- Dentinogenesis imperfecta
-
Dentinogenesis imperfecta Classification and external resources 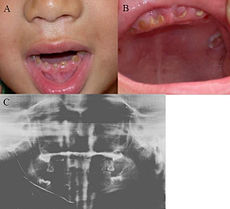
ICD-10 K00.5 ICD-9 520.5 MeSH D003811 Dentinogenesis imperfecta (hereditary Opalescent Dentin) is a genetic disorder of tooth development. This condition causes teeth to be discolored (most often a blue-gray or yellow-brown color) and translucent. Teeth are also weaker than normal, making them prone to rapid wear, breakage, and loss. These problems can affect both primary (baby) teeth and permanent teeth. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Dentinogenesis imperfecta affects an estimated 1 in 6,000 to 8,000 people.
Contents
Types
Types of dentinogenesis imperfecta with similar dental formalities usually an autosomal dominant trait with variable expressivity but can be recessive if the associated osteogenesis imperfecta is of recessive type. This type is no l
Type II : Occurs in people without other inherited disorders (i.e. Osteogenesis imperfecta).It is an autosomal dominant trait. A few families with type II have progressive hearing loss in addition to dental abnormalities.
Mutations in the DSPP gene have been identified in people with type II and type III dentinogenesis imperfecta. Type I occurs as part of osteogenesis imperfecta.
Clinical features
Clinical appearance is variable. However, the teeth usually involved and more severely affected are deciduous teeth in type 1; whereas in type 2 both the dentitions are equally affected.
The teeth may be gray to yellowish brown. They exhibit translucent or opalescent hue. Enamel is usually lost early due to loss of scalloping at the DEJ. However, the teeth are not more susceptible to dental caries than normal ones.
Radiographic features
Type I and II show total obliteration of the pulp chamber.
Type III shows thin dentin and extremely enormous pulp chamber.These teeth are usually known as Shell Teeth.
Histology
Dentinal tubules are irregular and are bigger in diameter. Areas of uncalcified matrix are seen. Sometimes odontoblasts are seen in dentin.
Treatment
One treatment option is bonding, putting lighter enamel on the weakened enamel of the teeth and with lots of treatments of this bonding, the teeth appear whiter to the eye, but the teeth on the inside and under that cover are still the same.
Due to the weakened condition of the teeth, many common cosmetic procedures such as braces and bridges are inappropriate for patients with Dentinogenesis imperfecta and are likely to cause even more damage than the situation they were intended to correct.
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
Developmental tooth disease/tooth abnormality (K00–K01, 520) Quantity Abnormalities of
size and formConcrescence · Fusion · Gemination · Dens evaginatus/Talon cusp · Dens invaginatus · Enamel pearl · Macrodontia · Microdontia · Taurodontism · Supernumerary rootsDisturbances in
formationOther hereditary disturbances
in structureOther Categories:- Genetic disorders with no OMIM
- Developmental tooth disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
