this group, a batch of MiddleJurassic (LowerCallovian , c.165-164 mya) specimens found atLa Voulte-sur-Rhône demonstrated that clearly vampyromorphid cephalopods were in existence for far longer than has been hitherto believed.These were described as "
Vampyronassa rhodanica ". The supposed vampyromorphids from theKimmeridgian -Tithonian (156-146 mya) ofSolnhofen , "Plesioteuthis prisca ", "Leptoteuthis gigas ", and "Trachyteuthis hastiformis ", cannot be positively assigned to this group; they are large species (from 35 cm in "P. prisca" to > 1 meter in "L. gigas") and show features not found in vampyromorphids, being somewhat similar to the true squids,Teuthida (Fischer & Riou 2002).References
* Bolstad, Kat (2003): [http://www.tonmo.com/science/public/deepseacephs.php Deep-Sea Cephalopods: An Introduction and Overview] . Version of 5/6/03, retrieved 2006-DEC-06.
* Ellis, Richard (1996): [http://www.thecephalopodpage.org/vsfh.php Introducing "Vampyroteuthis infernalis"] . "In: The Deep Atlantic: Life, Death, and Exploration in the Abyss". Alfred A. Knopf, New York. ISBN 0679433244. Online version retrieved 2007-APR-30.
* Fischer, Jean-Claude & Riou, Bernard (2002): "Vampyronassa rhodanica" nov. gen. nov sp., vampyromorphe (Cephalopoda, Coleoidea) du Callovien inférieur de la Voulte-sur-Rhône (Ardèche, France). "Annales de Paléontologie" 88(1) 1−17. [French with English abstract] DOI|10.1016/S0753-3969(02)01037-6 (HTML abstract)
* Pickford, Grace E. (1949): "Vampyroteuthis infernalis" Chun an archaic dibranchiate cephalopod. II. External anatomy. Dana Report ""32"":1–132.
* Robison, Bruce H.; Reisenbichler, Kim R.; Hunt, James C. & Haddock, Steven H. D. (2003): Light Production by the Arm Tips of the Deep-Sea Cephalopod "Vampyroteuthis infernalis". "Biological Bulletin" 205(2): 102-109. [http://www.biolbull.org/cgi/reprint/205/2/102.pdf PDF fulltext]
* Seibel, Brad A. (2001): [http://www.nhm.ac.uk/hosted_sites/tcp/vampy.html "Vampyroteuthis infernalis"] . Retrieved 2006-DEC-06.
* Seibel, Brad A., Thuesen, Erik V. & Childress, James J. (1998): Flight of the vampire: ontogenetic gait-transition in "Vampyroteuthis infernalis" (Cephalopoda: Vampyromorpha). "Journal of Experimental Biology" 201: 2413-2424. [http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/reprint/201/16/2413.pdf PDF fulltext]
* Seibel, Brad A.; Chausson, Fabienne; Lallier, Francois H.; Zal, Franck & Childress, James J. (1999): Vampire blood: respiratory physiology of the vampire squid (Cephalopoda:Vampyromorpha) in relation to the oxygen minimum layer. "Experimental Biology Online" 4(1): 1-10. doi| 10.1007/s00898-999-0001-2 (HTML abstract)
* Young, Richard E. (2002): [http://tolweb.org/accessory/Vampyroteuthidae_Taxa?acc_id=2420 Taxa Associated with the Family Vampyroteuthidae] . Version of June 2002, retrieved 2006-DEC-06.
External links
*CephBase Species|703
*Tree of Life: [http://tolweb.org/Vampyroteuthis_infernalis "Vampyroteuthis infernalis"] .
* [http://www.influks.com/post1054.html National Geographic video of a Vampire Squid]Images
* [http://www.cephbase.utmb.edu/imgdb/imgsrch3.cfm?ID=580 Image with velar filament in view, detailed caption]
* [http://tolweb.org/accessory/Vampyroteuthis_infernalis_Photophores?acc_id=1764 The vampire squid's photophores and photoreceptors]
* [http://tolweb.org/accessory/Vampyroteuthis_Hatchling?acc_id=1767 Diagram and images of a Vampyroteuthis hatchling]
* [http://www.biolbull.org/cgi/content/full/205/2/102/F6 Photomicrograph of arm tip fluorescence]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
