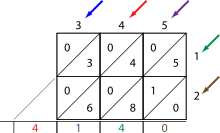- Dadda multiplier
-
The Dadda multiplier is a hardware multiplier design invented by computer scientist Luigi Dadda in 1965. It is similar to the Wallace multiplier, but it is slightly faster (for all operand sizes) and requires fewer gates (for all but the smallest operand sizes).[1]
In fact, Dadda and Wallace multipliers have the same 3 steps:
- Multiply (that is - AND) each bit of one of the arguments, by each bit of the other, yielding n2 results. Depending on position of the multiplied bits, the wires carry different weights, for example wire of bit carrying result of a2b3 is 32.
- Reduce the number of partial products to two layers of full and half adders.
- Group the wires in two numbers, and add them with a conventional adder.
However, unlike Wallace multipliers that reduce as much as possible on each layer, Dadda multipliers do as few reductions as possible. Because of this, Dadda multipliers have less expensive reduction phase, but the numbers may be a few bits longer, thus requiring slightly bigger adders.
To achieve this, the structure of the second step is governed by slightly more complex rules than in the Wallace tree. As in the Wallace tree, a new layer is added if any weight is carried by 3 or more wires. The reduction rules however are as follows:
- Take any 3 wires with the same weights and input them into a full adder. The result will be an output wire of the same weight and an output wire with a higher weight for each 3 input wires.
- If there are 2 wires of the same weight left, and the current number of output wires with that weight is equal to 2 (modulo 3), input them into a half adder. Otherwise, pass them through to the next layer.
- If there is just 1 wire left, connect it to the next layer.
This step does only as many adds as necessary, so that the number of output weights stays close to a multiple of 3, which is the ideal number of weights when using full adders as 3:2 compressors.
However, when a layer carries at most 3 input wires for any weight, that layer will be the last one. In this case, the Dadda tree will use half adder more aggressively (but still not as much as in a Wallace multiplier), to ensure that there are only two outputs for any weight. Then, the second rule above changes as follows:
- If there are 2 wires of the same weight left, and the current number of output wires with that weight is equal to 1 or 2 (modulo 3), input them into a half adder. Otherwise, pass them through to the next layer.
Contents
Algorithm example
This section explains the Dadda dot-diagram reduction example
- Let d1 = 2 and dj+1 = floor(3*dj/2)
- This generates the sequence: d1=2, d2=3, d3=4, ...
- Find the largest dj that is less than the maximum number of bits in any column.
- For our example to the right, this would be 6
- For every column, use full adders (FA) and half adders (HA) to ensure that the number of elements in each column will be <= nj
- When doing this, keep in mind that any column n that has an adder within it, will pass its sum bit to the next stage in column n and the carry bit to the n+1 column. The n+1 column will need to take this into account when determining the number of adders to use.
- First bank
- Columns 0-5 don't need any adders since they all have <= 6 bits
- Column 6 needs 1 HA (7 > 6) which reduces it to 6 bits and passes one carry bit to column 7.
- Column 7 can use a FA since it has 8 bits which would reduce the column to 6 bits, but since column 6 is passing in a carry bit, it needs one more HA to bring the total to 6 bits
- Column 8 needs a FA and a HA since it's getting 2 carry bits from column 7's adders.
- Column 9 only needs one FA
- Columns 10-14 do not need any adders since any carry bits from the previous columns don't result in a total greater than 6.
- Second bank
- The next bank's dj = 4
- Columns 0-3 don't need any adders since they have <=4 bits
- Column 4 needs a HA, (5 > 4)
- Column 5 needs a FA and a HA due to the carry bit
- Columns 6-10 need two FA since they all have 2 carry bits coming from the previous stage
- Column 11 only needs 1 FA to get to 4 bits after the carry bits come in
- Columns 12-14 don't need any adders since they all have < 4 bits
- 3rd bank
- The next bank's dj = 3
- Columns 0-2 don't need any adders since they have <=3 bits
- Column 3 only needs one HA to get to 3 bits
- Column 4-12 need a FA since they all have one carry-in bit coming in from the previous column
- Columns 13-14 don't need any adders since they have < 3 bits
- 4th bank
- The next bank's dj = 2
- Columns 0-1 don't need any adders since they have <=2 bits
- Column 2 only needs one HA to get to 2 bits
- Column 3-13 need a FA since they all have one carry-in bit coming in from the previous column
- Column 14 doesn't need an adder (1 < 2)
- 5th bank
- At this point, everything is reduced to two bits and the resultant can be calculated from a 14 bit adder.
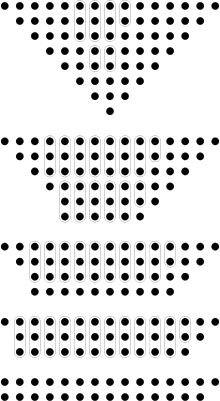
Example
n = 4, multiplying a3a2a1a0 by b3b2b1b0:
- Reduction layer 1:
- Pass the only weight-1 wire through, output: 1 weight-1 wire
- Pass the two weight-2 wires through, outputs: 2 weight-2 wires
- Add a full adder for weight 4, outputs: 1 weight-4 wire, 1 weight-8 wire
- Add a full adder for weight 8, and pass the remaining wire through, outputs: 2 weight-8 wires, 1 weight-16 wire
- Add a full adder for weight 16, outputs: 1 weight-16 wire, 1 weight-32 wire
- Pass the two weight-32 wires through, outputs: 2 weight-32 wires
- Pass the only weight-64 wire through, output: 1 weight-64 wire
- Wires at the output of reduction layer 1:
- weight 1 - 1
- weight 2 - 2
- weight 4 - 1
- weight 8 - 3
- weight 16 - 2
- weight 32 - 3
- weight 64 - 1
- Reduction layer 2: this layer will be the last because any weight has at most three input wires.
- Weights 1, 2, 4, 64 pass through.
- Add a full adder for weight 8, outputs: 1 weight-8 wire, 1 weight-16 wire
- Add a half adder for weight 16, outputs: 1 weight-16 wire, 1 weight-32 wire
Weight 8's full adder has already produced one weight-16 output wire. By using a half adder for the two weight-16 input wires, the Dadda's tree ensures that the last layer has only two output wires for any weight. - Add a full adder for weight 32, outputs: 1 weight-32 wire, 1 weight-64 wire
- Outputs:
- weight 1 - 1
- weight 2 - 2
- weight 4 - 1
- weight 8 - 1
- weight 16 - 2
- weight 32 - 2
- weight 64 - 2
Compared to a Wallace tree, which requires 10 between full adders and half adders, the reduction phase of the Dadda multiplier has the same delay but requires only six. On the other hand, the final adder has 6-bit inputs (weights 2 to 64), rather than 5-bit (weights 8 to 128) as in Wallace tree......
See also
- Booth's multiplication algorithm
- Fused multiply–add
- Wallace tree
- BKM algorithm for complex logarithms and exponentials
- Kochanski multiplication for modular multiplication
References
- Dadda, L. (1965). "Some schemes for parallel multipliers". Alta Frequenza 34: 349–356.
- Townsend, W.; Swartzlander, E.; Abraham , J. (2003-08-06). "A Comparison of Dadda and Wallace Multiplier Delays". SPIE Advanced Signal Processing Algorithms, Architectures, and Implementations XIII. http://www.cerc.utexas.edu/~whitney/pdfs/spie03.pdf.
Categories:- Digital circuits
- Computer arithmetic
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.