- List of crossings of the River Severn
-
Motorway crossings over the River Severn Queenhill Viaduct (M50 motorway) This is a list of crossings of the River Severn in Great Britain (including bridges, tunnels, ferries and fords), in order from source to mouth.
The Severn has historically been a very important and busy river, and has been bridged throughout history. The bridges that stand today are often of great historical and/or engineering interest — for example the world's first iron bridge, The Iron Bridge, built from cast iron crosses the River Severn at Ironbridge Gorge. The Iron Bridge is one of three bridges on the River Severn that are listed as grade I structures, including Bewdley Bridge and the Severn Bridge, which was opened in 1966. In total, 31 bridges that cross the River Severn are listed, either grade I, II* or II. Four bridges are Scheduled Monuments, including The Iron Bridge, which are nationally important archaeological bridges.
Many reaches of the Severn are prone to severe flooding, prompting the design of many unique bridges to cope with this.
Contents
Crossings
Key to heritage status Status Criteria[1] I Grade I listed. Bridge of exceptional interest, sometimes considered to be internationally important II* Grade II* listed. Particularly important bridge of more than special interest II Grade II listed. Bridge of national importance and special interest SM Scheduled Monument. Nationally important archaeological bridge. In order, moving downstream:
Crossing Date Coordinates Heritage
statusLocality Notes Image The source of the River Severn 52°29′36″N 3°44′04″W / 52.49347°N 3.73458°W - (Included for completeness) 
First culvert on the Severn 52°29′19″N 3°43′36″W / 52.48855°N 3.72676°W - Hafren Forest Provides Forestry Access. Also carries the Severn Way long distance footpath from left bank to right bank when heading downstream.

First footbridge on the Severn 52°29′13″N 3°43′20″W / 52.48681°N 3.72227°W - Hafren Forest Carries the Severn Way long distance footpath from right bank to left bank when heading downstream. 
Blaen Hafren Falls culvert 52°28′53″N 3°42′58″W / 52.48151°N 3.71618°W - Hafren Forest Provides forestry access. Also carries Severn Way long distance footpath from left bank to right bank when heading downstream.

Second footbridge on the Severn 1992 52°28′22″N 3°42′05″W / 52.47276°N 3.70141°W - Hafren Forest Previously known as the 'First Bridge On The Severn'. Opened May 1992 by Lady Hooson, wife of Emlyn Hooson, Baron Hooson. Also carries Severn Way long distance footpath from right bank to left bank when heading downstream. The Wye Valley Walk long distance footpath starts here. 
Rhyd-y-Benwch Ford 52°28′06″N 3°41′05″W / 52.46847°N 3.68475°W - Hafren Forest First ford on the Severn. Provides forestry access. 
Rhyd-y-Benwch Footbridge 1997 52°28′02″N 3°40′54″W / 52.46716°N 3.68180°W - Hafren Forest 
Cwm Ricket Bridge 52°27′59″N 3°40′42″W / 52.46636°N 3.67824°W - Cwm Ricket First road bridge on the river. Weight limit of 12.5T. 
Cwm Ricket Pipe Bridge 52°27′59″N 3°40′40″W / 52.46632°N 3.67775°W - Cwm Ricket Previously known as Irish Bridge and Paddy's Bridge. Provides forestry access, as nearby Cwm Ricket Bridge has a 12.5T weight limit. With high water, it becomes a ford. 
Severn Break Its Neck Footbridge 1995 52°28′00″N 3°40′30″W / 52.46665°N 3.67500°W - Rhyd-yr-Onnen Provides view of waterfall and gorge. 
Rhyd-yr-Onnen Footbridge 52°27′55″N 3°39′51″W / 52.46541°N 3.66407°W - Rhyd-yr-Onnen 
Hafodfeddgar Farm Bridge 52°27′32″N 3°39′25″W / 52.45902°N 3.65694°W - Hafodfeddgar Provides farm access. 
Geufron Farm Bridge 52°27′23″N 3°38′50″W / 52.45634°N 3.64720°W - Geufron Provides farm access. 
Tynwtra Footbridge 52°27′14″N 3°38′11″W / 52.45396°N 3.63637°W - Tan Hinon Has been dismantled - only abuttments remain. 
