- John L. Lewis
Infobox Person
name=John L. Lewis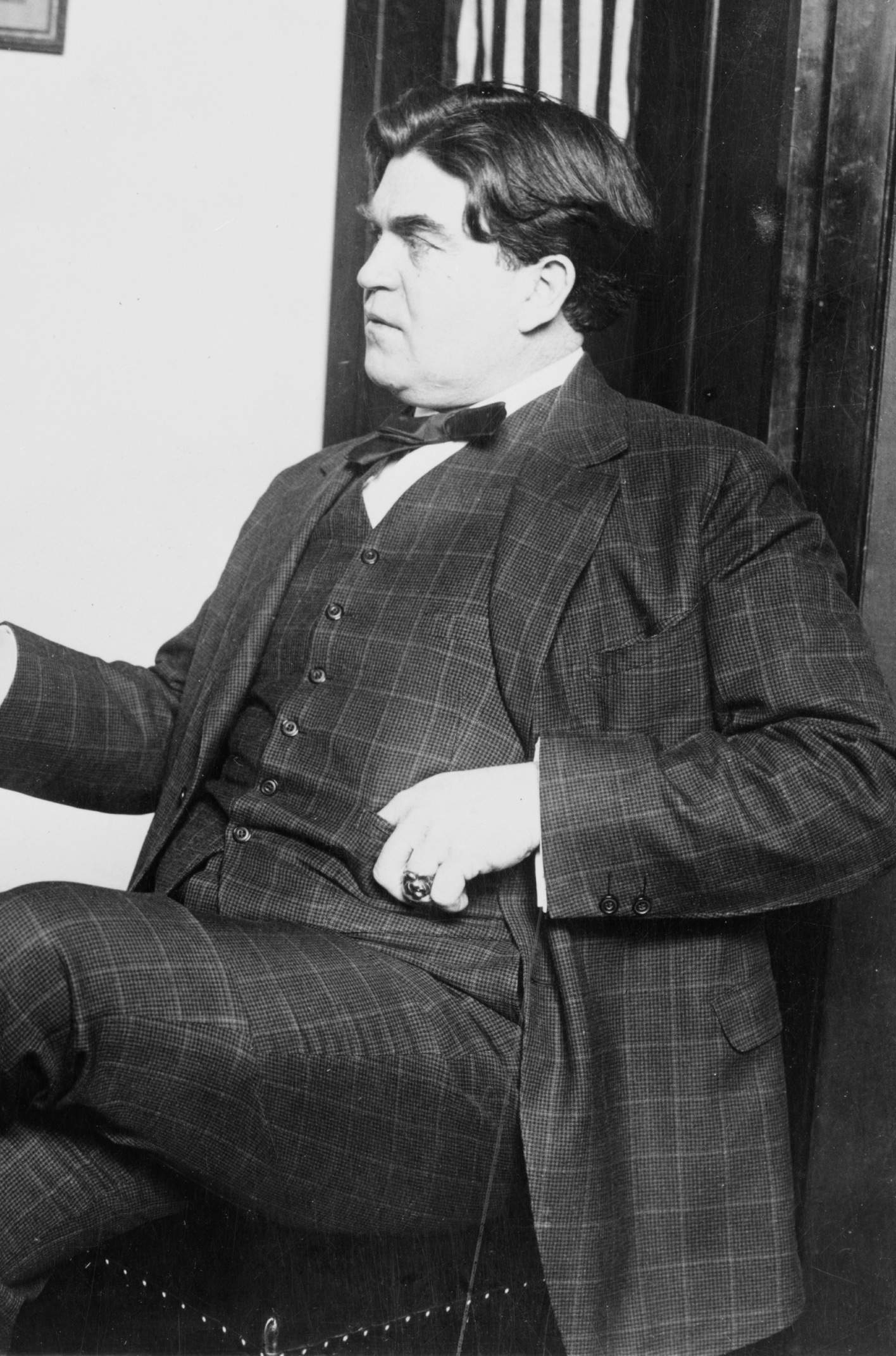
caption=9th President of theUnited Mine Workers of America
birth_date=February 12, 1880
birth_place=Lucas, Iowa
death_date=June 11, 1969
death_place=Alexandria, Virginia
occupation=Labor leader |
|John Llewellyn Lewis (
February 12 ,1880 –June 11 ,1969 ) was an American leader of organized labor who served as president of theUnited Mine Workers of America from 1920 to 1960. He was a major player in thehistory of coal mining . He was the driving force behind the founding of theCongress of Industrial Organizations , which established theUnited Steel Workers of America and helped organize millions of other industrial workers in the 1930s. After resigning as head of the CIO in 1941, he took the Mine Workers out of the CIO in 1942, then back into theAmerican Federation of Labor in 1944.Rise to Power
Lewis was born in
Cleveland, Iowa , the son of Thomas H. Lewis and Ann Watkins Lewis, both of whom had immigrated fromWales [ "Current Biography 1941", pp511-15 ] . Lewis began working in the "BIG HILL" Mine at Lucas as a teenager. He began working around the countryside as a "ten day miner" in the western United States. He moved toPanama, Illinois and then toSpringfield, Illinois in 1910 with other members of his family. He joined the United Mine Workers and was eventually elected to the position of branch secretary. In 1911 Lewis began organizing for the AFL full time. After serving as statistician and then as vice-president for the UMWA, Lewis became that union's acting president in 1919 [ "Current Biography 1941", p511] . On November 1 of that year, he called the first major coal union strike, as 400,000 miners walked off their jobs [ Id. at 511-12 ] . President Wilson obtained an injunction, which Lewis obeyed, telling the rank and file, "We cannot fight the Government." [ Id. at 512] . In 1920 he was elected president of the UMWA. Lewis quickly asserted himself as a dominant figure in what was then the largest and most influential trade union in the country.Lewis was considered by some a despotic leader of the Mine Workers: he expelled his political rivals within the UMWA, such as John Brophy,
Alexander Howat andAdolph Germer . Communists in District 26 (Nova Scotia ), including Canadian labor legend JB McLachlan, were banned from running for the union executive after a strike in 1923. McLachlan described him as "a traitor to the working class". Lewis nonetheless commanded great loyalty from many of his followers, even those he had exiled in the past.A powerful speaker and strategist, Lewis used the nation's dependence on coal to increase the wages and improve the safety of miners, even during several severe recessions. He masterminded a five-month strike, ensuring that the increase in wages gained during
