- Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Oružane snage Bosne i Hercegovine
Оружане снаге Босне и Херцеговине
Coat of Arms of Bosnia and HerzegovinaService branches Ground Forces
Air Force and Aircraft DefenceHeadquarters Sarajevo Leadership Commander-in-Chief President of Bosnia and Herzegovina Minister of Defence Selmo Cikotić Chairman of the Joint Staff and Commander Lt. Gen. Miladin Milojčić Manpower Military age 18 years of age Conscription Abolished in 2006 Available for
military service1,034,367, age 18-49 (2005 est.) Fit for
military service829,530, age 18-49 (2005 est.) Reaching military
age annually31,264 (2005 est.) Active personnel 13,500 (ranked 127) Reserve personnel 5,000 Deployed personnel  Iraq - 85 (only a dozen of officers)
Iraq - 85 (only a dozen of officers)
 Afghanistan - 45
Afghanistan - 45
 Democratic Republic of the Congo - 5 (all officers/advisers)
Democratic Republic of the Congo - 5 (all officers/advisers)Expenditures Budget $450 million (2007 est.)[1] Percent of GDP 4.5% (2005 est.)[1] Industry Domestic suppliers Zrak (Optics)
Igman (small arms ammunition)
ORAO A.D. (Turbojet engines and parts)
Unis Promex (ARMAMENT, AMMUNITION and MILITARY EQUIPMENT)
BNT Travnik (small arms ammunition)
GINEX Gorazde (small arms parts of ammunition)BINAS (small arms ammunition)
FSV - FABRIKA SPECIJALNIH VOZILA A.D (Spare parts for all types of combat vehicles and tank M-84)Foreign suppliers  United States
United States
 Russia
Russia
 Turkey
Turkey
 China
China
 Italy
Italy
 Germany
Germany
 Romania
RomaniaRelated articles History Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
History of the Army of Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
War in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Patriotic League
Territorial Defence Force of the Republic of Bosnia and HercegovinaRanks Military ranks and insignia of Bosnia and Herzegovina Army of Bosnia and Herzegovina brigades The Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian: Oružane snage Bosne i Hercegovine, OSBIH Cyrillic script: Оружане снаге Босне и Херцеговине, ОСБИХ) is the official military force of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Bosnian Armed forces were unified in 2005 and are composed of two founding armies: Bosniak-Croat, Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Bosnian Serb, Army of Republika Srpska.
The Ministry of Defense of Bosnia and Herzegovina, founded in 2004, is in charge of the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina. There are approximately 13,500 active troops, 5,000 reserve troops, and 500 civilian staff.
Contents
Chain of command
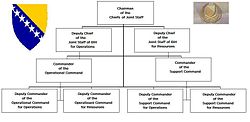
The supreme commander of the Bosnian Armed Forces is the current president of Bosnia and Herzegovina thus the Presidency commands the Bosnian Army, then the Bosnian Ministry of Defence with the minister Selmo Cikotić, then the Chiefs of Joint Staff with Sifet Podžić as the head of the chiefs. The BiH Chief of Joint Staff is Lieutenant General Miladin Milojčić. Conscription was completely abolished in Bosnia and Herzegovina effective on and from 1 January 2006.[2]
Defense law
The Bosnia and Herzegovina Defense Law addresses the following areas: the Military of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Government Institutions, Entity jurisdictions and structure, Budget and Financing, Composition of Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina, War declaration, Natural disasters, Conflict of interests and professionalism, Oath to Bosnia-Herzegovina, Flags, Anthem and Military Insignia, and transitional and end orders.
History
The AFBiH was formed from three armies of the Bosnian War period: the Bosnian (dominantly Bosniak with numbers of Serbs and Croats) Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Bosnian Serb Army of Republika Srpska, and the Croat Defence Council.
The Army of the Republic of Bosnia And Herzegovina was created on 15 April 1992 during the early days of the Bosnian War. Before the ARBiH was formally created, there existed Territorial Defence, an official military force of Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and a number of paramilitary groups such as the Green Berets, Patriotic League, and civil defense groups, as well as many criminal gangs and collections of police and military professionals. The army was formed under poor circumstances, with a very low number of tanks, APCs and no military aviation assets. The army was divided into Corps, each Corp was stationed in a territory. First commander was Sefer Halilović.