Glynhafren Farm Bridge 52°26′55″N 3°37′41″W / 52.44850°N 3.62806°W - Glynhafren Provides farm access. 
Old Hall Ford 52°26′53″N 3°36′52″W / 52.44819°N 3.61448°W - Old Hall Provides farm access. 
Glanhafren Bridge 1972 52°26′53″N 3°36′27″W / 52.44804°N 3.60761°W - Old Hall First tarmac-surfaced road bridge on the Severn. 
Nantyrhebog Footbridge 52°27′02″N 3°34′47″W / 52.45068°N 3.57978°W - Glan-y-Nant 
Cancoed Footbridge 52°26′35″N 3°33′19″W / 52.44294°N 3.55540°W - Glan-y-Nant 
Felindre Bridge 1848 52°26′35″N 3°33′19″W / 52.44294°N 3.55540°W II Mount Severn Designed by Thomas Penson, masonry arch bridge 
Colonel's Bridge 1975 52°26′41″N 3°32′54″W / 52.44465°N 3.54839°W - Llanidloes Timber bridge also known as Pen-y-Green Bridge, named after Colonel Davies-Jenkins 
Short Bridge 1850 52°26′57″N 3°32′33″W / 52.44911°N 3.54242°W II Llanidloes Designed by Thomas Penson 
Long Bridge 1826 52°27′04″N 3°32′21″W / 52.45104°N 3.53923°W II Llanidloes Designed by Thomas Penson, carried the B4518 road. 
Morfodion Farm Bridge 1859 52°27′26″N 3°30′32″W / 52.45735°N 3.50879°W - Llanidloes Timber bridge built as part of the Llanidloes and Newtown Railway, later becoming part of the Cambrian Railway's route from Newtown to Builth Wells; the railway was closed on 31 December 1962. Now used as a farm access bridge. 
Dolwen Bridge 1926 52°27′19″N 3°28′39″W / 52.45541°N 3.47737°W - Upper Penrhuddlan 
Llandinam Bridge 1843 52°29′11″N 3°26′13″W / 52.48645°N 3.43698°W II* Llandinam Iron arch bridge designed by Thomas Penson, the first of its type in Montgomeryshire. 
Caersws Railway Bridge 52°30′50″N 3°25′43″W / 52.51392°N 3.42867°W - Caersws Timber bridge carries the Cambrian Line. 
Caersws Bridge 1821 52°30′52″N 3°25′38″W / 52.51439°N 3.42713°W II Caersws Triple span arch bridge designed by Thomas Penson. Carries the A470 road. 
Festival Footbridge 1951 52°31′17″N 3°23′21″W / 52.52130°N 3.38919°W - Aberhafesp Suspension footbridge built by David Rowell & Co. 
Penstrowed Railway Bridge 52°30′33″N 3°21′55″W / 52.50905°N 3.36515°W - Penstrowed Carries the Cambrian Line. 
Glanhafren Hall Railway Bridge 52°30′21″N 3°21′08″W / 52.50594°N 3.35230°W - Glanhafren Hall Carries the Cambrian Line. 
Dolerw Park Footbridge 1973 52°30′54″N 3°19′12″W / 52.51497°N 3.31998°W - Newtown, Powys Suspension footbridge designed by Mott, Hay and Anderson 
The Long Bridge 1827 52°31′01″N 3°19′00″W / 52.51707°N 3.31675°W II Newtown Designed by Thomas Penson 
Halfpenny Footbridge 1972 52°30′56″N 3°18′48″W / 52.51548°N 3.31325°W - Newtown Fourth bridge on this site, the first dating from 1830 
Newtown Bypass Bridge 1993 52°30′53″N 3°18′34″W / 52.51482°N 3.30933°W - Newtown Carries the B4568 road, Cambrian Way. 
Cilgwrgan Bridge 1862 52°34′30″N 3°11′13″W / 52.57505°N 3.18681°W II Aberbechan 3-span brickwork arch bridge 
Abermule Bypass Bridge 1975 52°32′28″N 3°14′39″W / 52.54098°N 3.24416°W - Abermule 
Brynderwen Bridge 1852 52°32′52″N 3°14′12″W / 52.54774°N 3.23657°W II* Abermule Designed by Thomas Penson, built by the Brymbo Company of Wrexham. Bridge is inscribed: THIS SECOND IRON BRIDGE CONSTRUCTED IN THE COUNTY OF MONTGOMERY WAS ERECTED IN THE YEAR 1852. 
