- Sucker (parasitic worms anatomy)
-
For other uses, see Sucker (disambiguation).
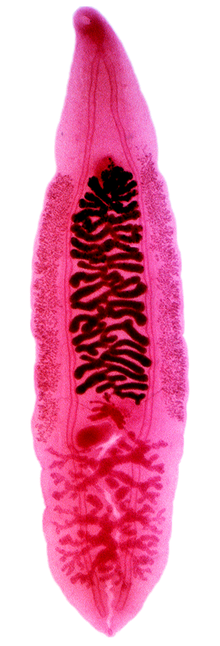 An adult Clonorchis sinensis has these main body parts: oral sucker, pharynx, caecum, ventral sucker, vitellaria, uterus, ovary, Mehlis' gland, testes, exretory bladder.
An adult Clonorchis sinensis has these main body parts: oral sucker, pharynx, caecum, ventral sucker, vitellaria, uterus, ovary, Mehlis' gland, testes, exretory bladder.
The sucker is an attachment organ of parasitic worms.
Contents
In Platyhelminths
In Platyhelminths (flatworms), the sucker is called bothridium.[1]
In the class Trematodes (flukes), there are an oral sucker and a ventral sucker or acetabulum as exemplified by Dicrocoelium dendriticum.[2]
In the class Cestoda (tapeworms), suckers can be found on the scolex as exemplified in the species Taenia saginata.
In the class Turbellaria, only the species of the order Temnocephalida are parasitic and possess an adhesive disc.
In the class Monogenea, buccal organs, also known as buccal suckers, are present in worm parasites of the order Mazocraeidea. They are known to have muscular, glandular, and sensory components thought to play some role in blood feeding.In Annelids
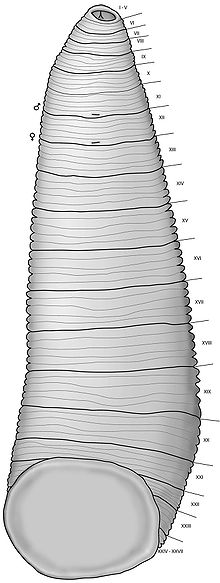
Leeches all have an anterior (oral) sucker formed from the first six segments of their body, which is used to connect to a host for feeding, and also release an anesthetic to prevent the host from feeling the leech. They use a combination of mucus and suction (caused by concentric muscles in those six segments) to stay attached and secrete an anti-clotting enzyme, hirudin, into the host's blood stream. The medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis) has two suckers, one at each end, called the anterior and posterior sucker. The posterior is mainly used for leverage while the anterior sucker, consisting of the jaw and teeth, is where the feeding takes place.
In Nematodes
The parasitic species Myleusnema bicornis differs from other nematodes in that it possess an extended oesophageal cavity, a ventral pre-anal sucker.
References
- ^ Bothridium on www.merriam-webster.com
- ^ Function of the acetabulum of digenetic trematodes, as exemplified by Dicrocoelium dendriticum. Neuhaus W., Z Parasitenkd. 1985;71(1), pp. 53-60, PubMed, doi:10.1007/BF00932918 (Article in German)
Categories:- Platyhelminth anatomy
- Annelid anatomy
- Invertebrate stubs
- Animal anatomy stubs
- Parasite stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.