The Army of Republika Srpska was created on 12 May 1992. Before the VRS was formally created, there were a number of paramilitary groups such as the Srpska Dobrovoljačka Garda, Beli Orlovi, as well as some Russian, Greek and other volunteers. The army was equipped with ex-JNA inventory. It had about 200 tanks, mostly T-55s and 85 M-84s, and 150 APCs with several heavy artillery pieces. The Air Defense of VRS has shot down several aircraft, like F-16, Mirage 2000, F-18 and one Croatian Air Force MiG-21. The VRS received support from the Yugoslav Army and FRY until 1994, when Slobodan Milošević stopped military relations with Republika Srpska.
The Croatian Defence Council was the main military formation of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia during the Bosnian War and it was first organized military force to with the aim to control the Croat populated areas. It is not to be confused with the Croatian Defence Forces (HOS) which was a separate Croatian military unit.
In 1995-96, a NATO-led international peacekeeping force (IFOR) of 60,000 troops served in Bosnia and Herzegovina, beginning on December 21, 1995 to implement and monitor the military aspects of the Dayton Peace Agreement. IFOR was succeeded by a smaller, NATO-led Stabilization Force or SFOR. The number of SFOR troops was reduced first to 12,000 and then to 7,000. SFOR was in turn succeeded by an even smaller, European Union-led European Union Force, EUFOR Althea. As of 2004, EUFOR Althea numbered around 7,000 troops.
As the joint AFBiH began to develop, troops began to be sent abroad. Bosnia and Herzegovina deployed a unit of 37 men to destroy munitions and clear mines, in addition to 6 command personnel as part of the Multinational force in Iraq. The unit was first deployed to Fallujah, then Talil Air Base, and is now located at Camp Echo. In December 2006, the Bosnian government formerly extended its mandate through June 2007. Bosnia and Herzegovina is planning to send another 49 soldiers from the 6th infantry division to Iraq in August 2008, their mission will be to protect/guard Camp Victory in Baghdad.
Structure
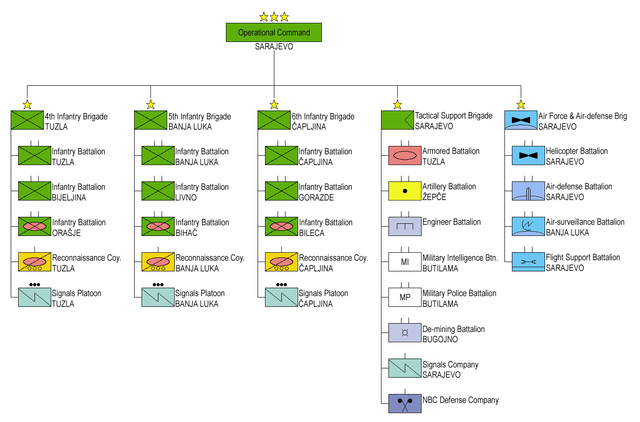
The Military units are commanded by the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina Joint Staff in Sarajevo. There are two major commands under the Joint Staff: Operational Command and Support Command.
There are three regiments that are each formed by soldiers from the three ethnic groups of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosniaks, Croats and Serbs and trace their roots to the armies that were created during the Bosnian war. These regiments have their distinct ethnic insignias and consist of three active battalions each. Each regiments three battalions divided evenly between the three active brigades of the Army.
- Operational Command (Sarajevo)[3]
- 4th Infantry Brigade (Tuzla)
- 5th Infantry Brigade (Banja Luka)
-
- Tactical Support Brigade (Sarajevo)
- Armored Battalion (Tuzla)
- Artillery Battalion (Žepče) (one battery detached to each brigade)
- Engineer Battalion (one company detached to each brigade)
- Military Intelligence Battalion (Butilama)
- Military Police Battalion (Butilama) (one platoon detached to each brigade)
- De-mining Battalion (Bugojno)
- Signals Company (Sarajevo)
- NBC Defense Company
- Air Force & Anti-Air Defense Brigade (Sarajevo, Banja Luka, Tuzla)
- Helicopter Battalion (Sarajevo) (one squadron detached to each brigade HQ)
- Air Defense Battalion (Sarajevo) (one company detached to each brigade)
- Early Warning & Surveillance Battalion (Banja Luka)
- Flight Support Battalion (Sarajevo, Banja Luka)
- Tactical Support Brigade (Sarajevo)
- Support Command (Banja Luka)
- Personnel Command
- Training and Doctrine Command
- Combat Training Center
- Armored Mechanized Battalion
- Combat Simulation Center
- Professional Development Center
- Officers School
- NCO School
- Foreign Language Center
- Combat Training Center
- Logistics Command
- Center for Movement Control
- Center for Material Management
- Main Logistics Base (Doboj and Sarajevo)
- 1st Logistics Support Battalion
- 2nd Logistics Support Battalion
- 3rd Logistics Support Battalion
- 4th Logistics Support Battalion
- 5th Logistics Support Battalion
Within the armed forces, there are a number of services. These include a Technical service, Air technology service, Military Police service, Communications service, Sanitary service, a Veterans service, Civilian service, Financial service, Information service, Legal service, Religious service, and a Musical service.