Fron Footbridge 1926 52°34′05″N 3°12′26″W / 52.56815°N 3.20727°W - Plas Meredydd Suspension footbridge by David Rowell & Co 
Caerhowel Bridge 1858 52°34′30″N 3°11′13″W / 52.57509°N 3.18681°W II Trwstllewelyn Designed by Thomas Penson. Bridge is narrow, with traffic lights. 
Cil-cewydd Bridge 1861 52°37′45″N 3°08′32″W / 52.62906°N 3.14230°W II Cil-cewydd Designed by Thomas Penson. 
Cil-cewydd Railway Bridge 52°37′47″N 3°08′30″W / 52.62964°N 3.14179°W - Cil-cewydd Built for Oswestry and Newtown Railway 
Leighton Bridge 1872 52°39′18″N 3°07′46″W / 52.65505°N 3.12958°W II Welshpool Carries the B4381 road. The listing description is "Bridge over channel N of Severn Lodge". 
Buttington Railway Bridge 52°40′19″N 3°06′57″W / 52.67185°N 3.11573°W - Welshpool 
Buttington Bridge 1872 52°40′21″N 3°06′58″W / 52.67253°N 3.11616°W II Welshpool Cast iron arch bridge, carries the A458 road. 
Pool Quay Farm Bridge 52°41′40″N 3°06′08″W / 52.69449°N 3.10209°W - Pool Quay 
Llandrinio Bridge 1775 52°44′45″N 3°02′27″W / 52.74595°N 3.04085°W II Llandrinio Stone arch bridge. Oldest surviving bridge on the river. Bridge is narrow with traffic lights. 
Crewgreen Bridge 1947 52°44′08″N 2°59′38″W / 52.73546°N 2.99390°W - Crewgreen Built as a railway bridge but converted to a road bridge. Crosses from Wales to England. 
Montford Bypass Bridge 1992 52°43′51″N 2°50′45″W / 52.73096°N 2.84589°W - Montford Carries the A5 road. Designed by Sir Owen Williams and Partners as part of the A5 Telford to Shrewsbury and A49 link improvement. 
Montford Bridge 1792 52°43′56″N 2°50′33″W / 52.73221°N 2.84262°W II Montford Bridge Masonry arch bridge by Thomas Telford. Former A5 route, now carried the B4380 road. 
Frankwell Footbridge 1979 52°42′38″N 2°45′18″W / 52.71064°N 2.75501°W - Frankwell, Shrewsbury Cable-stayed footbridge designed by Mott, Hay and Anderson 
St George's Bridge 52°42′37″N 2°45′24″W / 52.71028°N 2.75667°W - Shrewsbury Demolished in 1795 and replaced by the Welsh Bridge. It was also known as the Old Welsh Bridge. 
Welsh Bridge 1795 52°42′36″N 2°45′29″W / 52.71013°N 2.75807°W II* Frankwell, Shrewsbury 
Porthill Bridge 1922 52°42′30″N 2°45′49″W / 52.70842°N 2.76371°W - Shrewsbury Suspension footbridge by David Rowell & Co 
Kingsland Bridge 1881 52°42′16″N 2°45′32″W / 52.70437°N 2.75895°W II Shrewsbury Toll road bridge 
Greyfriars Footbridge 1879 52°42′17″N 2°44′56″W / 52.70467°N 2.74893°W - Coleham, Shrewsbury Wrought iron truss bridge 
English Bridge 1927 52°42′24″N 2°44′51″W / 52.70660°N 2.74748°W II* Shrewsbury Designed by John Gwynn. Completely rebuilt in the 1920s using the original 1774 stone work, but the bridge was widened by 26 feet (7.9 m) and the gradient reduced; reopened on October 26, 1927. It carries the A458 road. 
