- Peach-faced Lovebird
Taxobox | name = Peach-faced Lovebird
status = LC
status_system = iucn3.1
_-eating_sunflower_seeds.jpg)
image_caption = Eating sunflower seeds
image_width = 240px
regnum =Animalia
phylum =Chordata
classis = Aves
ordo =Psittaciformes
familia =Psittacidae
genus = "Agapornis "
species = "A. roseicollis"
binomial = "Agapornis roseicollis"
binomial_authority = (Vieillot, 1818)
range_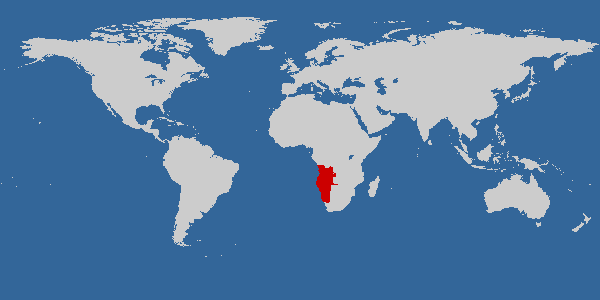
range_map_width = 240px
range_map_caption = Native ranges in theNamib Desert and arid areas of Namibia and AngolaThe Peach-faced Lovebird ("Agapornis roseicollis"), also known as the Rosy-faced Lovebird, is a species of
lovebird native to arid regions in southwesternAfrica such as theNamib Desert . A loud and constant chirper, these birds are very social animals and often congregate in small groups in the wild. They eat throughout the day and take frequent baths. Coloration can vary widely among populations but females are generally darker and greener, whilst males are smaller and brighter. Lovebirds are renowned for their sleep position in which they sit side-by-side and turn their faces in towards each other. Also, females are well noted to tear raw materials into long strips, "twisty-tie" them onto their backs, and fly distances back to make a nest.Taxonomy
It was described by the French ornithologist
Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot in 1818. It was originally named "Psittacus roseicollis" but later moved to the genus "Agapornis" with the other lovebirds. Twosubspecies are recognised: "A. r. roseicollis" inNamibia andSouth Africa and "A. r. catumbella" inAngola .Description
It is a fairly small bird, 17–18 cm long with an average wing length of 106 mm and tail length of 44–52 mm.McLachlan G. R. & Liversidge, R. (1981) "Roberts Birds of South Africa", John Voelcker Bird Book Fund, Cape Town. ISBN 0620031182] Wild birds are mostly green with a blue rump. The face and throat are pinkish, darkest on the forehead and above the eye. The bill is greenish-yellow, the iris is brown and the legs and feet are grey. Juvenile birds have a paler face and throat and a brownish
cere .It has various harsh, shrieking calls.
Distribution and habitat
It inhabits dry, open country in south-west Africa. Its range extends from south-west Angola across most of Namibia to the lower
Orange River valley in north-west South Africa. It occurs up to 1,600 metres above sea-level in broad-leaved woodland, semi-desert and mountainous areas. It is dependent on the presence of water sources and gathers around pools to drink.Escapes from captivity are frequent in many parts of the world and feral birds occur in
Arizona .tatus and conservation
Populations have been reduced in some areas by trapping for the pet trade. However numbers may have increased in other parts due to the creation by man of new water sources and the building of artificial structures which provide new nesting sites. Because of this the species is classed as
Least Concern by theInternational Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). [IUCN2006|assessors=BirdLife International|year=2004|id=48005|title=Agapornis roseicollis|downloaded=11 May 2006 Database entry includes justification for why this species is of least concern.]Behaviour in the wild
Feeding
The diet mainly consists of seeds and berries. When food is plentiful, it may gather in flocks containing hundreds of birds. It can sometimes be a pest in agricultural areas feeding on crops such as millet.
