- Gordon Bennett Cup (auto racing)
-
 Magazine spread of Britain's Gordon Bennett Cup Team, 1903
Magazine spread of Britain's Gordon Bennett Cup Team, 1903As one of three Gordon Bennett Cups established by James Gordon Bennett, Jr., millionaire owner of the New York Herald, the automobile racing award was first given in 1900 in France.
In 1899 Gordon Bennett offered the Automobile Club de France (ACF) a trophy to be raced for annually by the automobile clubs of the various countries. The trophy was awarded annually until 1905, after which the ACF held the first Grand Prix motor racing event at the Circuit de la Sarthe, in Le Mans.
The 1903 event in Ireland gave rise to the birth of British Racing Green.
Contents
Gordon Bennett races
The Gordon Bennett Cup auto races drew entrants from across Europe including future aviator Henry Farman and from the United States competitors such as Alexander Winton driving his Winton automobile. Under the rules, the races were hosted in the country of the previous year's winner. As the races were between national teams, it led to the reorganisation and standardisation of national racing colours. Reputedly as a concession to Ireland where the 1903 race was run (racing was illegal on British public roads), the British adopted shamrock green[1] which became known as British racing green, although the winning Napier of 1902 had already worn Olive Green. Britain had to choose a different colour to its usual national colours of red, white and blue, as these had already been taken by Italy, Germany and France respectively.
Gordon Bennett Cup winners
Year Track Winner Car Country 1900 Paris to Lyon, France  Fernand Charron
Fernand CharronPanhard  France
France1901 Paris to Bordeaux, France  Léonce Girardot
Léonce GirardotPanhard  France
France1902 Paris, France to Innsbruck, Austria  Selwyn Edge
Selwyn EdgeNapier  United Kingdom
United Kingdom1903 Athy, County Kildare, Ireland  Camille Jenatzy
Camille JenatzyMercedes  Germany
Germany1904 Taunus mountains in Germany  Léon Théry
Léon ThéryRichard-Brasier  France
France1905 Circuit d'Auvergne, Clermont-Ferrand, France  Léon Théry
Léon ThéryRichard-Brasier  France
France1900 Gordon Bennett Cup
Main article: 1900 Gordon Bennett CupThe international motor car race from Paris to Lyons for the Gordon Bennett Cup took place on June 14th 1900. The start from Paris was made at 3 o'clock in the morning and Charron was the first to reach Lyons, arriving at 12:23 p.m. M. Girardot finished second at 2 o'oclck.[2]
1901 Gordon Bennett Cup
In 1901 the Gordon Bennett Cup race was run in conjunction with the Paris-Bordeaux race on 29 May over a distance of 527.1 km. The race was won by Henri Fournier driving a Mors with a time of 6h 10m 44s. The first of the Gordon Bennett Cup contesters was Leonce Girardot driving a Panhard with a time of 8h 50m 59s.[3]
1902 Gordon Bennett Cup
Main article: 1902 Gordon Bennett CupThe 1902 Gordon Bennett Cup was run over a distance of 565 km from Paris to Innsbruck in conjunction with the Paris-Vienna motor car race. The race started in Paris on June 26. Competing were 30 heavy cars, 48 light cars, six voiturettes, three motor cycles and three motor cyclettes. Each nation was allowed to nominate up to three cars to compete for the Gordon Bennett Cup, but only six entries were received, three French and three British. The Automobile Club of Great Britain announced that car No. 160 driven by Mr White, and car No. 45, made by Napier & Son of London with Dunlop tyres, driven by Mr Edge would represent the club.[4] The Times announced on June 30th that Edge had won the Gordon Bennett Cup.[5] It was announced in Vienna on July 1st that M. Marcel Renault had won the Paris-Vienna race, with M. Henri Farman second.[6]
1903 Gordon Bennett Trophy in Ireland