Shrewsbury Railway Station Bridge 1838 52°42′38″N 2°44′52″W / 52.71069°N 2.74782°W - Shrewsbury Designed by Robert Stephenson and Joseph Locke 
Castle Walk Footbridge 1951 52°42′45″N 2°44′38″W / 52.71250°N 2.74382°W - Shrewsbury The first prestressed concrete balanced cantilever bridge in the UK 
Telford Way Bridge 1964 52°43′21″N 2°43′57″W / 52.72242°N 2.73255°W - Shrewsbury Prestressed concrete bridge. Designed by Scott Wilson Group, it carries the A5112 road. 
Shrewsbury Bypass Bridge 1992 52°43′20″N 2°42′24″W / 52.72236°N 2.70667°W - Shrewsbury Carries the A49 road. 
Shrewsbury Bypass Bridge 1992 52°43′01″N 2°42′17″W / 52.71701°N 2.70478°W - Shrewsbury Carries the A49 road. 
Belvidere Bridge 1848 52°42′30″N 2°42′46″W / 52.70825°N 2.71271°W II* Shrewsbury Designed by William Baker; carries the Wolverhampton to Shrewsbury Line. 
Shrewsbury Bypass Bridge 1992 52°41′39″N 2°42′34″W / 52.69417°N 2.70942°W - Shrewsbury Carries the A5/A49. 
Atcham New Bridge 1929 52°40′47″N 2°40′53″W / 52.6798°N 2.6813°W - Atcham Designed by L G Mouchel 
Atcham Bridge 1776 52°40′46″N 2°40′52″W / 52.67948°N 2.68124°W II* Atcham Masonry arch viaduct designed by John Gwynn 
SM Cressage Bridge 1913 52°38′13″N 2°36′00″W / 52.63702°N 2.60004°W - Cressage Carries the B4380 road. Reinforced concrete bridge by L G Mouchel 
Buildwas Bridge 1992 52°38′11″N 2°31′32″W / 52.63642°N 2.52567°W - Buildwas Carries the A4169 road. Replaced a bridge previously built in 1796 by Thomas Telford 
Ironbridge "A" Road Bridge 1932 52°38′11″N 2°30′47″W / 52.63637°N 2.51293°W - Ironbridge Coalbrookdale. Steel truss bridge providing access to Ironbridge Power Station 
Ironbridge "B" Road Bridge 1963 52°37′59″N 2°30′25″W / 52.63298°N 2.50683°W - Ironbridge Coalbrookdale. Prestressed concrete bridge providing access to Ironbridge Power Station 
Albert Edward Bridge 1864 52°37′50″N 2°30′12″W / 52.63061°N 2.50333°W II Designed by John Fowler; carries the remaining section of the Wellington to Craven Arms Railway The Iron Bridge 1779 52°37′35″N 2°28′23″W / 52.62637°N 2.47292°W I Ironbridge Arch bridge; the world's first cast iron bridge, built by Abraham Darby, now foot access only. In the 1970s, major work was undertaken to restore the bridge, including an inverted concrete arch in the river bed to keep the abutments apart. 
SM Free Bridge, Jackfield 1909 52°37′35″N 2°28′21″W / 52.62649°N 2.47259°W II Jackfield The Free Bridge, which was also known as the Haynes Memorial Bridge, opened in 1909 by public subscription, it was the first toll-free crossing of the Ironbridge Gorge. The bridge was the first bridge in England constructed using reinforced concrete and was designed by L G Mouchel. The bridge became unsafe and was demolished in 1993 to make way for the new Jackfield Bridge. 
Jackfield Bridge 1994 52°37′35″N 2°28′21″W / 52.62649°N 2.47259°W - Jackfield Cable-stayed footbridge designed by Gifford & Partners, carrying the B4373 road. 
Jackfield and Coalport Memorial Footbridge 1922 52°37′11″N 2°27′13″W / 52.61985°N 2.45369°W - Coalport A steel truss footbridge 
Coalport Bridge 1818 52°36′55″N 2°26′31″W / 52.61537°N 2.44208°W II* Coalport Iron arch bridge, replaced a crossing built in 1777 
SM Coalport Sewage Treatment Works Bridge 52°36′40″N 2°25′56″W / 52.61115°N 2.43211°W - Coalport Bridge serving the Coalport Sewage Treatment Works, owned by Severn Trent Water 
Apley Park Bridge 1905 52°34′55″N 2°26′04″W / 52.5819°N 2.4345°W - Suspension footbridge, designed and built by David Rowell & Co. This is a private road bridge for the Apley Park Estate, and is not a public footpath. Weight limit is 1 tonne, and only one vehicle allowed on the bridge at a time. 