World War I would not be lost. Lewis challengedSamuel Gompers , who had led the AFL for nearly forty years, for the Presidency of the AFL in 1921. William Green, one of his subordinates within the Mine Workers at the time, nominated him;William Hutcheson , the President of the Carpenters, supported him. Gompers won. Three years later, on Gompers' death, Green succeeded him as AFL President.in Coolidge's cabinet. Lewis declined, a move he later regretted. Without government support, the contract talks failed and coal operators hired non-union miners [ "Current Biography 1941", pp512 ] . The UMWA treasury was drained, but Lewis was able to maintain the union and his position within it. He was successful in winning the 1925 anthracite miners' strike by his oratorical skills.
Historian C.L. Sulzberger later described the technique in a 1938 book called "Sit Down with John L. Lewis", calling it the "Crust of Bread" speech. Operators who opposed a contract were often shamed into agreement by Lewis's accusations. A typical Lewis speech to operators would go, "Gentlemen, I speak to you for the miners' families... The little children are gathered around a bare table without anything to eat. They are not asking for a $100,000 yacht like yours, Mr.______..." (here, he would gesture with his cigar toward an operator), "...or for a Rolls Royce limousine like yours, Mr. _____..." (staring at another operator). They are asking only for a slim crust of bread." [ "Current Biography 1941", pp512 ] . With the full support of the AFL and the UMWA,
Franklin D. Roosevelt was nominated and elected President in 1932, and Lewis benefitted from theNew Deal programs that followed. Thanks to theWagner Act of 1935, labor union membership grew rapidly, especially in the UMWA. Lewis and the UMW were major backers of Roosevelt's reelection in 1936, and were firmly committed to theNew Deal .Lewis sent his best organizers into heavy industry in 1935-37, to organize the auto workers, the glass workers, the rubber workers and others. He supported the illegal sit-down strike (but did not use that tactic in the mines). When the AFL balked at organizing unskilled workers, Lewis withdrew his unions and formed a new organization, the CIO. By 1937-40 the CIO was spending as much time fighting the AFL as organizing, with the result that union political power was divided against itself. During the late-1930s struggle over the AFL's refusal to organize mass production workers, Green became the target of some of Lewis' most stinging attacks while Hutcheson was the recipient of a famous punch from Lewis that came to symbolize the dispute between the conservative AFL and the rebellious CIO.
