- Tritone paradox
-
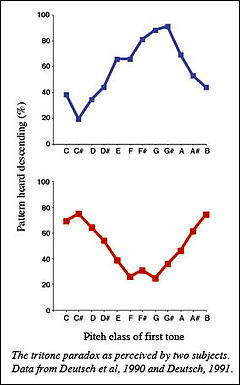
The tritone paradox is an auditory illusion in which a sequentially played pair of Shepard tones [1] separated by an interval of a tritone, or half octave, is heard as ascending by some people and as descending by others.[2] Different populations tend to favor one of a limited set of different spots around the chromatic circle as central to the set of "higher" tones. The tritone paradox was first reported by psychology of music researcher Diana Deutsch in 1986.[3]
Each Shepard tone consists of a set of octave related sinusoids, the amplitudes of which are scaled by a fixed bell shaped spectral envelope based on a log frequency scale. For example, one tone might consist of a sinusoid at 440 Hz, accompanied by sinusoid at the higher octaves (880 Hz, 1760 Hz, etc.) and lower octaves (220 Hz, 110 Hz, etc.). The other tone might consist of a 311 Hz sinusoid, again accompanied by higher and lower octaves (622 Hz, 155.5 Hz, etc.). The amplitudes of the sinusoids of both complexes are determined by the same fixed amplitude envelope - for example the envelope might be centered at 370 Hz and span a 6 octave range.
Shepard predicted that the two tones would constitute a bistable figure, the auditory equivalent of the Necker cube, that could be heard ascending or descending, but never both at the same time. Diana Deutsch later found that perception of which tone was higher depended on the absolute frequencies involved: an individual will usually find the same tone to be higher, and this is determined by the tones' absolute pitches. This is consistently done by a large portion of the population, despite the fact that responding differently to different tones must involve the ability to hear absolute pitch, which was thought to be extremely rare. This finding has been used to argue that latent absolute-pitch ability is present in a large proportion of the population. In addition, Deutsch found that subjects from the south of England and from California resolved the ambiguity the opposite way. Also, Deutsch, Henthorn and Dolson found that native speakers of Vietnamese, a tonal language, heard the tritone paradox differently from Californians who were native speakers of English.
See also
- Barber pole
- Flanging
Notes
- ^ R.N. Shepard. Circularity in judgments of relative pitch. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 36(12):2346–2353, 1964.
- ^ Deutsch's Musical Illusions
- ^ Deutsch (1986).
References
- Deutsch, D. (1986). "A musical paradox". Music Perception 3: 275–280.. Weblink PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (1986). "An auditory paradox". Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 80: s93. doi:10.1121/1.2024050. Weblink
- Deutsch, D. (1987). "The tritone paradox: Effects of spectral variables". Perception & Psychophysics 41 (6): 563–575. doi:10.3758/BF03210490. PMID 3615152. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D., North, T. and Ray, L. (1990). "The tritone paradox: Correlate with the listener's vocal range for speech". Music Perception 7: 371–384. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (1991). "The tritone paradox: An influence of language on music perception". Music Perception 8: 335–347. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (1992). "Paradoxes of musical pitch". Scientific American 267 (2): 88–95. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0892-88. PMID 1641627. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (1992). "Some new pitch paradoxes and their implications. In Auditory Processing of Complex Sounds". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, Series B 336 (1278): 391–397. doi:10.1098/rstb.1992.0073. PMID 1354379. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (1997). "The tritone paradox: A link between music and speech". Current Directions in Psychological Science 6 (6): 174–180. doi:10.1111/1467-8721.ep10772951. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D., Henthorn T. and Dolson, M. (2004). "Speech patterns heard early in life influence later perception of the tritone paradox". Music Perception 21 (3): 357–372. doi:10.1525/mp.2004.21.3.357. PDF Document
- Deutsch, D. (2007). "Mothers and their offspring perceive the tritone paradox in closely similar ways". Archives of Acoustics 32: 3–14. PDF Document
External links
Categories:- Auditory illusions
- Paradoxes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.