Severn Bridge, Bridgnorth 1823 52°32′03″N 2°24′58″W / 52.53413°N 2.41613°W II Bridgnorth Originally medieval, but rebuilt in 1795 with improvements made Thomas Telford in 1823 
Bridgnorth Bypass Bridge 1985 52°31′39″N 2°25′02″W / 52.52739°N 2.41721°W - Bridgnorth A458 
Hampton Loade Water Treatment Works bridge 1965 52°28′51″N 2°22′31″W / 52.48092°N 2.37533°W - Hampton Loade Bridge serving the Hampton Loade Water Treatment Works. The tubular welded blue arches are waterpipes that carry a small roadway suspended below. The bridge is owned by South Staffordshire Water. 
Hampton Loade Ferry <1600 52°28′34″N 2°22′26″W / 52.47606°N 2.37391°W - Hampton Loade The only 'Reaction Cable' ferry in the UK. The present boat dates from 2004. It is 20 feet (6.1 m) by 9 feet (2.7 m) and carries up to 12 passengers plus the operator. Operated by the Hampton Loade Community Trust at weekends during the summer provided the river level is suitable. 
Highley-Alveley Footbridge 2006 52°27′10″N 2°22′17″W / 52.45265°N 2.37136°W - Highley Replaced the Alveley Colliery Bridge, which was built in 1937 to take coal to Stourport Power Station. 
Arley footbridge 1971 52°25′06″N 2°20′45″W / 52.41820°N 2.34578°W - Upper Arley Truss footbridge, replaced a vehicular ferry 
Victoria Bridge 1861 52°24′38″N 2°20′41″W / 52.41048°N 2.34476°W II* Upper Arley. Cast iron arch designed by John Fowler. Carries the Severn Valley Railway. 
Elan aqueduct circa 1900 52°24′04″N 2°19′53″W / 52.40117°N 2.33145°W - Trimpley Carries water from the Elan Valley at Rhayader to Birmingham. It is also known as the Elan Valley Pipeline Bridge 
Dowles Bridge 1864 52°23′07″N 2°19′30″W / 52.38531°N 2.32495°W - On the former Tenbury & Bewdley Railway; dismantled 1965, piers only remaining. 
Bewdley Bridge 1798 52°22′35″N 2°18′50″W / 52.37646°N 2.31390°W I Bewdley Multiple masonry arches, designed by Thomas Telford. Listed as "Severn Bridge Including Flanking Arches and Balustrade". 
Bewdley Bypass Bridge 1987 52°21′59″N 2°18′15″W / 52.36629°N 2.30411°W - Bewdley Carries the A456 road 
Stourport Bridge 1870 52°20′14″N 2°16′59″W / 52.33713°N 2.28318°W II Stourport-on-Severn Single iron arch, replaced a 1775 bridge. Listed as "Bridge over River Severn" 
Holt Fleet Bridge 1828 52°16′05″N 2°15′32″W / 52.26818°N 2.25889°W II Holt Fleet Cast iron trussed arch; designed by Telford, opened 1828 and strengthened with reinforced concrete in 1928. Identical design to Galton Bridge, Smethwick over canal (1829). 
Bevere Island Bridge 1844 52°13′58″N 2°14′21″W / 52.23282°N 2.23913°W - Grimley Links island to East bank; not a full crossing. 
Sabrina Footbridge 1992 52°11′40″N 2°13′55″W / 52.19445°N 2.23205°W - Worcester Asymmetrical, cable-stayed bridge with one tower. 
Worcester Railway Bridge 1904 52°11′35″N 2°13′47″W / 52.19310°N 2.22974°W II Worcester Iron truss. Listed as "Railway Bridge, Worcester" 
Worcester Bridge 1781 52°11′27″N 2°13′35″W / 52.19083°N 2.22632°W II Worcester Multiple masonry arches designed by John Gwynn. Reconstructed in 1930. Carried the A44 
Worcester Cathedral Ferry Ancient - Worcester Also known as Priory Ferry. Operated every day till the 1950s. Service restarted in 1983. As of 2009, it is the only Rowing Ferry across the River Severn; it is operated by volunteers during the summer, every afternoon at weekends and bank holidays. 
