- Network card
Infobox Computer Hardware Generic
name = Network Card
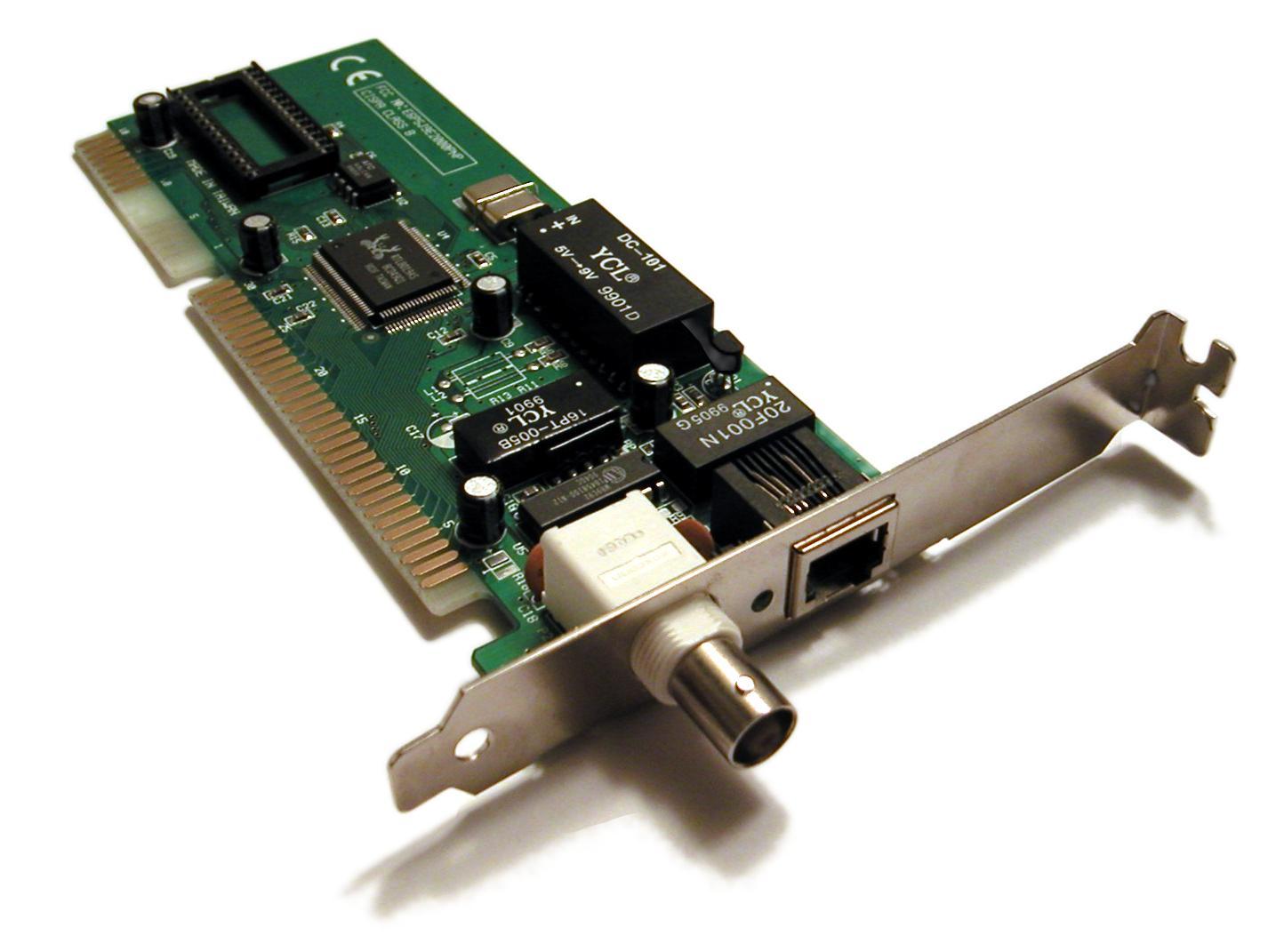
caption = A 1990sEthernet network interface controller card which connects to the motherboard via the now-obsoleteISA bus . This combination card features both a (now obsolete)bayonet cap BNC connector (left) for use in coaxial-based10base2 networks and anRJ-45 connector (right) for use intwisted pair -based10baseT networks. (The ports could not be used simultaneously.)
