- Dispersin B
-
Dispersin B 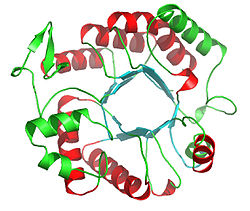
Ribbon diagram of Dispersin B Identifiers Symbol DspB PDB 1YHT RefSeq YP_001449721 UniProt Q840G9 Other data EC number 3.2.1.52 Dispersin B (EC 3.2.1.52) (also known as DspB or DispersinB) is a 42 kDa glycoside hydrolase enzyme produce by the periodontal pathogen Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.[1] Dispersin B catalyzes the hydrolysis of poly-N-acetylglucosamine, a sticky extracellular polysaccharide produce by various Gram-positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, as well as many Gram-negative bacteria including Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis and Bordetella spp. Poly-N-acetylglucosamine is sometimes called polysaccharide intercellular adhesin or PIA.
Contents
Function
Dispersin B plays a role in the detachment and dispersal of bacterial cells from Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans biofilms. [1]
Structure
The three dimensional structure of dispersin B has been determined.[2]
Applications
Dispersin B may be useful for treating and preventing biofilm-associated infections caused by poly-N-acetylglucosamine-producing bacteria.
Commercial development
Dispersin B is being commercially developed as a wound care gel and medical device coating by Kane Biotech, Inc., a Canadian biotech company. Pharmaceutical-grade dispersin B has been successfully manufactured by BioVectra, Inc., Charlottetown, P.E.I., Canada, and is currently undergoing biocompatibility testing. Clinical trials to test the effectiveness of dispersin B for the treatment and prevention of diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores should begin in 2010.
References
- ^ a b Kaplan JB, Ragunath C, Ramasubbu N, Fine DH (August 2003). "Detachment of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans biofilm cells by an endogenous beta-hexosaminidase activity". J. Bacteriol. 185 (16): 4693–8. doi:10.1128/JB.185.16.4693-4698.2003. PMC 166467. PMID 12896987. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=166467.
- ^ PDB 1YHT; Ramasubbu N, Thomas LM, Ragunath C, Kaplan JB (June 2005). "Structural analysis of dispersin B, a biofilm-releasing glycoside hydrolase from the periodontopathogen Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans". J. Mol. Biol. 349 (3): 475–86. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.082. PMID 15878175.
Categories:- EC 3.2.1
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