Diglis Bridge June 2010 52°10′34″N 2°13′29″W / 52.17624°N 2.22474°W - Worcester Located just downstream of Diglis Island. Carrying pedestrians and Route 46 of the National Cycle Network[2][3] 
Carrington Bridge 1985 52°09′46″N 2°13′04″W / 52.16290°N 2.21774°W - Worcester Carrying the A4440 Southern Link Road [4] 
Rhydd Ferry 52°06′27″N 2°14′32″W / 52.10758°N 2.24233°W - Worcester Ferry was working until approximately 1914.[5] 
Upton-upon-Severn bridge 1940 52°03′56″N 2°13′04″W / 52.06560°N 2.21767°W - Upton-upon-Severn Girder bridge, latest of several here dating back to 1539. 
Queenhill Viaduct 1960 52°01′49″N 2°11′43″W / 52.03026°N 2.19541°W - Queenhill Carrying the M50 Motorway 
Mythe Bridge 1826 52°00′07″N 2°09′49″W / 52.00203°N 2.16358°W II* Mythe Near Tewkesbury. Cast iron arch, built by Telford. Opened as a toll bridge; now free. Major repair work in 1993/94; now single lane with 3m width limit and 17 ton weight limit and controlled by traffic lights. Crosses from Worcestershire to Gloucestershire. 
Haw Bridge 1961 51°56′56″N 2°13′36″W / 51.94899°N 2.22671°W - Near the village of Apperley West of Tewkesbury. steel beam bridge. 
X
X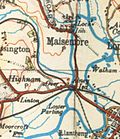
The River Severn splits at the Upper Parting between the 2 mi (3.2 km) long West Channel,
known locally as the Maisemore Channel,[6] and the 3.6 mi (5.8 km) long East Channel around Alney Island[7]X
XWest Channel crossings Maisemore Bridge 1956 51°53′19″N 2°16′04″W / 51.88860°N 2.26772°W - Maisemore Carries the A417. Single masonry arch, latest of several bridges here dating back to 1230. 
New Over Bridge (Northern Bypass) 1974 51°52′30″N 2°16′04″W / 51.87501°N 2.26790°W - Gloucester A40 
Over Bridge 1829 51°52′28″N 2°16′05″W / 51.87448°N 2.26797°W SM Gloucester Single masonry arch, built by Telford. 
Over Railway Bridge 1957 51°52′26″N 2°16′05″W / 51.87378°N 2.26818°W - Gloucester Railway bridge on the Gloucester to Newport Line 
East Channel crossings Waltham bridge (Northern Bypass) 1983 51°52′30″N 2°16′01″W / 51.87502°N 2.26682°W - Gloucester A40 Black Bridge 51°52′30″N 2°16′01″W / 51.87502°N 2.26682°W - Gloucester Railway bridge on the Gloucester to Newport Line Westgate Bridge (eastbound) 2000 51°52′12″N 2°15′24″W / 51.86997°N 2.25661°W - Gloucester A417. It replaced an earlier bridges opened in 1189, 1809 and 1974. 
Westgate Footbridge March 2000 51°52′11″N 2°15′24″W / 51.86977°N 2.25669°W - Gloucester 
Westgate Bridge (westbound) 2000 51°52′10″N 2°15′25″W / 51.86957°N 2.25682°W - Gloucester A417. It replaced an earlier bridge opened in 1974. 
Castle Meads Footbridge 1987 51°51′52″N 2°15′12″W / 51.86454°N 2.25329°W - Gloucester 
Castle Meads Bridge 2005 51°51′45″N 2°15′27″W / 51.86262°N 2.25743°W - Gloucester A430 Llanthony Railway Bridge (disused) 51°51′45″N 2°15′29″W / 51.86252°N 2.25816°W - Gloucester 
Disused footbridge 51°51′44″N 2°15′33″E / 51.86234°N 2.25906°E - Gloucester 
The East and West Channels rejoin at the Lower Parting[7] Severn Railway Bridge 1876 51°43′56″N 2°28′28″W / 51.73234°N 2.47441°W - Lydney – Sharpness Demolished 1970 after accident. 
