- p300-CBP coactivator family
-
E1A binding protein p300 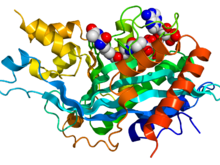
Crystallographic structure of the histone acetyltrans-ferase domain of EP300 (rainbow colored, N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with the inhibitor lysine-CoA (space-filling model, carbon = white, oxygen = red, nitrogen = blue, phosphorus = orange).[1] Identifiers Symbol EP300 Alt. symbols p300 Entrez 2033 HUGO 3373 OMIM 602700 PDB 3biy RefSeq NM_001429 UniProt Q09472 Other data EC number 2.3.1.48 Locus Chr. 22 q13.2 CREB binding protein (CBP) Identifiers Symbol CREBBP Alt. symbols CBP, RSTS Entrez 1387 HUGO 2348 OMIM 600140 PDB 3dwy RefSeq NM_004380 UniProt Q92793 Other data EC number 2.3.1.48 Locus Chr. 16 p13.3 The p300-CBP coactivator family is composed of two closely related transcriptional co-activating proteins (or coactivators):
- p300 (also called EP300 or E1A binding protein p300)
- CBP (also known as CREB-binding protein or CREBBP)
Both p300 and CBP interact with numerous transcription factors and act to increase the expression of their target genes.[2][3]
Contents
Protein structure
p300 and CBP have similar structures. Both contain five protein interaction domains: the nuclear receptor interaction domain (RID), the CREB and MYB interaction domain (KIX), the cysteine/histidine regions (TAZ1/CH1 and TAZ2/CH3) and the interferon response binding domain (IBiD). The last four domains, KIX, TAZ1, TAZ2 and IBiD of p300, each bind tightly to a sequence spanning both transactivation domains 9aaTADs of transcription factor p53.[4][5] In addition p300 and CBP each contain a protein or histone acetyltransferase (PAT/HAT) domain and a bromodomain that binds acetylated lysines and a PHD finger motif with unknown function.[6] The conserved domains are connected by long stretches of unstructured linkers.

Regulation of gene expression
p300 and CBP are thought to increase gene expression in three ways:
- by relaxing the chromatin structure at the gene promoter through their intrinsic histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity.
- recruiting the basal transcriptional machinery including RNA polymerase II to the promoter.
- acting as adaptor molecules.[7]
Function in G protein signaling
An example of a process involving p300 and CBP is G protein signaling. Some G proteins stimulate adenylate cyclase that results in elevation of cAMP. cAMP stimulates PKA, which consists of four subunits, two regulatory and two catalytic. Binding of cAMP to the regulatory subunits causes release of the catalytic subunits. These subunits can then enter the nucleus to interact with transcriptional factors, thus affecting gene transcription. The transcription factor CREB, which interacts with a DNA sequence called a cAMP response element (or CRE), is phosphorylated on a serine (Ser 113) in the KID domain. This modification is PKA mediated, and promotes the interaction of the KID domain of CREB with the KIX domain of CBP or p300 and enhances transcription of CREB target genes, including genes that aid gluconeogenesis. This pathway is initiated by adrenaline binding to the cell of interest.[8]
Clinical significance
Mutations in CBP, and to a lesser extent p300, are the cause of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome,[9] which is characterized by severe mental retardation. These mutations result in the loss of one copy of the gene in each cell, which reduces the amount of CBP or p300 protein by half. Some mutations lead to the production of a very short, nonfunctional version of the CBP or p300 protein, while others prevent one copy of the gene from making any protein at all. Although researchers do not know how a reduction in the amount of CBP or p300 protein leads to the specific features of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, it is clear that the loss of one copy of the CBP or p300 gene disrupts normal development. Defects in CBP HAT activity appears to cause problems in long-term memory formation.[10] CBP and p300 have also been found to be involved in multiple rare chromosomal translocations that are associated with acute myeloid leukemia.[7] For example, researchers have found a translocation between chromosomes 8 and 22 (in the region containing the p300 gene) in several people with a cancer of blood cells called acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Another translocation, involving chromosomes 11 and 22, has been found in a small number of people who have undergone cancer treatment. This chromosomal change is associated with the development of AML following chemotherapy for other forms of cancer. Mutations in the p300 gene have been identified in several other types of cancer. These mutations are somatic, which means they are acquired during a person's lifetime and are present only in certain cells. Somatic mutations in the p300 gene have been found in a small number of solid tumors, including cancers of the colon and rectum, stomach, breast and pancreas. Studies suggest that p300 mutations may also play a role in the development of some prostate cancers, and could help predict whether these tumors will increase in size or spread to other parts of the body. In cancer cells, p300 mutations prevent the gene from producing any functional protein. Without p300, cells cannot effectively restrain growth and division, which can allow cancerous tumors to form.
Mouse models
CBP and p300 are critical for normal embryonic development, as mice completely lacking either CBP or p300 protein, die at an early embryonic stage.[11][12] In addition, mice which lack one functional copy (allele) of both the CBP and p300 genes (i.e. are heterozygous for both CBP and p300) and thus have half of the normal amount of both CBP and p300, also die early in embryogenesis.[11] This indicates that the total amount of CBP and p300 protein is critical for embryo development. Interestingly, data suggest that some cell types can tolerate loss of CBP or p300 better than the whole organism can. Mouse B cells or T cells lacking either CBP and p300 protein develop fairly normally, but B or T cells that lack both CBP and p300 fail to develop in vivo.[2][13] Together, the data indicates that while individual cell types require different amounts of CBP and p300 to develop or survive and that some cell types are more tolerant of loss of CBP or p300 than the whole organism; it appears that many, if not all cell types may require at least some p300 or CBP to develop.