On Thursday, 2 July 1903 the Gordon Bennett Cup was the first international motor race to be held in Ireland, an honorific to Selwyn Edge who had won the 1902 event in the Paris-Vienna race driving a Napier. The Automobile Club of Great Britain and Ireland wanted the race to be hosted in the British Isles, and their secretary, Claude Johnson, suggested Ireland as the venue because racing was illegal on British public roads. The editor of the Dublin Motor News, Richard Mecredy, suggested an area in County Kildare, and letters were sent to 102 Irish MPs, 90 Irish peers, 300 newspapers, 34 chairmen of county and local councils, 34 County secretaries, 26 mayors, 41 railway companies, 460 hoteliers, 13 PPs, plus the Bishop of Kildare and Leighlin, Patrick Foley, who pronounced himself in favour. Local laws had to be adjusted, ergo the 'Light Locomotives (Ireland) Bill' was passed on 27 March 1903. Kildare and other local councils drew attention to their areas, whilst Queen’s County declared That every facility will be given and the roads placed at the disposal of motorists during the proposed race. Eventually Kildare was chosen, partly on the grounds that the straightness of the roads would be a safety benefit. As a compliment to Ireland the British team chose to race in Shamrock green[a] which thus became known as British racing green, although the winning Napier of 1902 had been painted Olive green.[7][8][9]
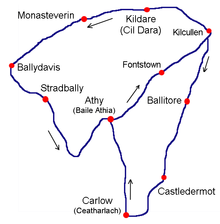
There was considerable public concern about safety after the 1901 Paris-Bordeaux Rally, in which at least eight people had been killed, and severe accidents during the May 24th 1903 Paris-Madrid race where more than 200 cars competed over a distance of 800 miles (1,287 km) but which had to be halted at Bordeaux because there had been so many accidents. To allay these fears the 1903 race was held over a closed course which had been carefully prepared for the event, and was marshalled by 7,000 police officers assisted by troops and club stewards, with strict instructions to keep spectators off the roads and away from corners.[10][11] The route consisted of two loops that comprised a figure of eight, the first was a 52-mile loop that included Kilcullen, The Curragh, Kildare, Monasterevin, Stradbally, Athy, followed by a 40-mile loop through Castledermot, Carlow, and Athy again. The race started at the Ballyshannon cross-roads (53°05′07″N 6°49′12″W / 53.0853°N 6.82°W) near Calverstown on the contemporary N78 heading north, then followed the N9 north; the N7 west; the N80 south; the N78 north again; the N9 south; the N80 north; the N78 north again.
The official timekeeper of the race was Mr. T. H. Woolen of the Automobile Club of Great Britain and Ireland. Ninety one Chronographs for timing the race were supplied by the Anglo-Swiss firm Stauffer Son & Co. of La Chaux-de-Fonds and London. Competitors were started at seven minute intervals and had to follow bicycles through the 'control zones' in each town. The 328 miles (528 km) race was won by the famous Belgian Camille Jenatzy, driving a Mercedes in German colours.[7][12]
1904 Gordon Bennett Trophy in Germany
The Times reported the 1904 Gordon Bennett motor race took place in Germany on June 17th over 342 miles (550 km), consisting of four laps of a course in the neighbourhood of Homburg.[13] From Saalburg the course ran nort to Usingen, where there was a control point (an inhabited or built up area where the cars had to travel slowly under the supervision of course officials) then through Graefenwiesbach to Weilburg, where there was a second control point, then past Allendorf and Obertiefenbach to Limburg. This section was reported to be the best part of the course for high speed and in practice some cars travelled at 150 km/h (93 mph). At Limburgh there was another control, then the course ran through Kirberg to Neuhof, where there was a very bad turn, and then to Idstein where there was another control. It then ran through Glashuetten to Koenigstein (control), then via Friedrichshof and Oberursel (control) to Homburg (control) and back to Saalburg.
Officiating were Baron von Molitor of the German Automobile Club, who official starter, and M. Tampier of the French Automobile Club, who was timekeeper. The chronographs for timing the event were supplied by the Anglo-Swiss firm of Stauffer Son & Co. Officials from the other competing counties were also present.