Severn-Wye Cable Tunnel Circa 1970 51°36′40″N 2°40′09″W / 51.61098°N 2.66921°W (west)
51°36′30″N 2°36′55″W / 51.6083446°N 2.6153657°W (east)- Beachley – Aust The tunnel is 47.5 metres deep, with a diameter of 3.05m and a total length of 3,678m.[8] The tunnel carries two 400KV circuits, each with three cables.[9] The tunnel is owned by npower. The image to the right shows the cables on pylons entering the Aust (eastern) end of the tunnel before going underground. 
Severn Bridge 1966 51°36′33″N 2°38′18″W / 51.60903°N 2.63837°W I Chepstow – Aust Steel suspension bridge. Listed as "Severn Bridge and Aust Viaduct, First Severn Crossing". 
Aust Ferry 1827 51°35′56″N 2°37′59″W / 51.59888°N 2.63301°W - Beachley – Aust Closed circa 1860. Service recommenced 1926, finally closed 1966. 
Aust Severn Powerline Crossing 51°36′21″N 2°38′29″W / 51.60578°N 2.64136°W - Longest powerline span in the UK at 1 mile (1,618 metres). 
Severn Tunnel 1886 51°34′30″N 2°41′20″W / 51.575°N 2.6889°W - Railway tunnel, part of the South Wales Main Line 
Second Severn Crossing 1996 51°34′24″N 2°41′50″W / 51.57331°N 2.69725°W - A cable-stayed bridge which marks the official start of the Severn Estuary. 
See also
- List of disasters on the Severn
- Severn bore
- List of bridges in Wales
Bibliography
- Witts, Chris, A Century of Bridges, River Severn Publications, 2nd ed, 1998
Notes
- ^ Listed Buildings, English Heritage, http://www.english-heritage.org.uk/caring/listing/listed-buildings/, retrieved 22 April 2011
- ^ "It's all systems go for July official opening as new cycle and footbridge gradually takes shape (From Worcester News)". Worcester News. Newsquest. http://www.worcesternews.co.uk/news/8243117.Latest_bridge_over_Severn_on_schedule_for_completion/. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ^ "New bridge over River Severn in Worcester opens". BBC Online. BBC. 20 July 2010. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-england-hereford-worcester-10695754. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ http://archive.worcesternews.co.uk/2002/7/8/261801.html
- ^ "Rhydd Ferry". H W Gwilliam. whepages. 1982. http://whe.multiservers.com/whepages/Severn/rhyddfe.htm. Retrieved 28 May 2011.
- ^ "Over Bridge history and research". English Heritage. http://www.english-heritage.org.uk/daysout/properties/over-bridge/history-and-research/. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
- ^ a b "River Severn at Gloucester: Flood Risk Management Study". Environment Agency. http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/static/documents/Leisure/gloucester3_1_1250294.pdf. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
- ^ "Mono Severn Wye Tunnel Project wins award.". HighBeam. http://business.highbeam.com/411917/article-1G1-135814115/mono-severn-wye-tunnel-project-wins-award. Retrieved 10 May 2011.
- ^ "Severn-Wye Cable Tunnel refurb". Global Trade Media. http://www.convertingtoday.co.uk/story.asp?sectioncode=12&storycode=32816. Retrieved 10 May 2011.
External links
 Media related to Bridges across the River Severn at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bridges across the River Severn at Wikimedia CommonsRiver Severn, Great Britain Administrative areas Settlements Llanidloes · Newtown · Welshpool · Shrewsbury · Ironbridge · Bridgnorth · Bewdley · Stourport · Worcester · Tewkesbury · Gloucester · Berkeley · Chepstow · AvonmouthMajor tributaries River Vyrnwy · River Tern · Cound Brook · River Stour · River Teme · Warwickshire Avon · River Wye · Bristol Avon · River UskFlows into Linked canals Major crossings Welsh Bridge · English Bridge · The Iron Bridge · Mythe Bridge · Over Bridge · Severn Bridge · Aust Severn Powerline Crossing · Severn Tunnel · Second Severn Crossing · All crossings of the River SevernCategories:- Bridges across the River Severn
- Lists of bridges
- Crossings by river
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