invent-date =
invent-name =
conn1 = Motherboard
via1_1 = Integrated
via1_2 = PCI Connector
via1_3 = ISA Connector
viawat up its kyle withorn1_4 =PCI-E
conn2 = Network
via2_1 =Fast Ethernet
via2_2 =Gigabit Ethernet
via2_3 =Optical fiber
via2_4 =Token ring
class-name = Speeds
class1 = 10 Mbit/s
class2 = 100 Mbit/s
class3 = 1000 Mbit/s
class4 = up to 160 Gbit/s
manuf1 =Novell
manuf2 =Intel
manuf3 =Realtek
manuf4 = OthersA Network card, Network Adapter, LAN Adapter or NIC (network interface card) is a piece of
computer hardware designed to allow computers to communicate over acomputer network . It is both an OSI layer 1 (physical layer ) and layer 2 (data link layer ) device, as it provides physical access to a networking medium and provides a low-level addressing system through the use ofMAC address es. It allows users to connect to each other either by using cables or wirelessly.Although other network technologies exist,
Ethernet has achieved near-ubiquity since the mid-1990s. Every Ethernet network card has a unique 48-bit serial number called aMAC address , which is stored in ROM carried on the card. Every computer on an Ethernet network must have a card with a unique MAC address. No two cards ever manufactured share the same address. This is accomplished by theInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE ), which is responsible for assigning unique MAC addresses to the vendors of network interface controllers.Whereas network cards used to be
expansion card s that plug into a computer bus, the low cost and ubiquity of the Ethernet standard means that most newer computers have a network interface built into themotherboard . These either have Ethernet capabilities integrated into the motherboard chipset, or implemented via a low cost dedicated Ethernet chip, connected through the PCI (or the newerPCI express bus). A separate network card is not required unless multiple interfaces are needed or some other type of network is used. Newer motherboards may even have dual network (Ethernet) interfaces built-in.The card implements the electronic circuitry required to communicate using a specific
physical layer anddata link layer standard such asEthernet ortoken ring . This provides a base for a full networkprotocol stack , allowing communication among small groups of computers on the sameLAN and large-scale network communications through routable protocols, such as IP.There are four techniques used to transfer data, the NIC may use one or more of these techniques.
*Polling is where the
microprocessor examines the status of theperipheral under program control.
*ProgrammedI/O is where themicroprocessor alerts the designatedperipheral by applying its address to the system'saddress bus .
*Interrupt-drivenI/O is where theperipheral alerts themicroprocessor that it's ready to transfer data.
*DMA is where the intelligentperipheral assumes control of thesystem bus to access memory directly. This removes load from the CPU but requires a separate processor on the card.A network card typically has a
twisted pair , BNC, or AUI socket where the network cable is connected, and a few LEDs to inform the user of whether the network is active, and whether or not there is data being transmitted on it. Network Cards are typically available in 10/100/1000 Mbit/s varieties. This means they can support a transfer rate of 10, 100 or 1000 Megabits per second.Network interface controller
A Network Interface Controller (NIC) is a hardware interface that handles and allows a network capable device access to a
computer network such as theinternet . The NIC has a ROM chip that has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) Address burned into it. The MAC address identifies the vendor and the serial number of the NIC which is unique to the card. Every NIC has a unique MAC address which identifies it on the LAN. The NIC exists on both the 'Physical Layer ' (Layer 1) and the 'Data Link Layer' (Layer 2) of theOSI model .Sometimes the word 'controller' and 'card' is used interchangeably when talking about networking because the most common NIC is the Network Interface Card. Although 'card' is more commonly used, it is in less encompassing. The 'controller' may take the form of a network card that is installed inside a
computer , or it may refer to an embedded component as part of a computer motherboard, arouter ,expansion card , printer interface, or aUSB device.A MAC Address is a unique 48 bit network hardware identifier that is burned into a ROM chip on the NIC to identify that device on the network. The first 24 bits is called the
Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and is largely manufacturer dependent. Each OUI allows for 16,777,216 Unique NIC Addresses.Smaller manufacturers that do not have a need for over 4096 unique NIC addresses may opt to purchase an
Individual Address Block (IAB) instead. An IAB consists of the 24 bit OUI, plus a 12 bit extension (taken from the 'potential' NIC portion of theMAC address )ee also
*
MAC address
*TCP Offload Engine (TOE)
*Host bus adapter (HBA)
*Wireless network interface card (WNIC)
*Ethernet
*Gigabit Ethernet
*Router
*IPMP References
* [http://www.examcram2.com/articles/article.asp?p=438038&seqNum=2&rl=1 CCNA Exam Prep: Data Link Networking Concepts]
* [http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml IEEE Registration Authority - IEEE OUI and Company_id Assignments]
* [http://standards.ieee.org/faqs/OUI.html IEEE Registration Authority - FAQ]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
