- Phloretin
-
Phloretin 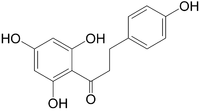 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-1-oneOther namesDihydronaringenin
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-1-oneOther namesDihydronaringenin
Phloretol
Naringenin chalconeIdentifiers CAS number 60-82-2 PubChem 4788 UNII S5J5OE47MK 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC(=CC=C1CCC(=O)C2=C(C=C(C=C2O)O)O)O
Properties Molecular formula C15H14O5 Molar mass 274.26 g/mol Exact mass 274.084124 u  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Phloretin is a dihydrochalcone, a type of natural phenols. It is the phloroglucin ester of paraoxyhydratropic acid. It can be found in apple tree leaves.[1]
Contents
Metabolism
Phloretin hydrolase uses phloretin and water to produce phloretate and phloroglucinol.
Glycosides
- Phlorizin is the 2'-glucoside of phloretin.
- Naringin dihydrochalcone is a diglycoside of phloretin.
See also
- Phloretin-glucosidase
References
- ^ Picinelli A.; Dapena E.; Mangas J. J. (1995). "Polyphenolic pattern in apple tree leaves in relation to scab resistance. A preliminary study". Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 43 (8): 2273–2278. doi:10.1021/jf00056a057. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=3653265.
Dihydrochalcones: 3′,5′-dihydroxy-2′,4′,6′-trimethoxydihydrochalcone | 2′-hydroxy-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetramethoxydihydrochalcone (dihydrokanakugiol) | 2′-hydroxy-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetramethoxychalcone (kanakugiol) | 5-hydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (alnetin) | methyl linderone | 2′,3′,4′,5′,6′-pentamethoxychalcone (pedicellin) | Phloretin | Pinocembrin chalconeDihydrochalcone glycosides: This article about a natural phenol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