In the Presidential election of 1940, Lewis, heavily dependent on pro-Soviet organizers, rejected Roosevelt and supported
Wendell Willkie , a Republican candidate, fearing Roosevelt's intention for American involvement in World War II. After the Japanese attack onPearl Harbor the miners issued a no-strike pledge "for the duration" in support of the war effort. However, Lewis repeatedly violated the pledge, most notably in 1943 when half a million workers walked off the job. Public opinion was extremely angry and demanded new laws. President Roosevelt, a traditional ally of labor, felt he had no choice but to seize the mines. Even so, some steel mills closed for weeks and power shortages crippled production.The 1950s
nonetheless eliminated many of the jobs in his industry while scattered non-union operations persisted.
Lewis continued to be as autocratic as ever within the UMWA: until the passage of the Landrum-Griffin Act in 1959, the UMWA had kept a number of its districts in trusteeship for decades, meaning that Lewis appointed union officers who otherwise would have been elected by the membership.
Lewis retired as president of the UMWA in 1960 and was succeeded as president by Thomas Kennedy until his death in, 1963, when he was succeeded by Lewis-anointed successor
W. A. Boyle , who was just as dictatorial, but without any of Lewis' leadership skills or vision.Retirement and Final Years
On
September 14 ,1964 , four years after his retirement from the UMWA, Lewis was awarded thePresidential Medal of Freedom by PresidentLyndon Johnson , [ " [http://www.medaloffreedom.com/JohnLewis.htm Presidential Medal of Freedom citation] at www.medaloffreedom.com" ] his citation reading:" [An] eloquent spokesman of labor, [Lewis] has given voice to the aspirations of the industrial workers of the country and led the cause of free trade unions within a healthy system of free enterprise."
Lewis retired to his family home, the "
Lee-Fendall House ", inAlexandria, Virginia , where he had lived since 1937. He lived there until his death onJune 11 ,1969 . He is buried inOak Ridge Cemetery ,Springfield, Illinois . [http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=19560]References in popular culture
*In the 1938 motion picture "Holiday" the character of Linda Seton played by
Katharine Hepburn describes how she tried to help some strikers in Jersey. "I never could decide whether I wanted to beJoan of Arc ,Florence Nightingale orJohn L. Lewis ." Fact|date=April 2008
*In an episode of theJack Benny radio program, a friend brings a baby over to Benny's house. When the infant breaks a jar of home-madechili , Benny demands fifteen cents as compensation. When his friend protests by saying that he shouldn't have to pay because the baby is aminor . Benny retorts: "I don't care if he's John L. Lewis!" causing the audience to roar with laughter at theminor /miner play on words . Fact|date=April 2008Notes
References
*Alinsky, Saul. "John L. Lewis: An Unauthorized Biography." Reprint paperback ed. Vancouver, Wash.: Vintage Books, 1970. ISBN 0394708822 (Originally published in 1949.)
*Bernstein, Irving. "The Turbulent Years: A History of the American Worker, 1933-1941." Paperback edition. Boston: Houghton-Mifflin Co., 1970. ISBN 039511778X (Originally published 1969.)
*Cantril, Hadley and Strunk, Mildred, eds. "Public Opinion, 1935-1946." Princeton, N.J." Princeton University Press, 1951.
*Dubofsky, Warren and Van Tine, Warren. "John L. Lewis: A Biography." Reprint ed. Champaign, Ill.: University of Illinois Press, 1992. ISBN 081290673X
*Galenson, Walter. "The CIO Challenge to the AFL: A History of the American Labor Movement, 1935-1941." Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1960. ISBN 0674131509
*Zieger, Robert. "The CIO, 1935-1955." Reprint ed. Chapel Hill, N.C.: University of North Carolina Press, 1997. ISBN 0807846309External links
* [http://www.umwa.org/history/lewis/ Lewis's biography] on the [http://www.umwa.org/ United Mine Workers of America's website]
* [http://www.u-s-history.com/pages/h1625.html Medium-length biography from a history site]
* [http://famousspeeches.blogspot.com/2007/11/famous-speeches-john-l-lewis-labor-and.html Transcript of Lewis' speech] "Labor and the Nation".
* [http://www.iowaaflcio.org/john_l__lewis.htm John L. Lewis Museum of Mining and Labor] in Lucas, IowaPersondata
NAME=Lewis, John Llewellyn
SHORT DESCRIPTION=U.S. labor leader
DATE OF BIRTH=February 12 ,1880
PLACE OF BIRTH=Lucas, Iowa ,United States
DATE OF DEATH=June 11 ,1966
PLACE OF DEATH=Alexandria, Virginia ,United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