Uniform and Insignia
Main article: Military ranks and insignia of Bosnia and HerzegovinaArmed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina were unified in 2005 and at that time they needed a uniform for the newley founded army. MARPAT where the future uniform of AFBIH.
Insignia is found on military hats or berets, on the right and left shoulder on the uniform of all Soldiers of the Armed Forces. All, except for generals, wear badges on their hats or berets with either the land force badge or air force badge. Generals wear badges with the coat of arms of Bosnia surrounded with branches and two swords.All soldiers of the armed forces have on their right shoulder a flag of Bosnia and Herzegovina. All members of the 3 regiments wear their regiment insignia on the left shoulder. There are other insignias, brigades or other institution are worn under the regiment insignia. The name of the soldiers is worn on the left part of the chest while the name "Armed Forces of BiH" is worn on the right part of the chest.
Equipment
Infantry weapons
Assault Rifle Origin Type Versions Notes M16 rifle  United States
United StatesAssault Rifle A1 and A2 From 2010 OSBiH will scrap the A1 versions, and use A2 and A4 versions. Standard issue rifle of Bosnian and Herzegovina military and delivered from USA's Colt Arsenal in Hartford. M16 rifle  United States
United StatesAssault rifle A4 Entered service in 2010 AR-15  United States
United StatesAssault rifle 1,000 Donated by  United States 1999 and 22,000 purchased by FABiH 2000 - 2004
United States 1999 and 22,000 purchased by FABiH 2000 - 2004M4 carbine  United States
United StatesAssault rifle SOPMOD HK33  Germany
GermanyAssault rifle Donated by Turkey 1997 Heckler & Koch MP5  Germany
GermanySubmachine gun Used by the Military Police and Bosnian Special Forces AK-47  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionAssault rifle AKM  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionAssault Rifle Zastava M80  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaAssault Rifle Zastava M70  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaAssault rifle PP-19  Russia
RussiaSubmachine gun 250 donated by Russia and 1,000 purchased by the Bosnian government, only used by the Special Forces and the Special Anti-terrorist Unit SIPA FN FAL  Belgium
BelgiumBattle rifle H&K G3  Germany
GermanyBattle rifle A2 and A3 A2 donated by Turkey 1998, A3 was later purchased by the Bosnian government Skorpion vz. 61  Czech Republic
Czech RepublicSubmachine gun M84 Yugoslav Version M203  United States
United StatesGrenade Launcher Milkor MGL  South Africa
South AfricaGrenade Launcher Sniper rifle
Sniper rifle Origin Type Versions Notes Zastava M76  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaSniper rifle Dragunov SVD  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionSniper Rifle M48 Mauser  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaBolt-Action Rifle Used with Zrak 4*32 Scope MACS M3  Croatia
CroatiaAnti-Material Rifle Pistol
Pistol Origin Type Versions Notes Glock 17  Austria
AustriaPistol CZ-99  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaPistol TT-33  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionPistol Machine gun
Machine gun Origin Type Versions Notes M60  United States
United StatesMachine gun M2 .50 caliber  United States
United StatesMachine gun M240 machine gun  United States
United StatesMachine gun Zastava M84  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMachine gun Zastava M72  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMachine gun M72A and M72B 250,000 sold to Iraq Ultimax 100  Singapore
SingaporeMachine gun Few DShK 1938  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionMachine gun PK machine gun  Soviet Union
Soviet Unionmachine gun Rocket Launcher
Rocket Launcher Origin Type Versions Notes M80 Rocket Launcher  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaRocket Launcher M79 Osa  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaRocket Launcher AT4  Sweden
SwedenRocket Launcher RPG-7  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionRocket Launcher Main battle tanks
Tanks Origin Type Versions In service Notes M60A3  United States
United StatesMain battle tank (MBT) A3 45 In service due to NATO compatibility, possible replacements:Leopard 2A6, Leclerc, M1 Abrams or Merkava AMX-30B2  France