Reproduction
For breeding these birds we need a pair which is not easy because their sex is not easily determined we can find the sex by the pelvis bones which in males measure 1-3 mm in females it measures 6-8mm The nest is built in a rock crevice or within a compartment of the large communal nests built by
Sociable Weaver s. Man-made structures such as the roofs of houses may also be used. 4-6 eggs are laid between February and April. They are dull white and measure 23.5 mm by 17.3 mm. They are incubated for about 23 days. The young birdsfledge after 43 days.Aviculture
Housing
Lovebirds, being an active bunch, need some room to move in their cage. A cage approximately 24" W x 14" D x 30" H (60 W x 35 D x 75 H cm) is a good size, but if you can afford it, the bigger the better. Make sure the bars are spaced no wider than 3/8" (1 cm) apart, otherwise your bird will be able to stick its head through the bars. Add a variety of perches, so your lovebird can exercise its feet to prevent arthritis. The perches should be at least 4" (10 cm) long and 1/2" (13 mm) in diameter. A variety of different toys placed in the cage may prevent a pet parrot from boredom and loneliness. The parrot's chewing and playing may break some toys and small detachable parts may be dangerous to the parrot.
Feeding
Peach-faced Lovebirds require a variety of foods, including vegetables, seeds, and fruits; nevertheless, some human foods are unsuitable or poisonous for them, including dairy products, chocolate, cheese, avocado, rhubarb, and strawberries (which contain trace amounts of carcinogenic pesticides). Perishable food that has been placed in the birds' housing for more than 24 hours is also likely to be unsuitable. Grapes, carrots, beans, squash, corn, millet, quinoa, and winterwheat are excellent foods. They can also eat various manufactured food pellets and pastas. Suitable seed and pellet mixes include a large array of different seed types.
Personality
Peach-faced Lovebirds get their name for their affection towards their owner or other birds. Lovebirds are very playful and love to have all the attention centered around them. If trained correctly, Peach-faced Lovebird will happily perch on your shoulder. All lovebirds are unique; they all have different temperaments. Some are calmer than others, while some are extremely stubborn. One thing you will find in every lovebird is that they need companionship. If you cannot provide attention, you will be suggested to purchase another one. But be warned: If you buy two lovebirds, they may not interact with you as much as if they were by themselves. Two lovebirds may not get along, and may have to be separated.
Dangers and toxins
*
blue-green algae
*avocado
*Teflon
*chocolate
*alcohol
*dog andcat saliva
*household cleaners and detergentsMutations
Peach-faced Lovebirds have the widest range of colour mutations of all the Agapornis species. Generally speaking, these mutations fall into the genetic categories of
Dominant ,Co-dominant ,Recessive , and Sex-Linked Recessive (referred to simply as "sex-linked "). While this seems fairly straight-forward, it can quickly become confusing when a single specimen has multiple examples of these mutational traits.
Right: Lutino
Right: Pied Wild Green)
References
*cite web| publisher =BirdLife International (2008) |url = http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=1510&m=0 |title = Species factsheet: "Agapornis roseicollis" |accessdaymonth = 9 July | accessyear = 2008
* (2007): "Parrots of Africa" (1st edition). Halberstadt, Germany. ISBN 978-3833484452External links
* [http://www.lovebirds.co.nz/mutations/peach.php Peach Faced Lovebird mutation information] Information on PFLB mutations
* [http://www.lovebirds.co.nz/introduction/spec.php#peac Peach Faced Lovebird information] More information and photos, Peach Faced Lovebird
* [http://www.roseicollis.net www.roseicollis.net] Peach-faced website for breeding information.
* [http://www.roseicollis.info www.roseicollis.info] French website
* [http://mirror-pole.com/collpage/pf_loveb/pfl_1.htm Peach-faced Lovebird] Range Expansion Data in Greater Phoenix, Arizona
* [http://www.africanlovebirdsociety.com/ African Love Bird Society] An international organization dedicated to the keeping, breeding, and showing of Love Birds.
* [http://pets.groups.yahoo.com/group/LB_List/ Yahoo Groups Lovebird List] The largest lovebird list on the Internet
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