References
- ^ PDB 3BIY; Liu X, Wang L, Zhao K, Thompson PR, Hwang Y, Marmorstein R, Cole PA (February 2008). "The structural basis of protein acetylation by the p300/CBP transcriptional coactivator". Nature 451 (7180): 846–50. Bibcode 2008Natur.451..846L. doi:10.1038/nature06546. PMID 18273021.
- ^ a b Kasper LH, Fukuyama T, Biesen MA, Boussouar F, Tong C, de Pauw A, Murray PJ, van Deursen JM, Brindle PK (2006). "Conditional knockout mice reveal distinct functions for the global transcriptional coactivators CBP and p300 in T-cell development". Mol. Cell. Biol. 26 (3): 789–809. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.3.789-809.2006. PMID 16428436.
- ^ Vo N, Goodman RH (2001). "CREB-binding protein and p300 in transcriptional regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (17): 13505–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.R000025200. PMID 11279224.
- ^ Teufel DP, Freund SM, Bycroft M, Fersht AR (April 2007). "Four domains of p300 each bind tightly to a sequence spanning both transactivation subdomains of p53". PNAS 104 (17): 7009–7014. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702010104.; Piskacek S, Gregor M, Nemethova M, Grabner M, Kovarik P, Piskacek M (June 2007). "Nine-amino-acid transactivation domain: establishment and prediction utilities". Genomics 89 (6): 756–68. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.02.003. PMID 17467953.; Piskacek M (2009-11-05). "9aaTAD is a common transactivation domain recruits multiple general coactivators TAF9, MED15, CBP/p300 and GCN5". Nature Precedings Pre-publication. doi:10.1038/npre.2009.3488.2.; Piskacek M (2009-11-05). "9aaTADs mimic DNA to interact with a pseudo-DNA Binding Domain KIX of Med15 (Molecular Chameleons)". Nature Precedings Pre-publication. doi:10.1038/npre.2009.3939.1.; Piskacek M; Piskacek, Martin (2009-11-20). "9aaTAD Prediction result (2006)". Nature Precedings Pre-publication. doi:10.1038/npre.2009.3984.1.
- ^ The prediction for 9aaTADs (for both acidic and hydrophilic transactivation domains) is available online from ExPASy http://us.expasy.org/tools/ and EMBnet Spain http://www.es.embnet.org/Services/EMBnetAT/htdoc/9aatad/
- ^ Spiegelman BM, Heinrich R (2004). "Biological control through regulated transcriptional coactivators". Cell 119 (2): 157–67. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.037. PMID 15479634.
- ^ a b Goodman RH, Smolik S (2000). "CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development". Genes Dev. 14 (13): 1553–77. doi:10.1101/gad.14.13.1553. PMID 10887150.
- ^ Mayr B, Montminy M (2001). "Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2 (8): 599–609. doi:10.1038/35085068. PMID 11483993.
- ^ Petrij F, Giles RH, Dauwerse HG, et al. (July 1995). "Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome caused by mutations in the transcriptional co-activator CBP". Nature 376 (6538): 348–51. Bibcode 1995Natur.376..348P. doi:10.1038/376348a0. PMID 7630403.
- ^ Korzus E, Rosenfeld MG, Mayford M (2004). "CBP histone acetyltransferase activity is a critical component of memory consolidation". Neuron 42 (6): 961–72. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.002. PMID 15207240.
- ^ a b Yao TP, Oh SP, Fuchs M, Zhou ND, Ch'ng LE, Newsome D, Bronson RT, Li E, Livingston DM, Eckner R (1998). "Gene dosage-dependent embryonic development and proliferation defects in mice lacking the transcriptional integrator p300". Cell 93 (3): 361–72. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81165-4. PMID 9590171.
- ^ Tanaka Y, Naruse I, Hongo T, Xu M, Nakahata T, Maekawa T, Ishii S (2000). "Extensive brain hemorrhage and embryonic lethality in a mouse null mutant of CREB-binding protein". Mech. Dev. 95 (1-2): 133–45. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(00)00360-9. PMID 10906457.
- ^ Xu W, Fukuyama T, Ney PA, Wang D, Rehg J, Boyd K, van Deursen JM, Brindle PK (2006). "Global transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein and p300 are highly essential collectively but not individually in peripheral B cells". Blood 107 (11): 4407–16. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-08-3263. PMID 16424387.
External links
Transcription coregulators Coactivators Corepressors ATP-dependent remodeling factors Transferases: acyltransferases (EC 2.3) 2.3.1: other than amino-acyl groups acetyltransferases: Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase - N-Acetylglutamate synthase - Choline acetyltransferase - Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase - Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase - Beta-galactoside transacetylase - Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase - N-acetyltransferase (Serotonin N-acetyl transferase, HGSNAT, ARD1A) - Histone acetyltransferase (P300/CBP, NAT2)
palmitoyltransferases: Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase (CPT1, CPT2) - Serine C-palmitoyltransferase (SPTLC1, SPTLC2)
other: Acyltransferase like 2 - Aminolevulinic acid synthase - Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase - Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase - Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
Glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase - 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase - 2-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase - ABHD52.3.2: Aminoacyltransferases 2.3.3: converted into alkyl on transfer Categories:- Genes on chromosome 22
- Genes on chromosome 16
- Genes
- G proteins
- Membrane biology
- EC 2.3.1
- Transcription coregulators
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