There were 18 starters including three British entrants. The first car started from Saalburg at 7 a.m. The winner was Théry of France, who accomplished the four laps in 5hr 50min 3sec, an average speed of 58.62 miles per hour (94.34 km/h). Jenatzy was second, driving a Mercedes. The only British competitor placed was Girling driving a Wolseley. Australia's[14] S. F. Edge, the previous year's winner and who again drove a Napier, was reported to have held a good position during the first two laps, but was disqualified[15] on lap three after receiving outside assistance due to tyre problems.[16]
1905 Gordon Bennett Trophy in France
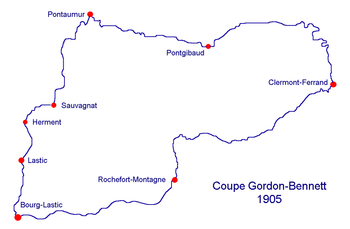
In 1905, The Times reported on the last of the six Gordon-Bennett Cup Races, which took place in France on July 5th over a 137 km mountainous circuit in the Auvergne near to Clermont-Ferrand. After four circuits of the course, a total of 548 km, which he completed in 7hr 2min 42sec, an average speed of 77.78 km/h, the Frenchman Léon Théry on a 96 hp Richard-Brasier won for the second year in a row. Lancia on a FIAT for Italy was fastest over the first two laps, but broke down with radiator problems during his third lap. Théry eventually came in first ahead of Nazzari, also on a FIAT, who finished in 7hr 19min 9sec.[17]
Chronographs for timing for the event were again supplied by Stauffer Son & Co.[18]
The race took place on the doorstep of the Clermont-Ferrand headquarters of Michelin, and cars fitted with Michelin tyres took the first four places.[19]
Notes
a. ^ According to Leinster Leader, Saturday, 11 April 1903, Britain had to choose a different colour to its usual national colours of red, white and blue, as these had already been taken by Italy, Germany and France respectively. It also stated red as the color for American cars in the 1903 Gordon Bennett Cup.
References
- ^ According to Leinster Leader, Saturday, 11 April 1903, which also states red as the color for American cars in the 1903 Gordon Bennett Cup.
- ^ The Times. Friday, June 15, 1900.
- ^ http://www.teamdan.com/archive/gen/upto1903/1901.html#gord
- ^ The Times. Friday June 27, 1902
- ^ The Times. June 30th 1902, page 9
- ^ The Times. Wednesday July 2nd 1902.
- ^ a b Leinster Leader, Saturday, 11 April 1903
- ^ Forix 8W – Britain's first international motor race by Brendan Lynch, based on his Triumph of the Red Devil, the 1903 Irish Gordon Bennett Cup Race. October 22, 2003
- ^ The Gordon Bennett races – the birth of international competition. Author Leif Snellman, Summer 2001
- ^ The Times, Tuesday, May 26, 1903; pg. 8
- ^ Daily Telegraph (London, England) (July 9, 2005): p.005
- ^ Bleacher report, The Birth of British motor racing
- ^ The Times. Saturday, June 18th 1904
- ^ Hull, Peter G. "Napier: The Stradivarius of the Road", in Northey, Tom, ed. The World of Automobiles (London: Orbis, 1974), Volume 13, p.1483.
- ^ Hull, p.1488.
- ^ Onlookers helped throw buckets of water over the wheels to cool the tyres.
- ^ The Times, London. July 6th 1905, page 11.
- ^ La Federation Horlogere Suisse. 24 September 1905, page 399
- ^ Daily Telegraph (London, England) (July 9, 2005): p.005.
External links
- http://kildare.ie/heritage/Gordon-Bennett-Race/January-1903.asp
- The day the country stopped to watch the Great Race, Leinster Express
- 1903 route map and descriptive brochure
- 1903 illustrated article – The Gordon Bennet Race
- Circle Genealogic and Historic Champanellois – all about the french edition in 1905
Categories:- Gordon Bennett Cup
- 1901 in motorsport
- 1903 in motorsport
- 1904 in motorsport
- 1905 in motorsport
- Edwardian era
- Recurring sporting events established in 1900
- Recurring events disestablished in 1905
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.