- Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Railway
-
Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Railway Legend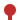
Rowsley South 

Park Side The Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Railway (DDDNGR) is a short, 2 ft (610 mm) railway located at Rowsley South[1] at Peak Rail. It operates ex-industrial diesel locomotives and carriages similar to the Golden Valley light railway at Butterley.
Rowsley South is the main station on the DDNGR.
Contents
Establishment
The DDNGR was established by Henry and Mary Frampton-Jones at Rowsley South during the 1990s.[2] They had accumulated a collection of narrow gauge rolling stock at various other railways and needed a running line. At Rowsley South the area behind the turntable was found to be suitable and work started on clearing and laying the track. 1998 saw the arrival of the first items of rolling stock, and the two 40-foot containers used as engine sheds.
In 2001 the Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Supporters Group formed to support the narrow gauge operation.
Initially, the main running line ran from Nannygoat crossing, through Parkside Station, across a level crossing to a buffer stop beyond where the containers were positioned. A loop was created at Parkside and various sidings laid to access the containers. Top and tail operation was the norm, with a locomotive formed either side of the carriages.
During 2004 HMRI approval was gained and the first DDNGR passengers were carried on Easter Sunday (11 Apr 2004).
During 2009, the railway operated on 44 days (mostly Sundays) and carried approximately 1,400 passengers.
Rolling Stock
Locomotives
All are 2 ft (610 mm), although some were built/rebuilt to different gauges.[3]
Builder Works Number Build Year Details Image Motor Rail 435
36631917
rebuilt 192440HP Simplex 4wDM. Built for the First World War battlefield supply lines as WD 2156. Originally fully open, but later fitted with the armour protection. Rebuilt in 1924 by Motor Rail 3663 and re-gauged to 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) and sent to St Kitts. Later brought back from Antigua and re-gauged back to 2 ft (610 mm).[4] Motor Rail 4572 1929 ex-Birmingham and Rea District Drainage Board (Water Orton)[2] Motor Rail 5853 1934 Initially hired out to Merton Eng Co Ltd, Feltham via Petrol Loco Hirers Ltd (a Motor Rail subsidary) and subsequently sold to them on 23/5/1934. It changed hands before eventually being acquired by the late Rev E R (Teddy) Boston at the Cadeby Light Railway in 1964 and subsequently sold to Pete Wood in 1974.[4] Motor Rail 8756 1942 ex-Joseph Arnold and Sons Ltd Silica Sand Quarries, Leighton Buzzard[2] Ruston & Hornsby 393325 1952 ex-BR 85049, previously used at Chesterton Junction permanent way depot near Cambridge[2] Ruston & Hornsby 404967 1957 ex-BR 85051, previously used at Chesterton Junction permanent way depot near Cambridge[2] 
Motor Rail 22070 1960 From the London Brick Co.'s Kempston Works, Bedfordshire[2] Ruston & Hornsby 487963 1963 4wDM, ex-Butlins, Minehead and Stanley Gravel Pits, Wakefield[2] Hunslet 8917 1980 ex Linby Colliery (Nottingham) and Sutton Manor Colliery (Lancashire). Flameproof 4wDHF.[2] References
- ^ "Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Railway". Peak Rail. http://www.peakrail.co.uk/ddngr.html. Retrieved 28 October 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Timperley, Dave (Spring 2010). "The Complete and Utter History of..." (pdf). The Peak Express. http://xa.yimg.com/kq/groups/39305493/1978802906/name/The. Retrieved 18 August 2011.
- ^ Industrial Railway Society (2009). Industrial Locomotives (15EL). Industrial Railway Society. ISBN 978 1 901556 53 7.
- ^ a b Loveday, Ian (September 2008). "Derbyshire Dales Narrow Gauge Railway/Peak Rail Diesel Weekend". http://groups.yahoo.com/group/PresGen/message/1804.
Links
DDNGR page on Peak Rail Website Coordinates: 53°10′29″N 1°36′34″W / 53.1746°N 1.6095°W
Categories:- Heritage railways in the United Kingdom
- 2ft gauge railways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