FranceMain battle tank (MBT) B2 32 In service due to NATO compatibility,possible replacements:Leopard 2A6, Leclerc, M1 Abrams or Merkava M-84  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMain battle tank A1 As of 2010 16 in service As of 2008, 50 AB variants operational tanks have been withdrawn due to insufficient funds. T-55  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionMain battle tank 150 in reserve Currently there are 15 T-55s in service. Armoured fighting vehicles
APC/AFC Origin Type Versions In service Notes M113A2  United States
United StatesAPC A2 and A3 90 A2 + 60 A3 BVP M-80  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaIFV/ICV A and ALT 60 A + 30 ALT As of 2008 35 operational IFV have been withdrawn due to insufficient funds. Panhard AML
 France
FranceARV 90mm 4x4 41 BOV (APC)  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaIFV/ICV BOV-VP and BOV-3 & BOV-1 34 BOV-VP and 39 BOV-3 & 29 BOV-1 WZ-551(Type-92)  China
ChinaAPC 10 Humvee  United States
United StatesAPC 25 AMX-10P  France
FranceAPC/AFC P 35 Anti-tank weapons
Machine gun Origin Type Versions Notes AT-4 Spigot  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionAnti-tank missile AT-3 Sagger  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionAnit-tank missile Milan ATGM  Germany
GermanyAnit-tank missile HJ-8  China
ChinaAnti-tank missile Baktar-Shikan, HJ-8E Was supplied to ARBiH in early 1990s, ~50 pieces Artillery
Artillery Origin Type Versions In service Notes M101 howitzer  United States
United StatesHowitzer 40-50 M114 howitzer (M-114A-1) 155mm  United States
United StatesTowed howitzer 126 M1954  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionField gun 61 D-30  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionHowitzer D-30J 86 + 35 in reserve BM-21 Grad  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionMultiple rocket launcher BM-21 Grad/RM-70 29 M-63 Plamen  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMultiple rocket launcher Plamen 5 M-63 M-77 Oganj  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMultiple rocket launcher Oganj 7 M-87 Orkan  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaMultiple Rocket Launcher Orkan 3 Type 63 multiple rocket launcher  China
ChinaMultiple Rocket Launcher 200-250 Logistics
Logistics Origin Type Versions In service Notes Mercedes-Benz G-270  Germany
GermanyLogistics 33 Donated by Germany, used by Military Police/Officers Mercedes-Benz Unimog  Germany
GermanyLogistics 40 Donated by Germany TAM  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaUtility trucks Large number Chars Transportation  United States
United StatesTransportation 700 400 donated by U.S forces Iveco LMV  Italy
Italy15 Helicopters
Aircraft Origin Type Versions In service Notes UH-1H  United States
United StatesUtility helicopter H 14 Mil Mi-8  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionUtility helicopter Mi-8T, Mi-8MTV-1 9 Mi-8T, 2 Mi-8MTV-2 Mil Mi-17  Soviet Union
Soviet UnionUtility helicopter Mi-17 3 in service Soko Gazelle Gama  Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaUtility helicopter Light Attack Helicopter
4 in service Mil Mi-34  Russia
RussiaUtility helicopter 1 used by air forces for training Other equipment
Equipment Origin Type In service Hughes/Magnavox AN/PRC-126  United States
United StatesHand held radios 11,000 ~ NAPCO AN/PRC-77  United States
United Statesman pack radios 5,600~ Tactical telephones  United States/
United States/ Yugoslavia
YugoslaviaTactical telephones over thousand units Binoculars  Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina~ several thousands 10/20 kW generators  Germany/
Germany/ United States
United StatesGenerators 500 References
Further reading
- Jim Dorschner, 'Endgame in Bosnia,' Jane's Defence Weekly, 18 April 2007, p. 24-29
External links
- Ministry of Defense of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- MILITARY INDUSTRY - Bosnia and Herzegovina
- European Union Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina - EUFOR (English)
- OSCE Mission to Bosnia and Herzegovina (English)
- NATO Headquarters Sarajevo Security Sector Reform information
Military of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Other entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Categories: - Operational Command (Sarajevo)[3]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.