- Republic of China presidential election, 1996
Infobox Election
election_name = Republic of China
presidential election, 1996
country = Republic of China
type = presidential
ongoing = no
previous_election =
previous_year =
next_election = Republic of China presidential election, 2000
next_year = 2000
election_date =March 23 ,1996
nominee1 =Lee Teng-hui
party1 = Kuomintang
home_state1 =Taipei
running_mate1 =Lien Chan
popular_vote1 = 5,813,699
percentage1 = 54.0%
swing1 =
nominee2 =Peng Ming-min
party2 = Democratic Progressive Party
home_state2 =Kaoshiung
running_mate2 =Frank Hsieh
popular_vote2 = 2,274,586
percentage2 = 21.1%
swing2 =
nominee3 =Lin Yang-kang
party3 = Independent (politician)
home_state3 =Taipei
running_mate3 =Hau Pei-tsun
popular_vote3 = 1,603,790
percentage3 = 14.9%
swing3 =
map_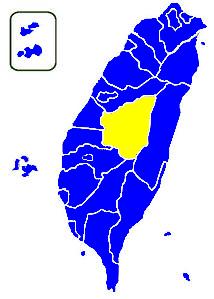
map_size = 250px
map_caption = Lee Teng-hui (blue) vs. Lin Yang-kang (yellow). Although the DPP was the runner-up, it did not win any county or city in Taiwan.
title = President
before_election =Lee Teng-hui
before_colour = 000099
after_election =Lee Teng-hui
after_colour = 000099
before_party = Kuomintang
after_party = KuomintangThe Election for the 9th-term President and Vice-President of the Republic of China (第九任中華民國總統 、副總統選舉), the first ever direct elections for President and Vice President of theRepublic of China onTaiwan , occurred onMarch 23 ,1996 . The previous eight ROC presidential and vice presidentialelection s under the 1947 Constitution were by the deputies of the National Assembly.Incumbent
Lee Teng-hui of the rulingKuomintang won a majority of 54% of the votes following missile tests by thePeople's Republic of China intended to intimidate the Taiwanese electorate against him.Candidates
The ruling
Kuomintang nominatedLee Teng-hui inAugust 1995 at its 14th Party Congress after plans to institute a closed primary system by his opponents were thwarted. As his running mate, Lee choseLien Chan , who promised to resign as Premier if he were elected Vice President.The Democratic Progressive Party conducted an extensive nomination process: the presidential candidate was selected after two rounds of voting and fifty public debates by the two finalists.
Hsu Hsin-liang ,Lin Yi-hsiung ,Yu Ching , andPeng Ming-min contended for this position. The seventy-two-year-old Peng emerged victorious and nominated legislatorFrank Hsieh to be his running mate. Peng opposed trade withmainland China unless the PRC promised to "treat Taiwan as an equal." Though he argued that theOne-China policy would lead to another228 Incident , he took the position that Taiwan was already "de facto" independent so a formal declaration ofTaiwan independence was unnecessary unless the PRC attacked.Former Taiwan Provincial Governor
Lin Yang-kang ran as an independent with former PremierHau Pei-tsun as his running mate. After the pair registered as candidates on November 27, 1995, a small protest inTaichung demanded their expulsion from the KMT. On the recommendation of the KMT Disciplinary Committee, their party memberships were "cancelled" (a step short of "expelled") in December for "viciously attacking" Lee Teng-hui and "seriously damaging the party's image and prestige." They were endorsed by New Party after its own nominee dropped out. Lin and Hau likewise campaigned on behalf of the New Party. They supported the One-China Principle and favored opening direct links with the mainland. They argued that the KMT was too corrupt to govern.A second independent ticket consisted of former Control Yuan President
Chen Li-an for President and Control Yuan MemberWang Ching-feng for Vice President. Chen Li-an, the son of former Premier and Vice PresidentChen Cheng , used hisBuddhist background (lay leader of theFo Guang Shan order) and stressed moral purity and honest government. He walked for eighteen days wearing a famer's straw hat to spread his views.1996 Taiwan Straits Crisis
From
March 8 toMarch 15 , thePeople's Liberation Army sentballistic missiles within 25 to 35 miles (just inside the ROC's territorial waters) off the ports of Keelung and Kaohsiung. This action was intended to intimidate the Taiwanese electorate into voting against Lee and Peng, which Beijing branded "absolutely identical in attempting to divide the motherland." Similarly, Chen Li-an warned, "If you vote for Lee Teng-hui, you are choosing war." The crisis came to an end when two U.S.aircraft carrier battle groups were positioned near Taiwan.Lee, who told his people to resist "state terrorism," was boosted in popularity by the widespread anger (as opposed to fear) caused by the missile tests. Most analysts believed that Lee was boosted 5% in the polls, just enough to have earned him a majority (as opposed to a plurality) in the election.
Election result
External links
* [http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/iaps/taiwan/results96.htm B/w candidate portraits]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
