- Curlew (steamboat)
-
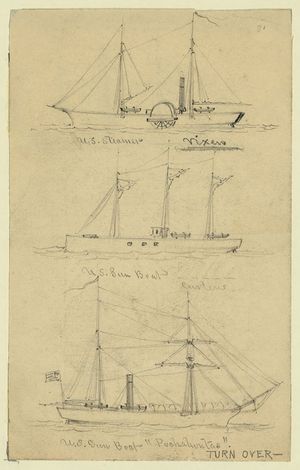
U.S. Gunboat Curlew is the center ship in a sketch by Alfred Waud done on the Port Royal ExpeditionCareer (U.S.) 
Name: Curlew Owner: Commercial Steamboat Company, Providence R.I., 1856 Port of registry: Providence, R.I.  United States
United StatesBuilder: Samuel Sneden, Greenpoint, N.Y. Completed: 1856 Fate: Sank in Chesapeake Bay 5 November 1863 after colliding with the Louisiana General characteristics Class and type: Propeller Steamer Tonnage: 343 Tons Burden Length: 150 ft (46 m) Beam: 28 ft (8.5 m) Draft: 8 ft (2.4 m) Depth: 8.75 ft (2.67 m) Propulsion: Propeller, direct acting vertical engine The Curlew was built in 1856 as a wooden hulled propeller freight boat for the run between Providence and New York. She served in several capacities during the Civil War.
Contents
Merchant Service
The 150-foot (46 m) wooden propeller steamer Curlew, was built in 1856 by Samuel Sneden of Greenpoint, New York for the Commercial Steamboat Company of Providence, Rhode Island. She was equipped with a direct-acting, two cylinder, vertical engine with a bore of 32 inches and a stroke of 2 feet. The boiler was on the main deck. Curlew was rigged as a three masted schooner as were many of the propeller steamers in this service. She was configured with a full length spar deck which was enclosed above the main deck.[1][2]
Curlew sank off of Point Judith, R.I. in May 1859 when a steam pipe burst and she began to fill with water.[3] She was salvaged and a new boiler and engine were installed in 1860.[2]
Civil War Service
Curlew was purchased for $44,000 by the U.S.Navy in 1861 for the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron.[4] She was outfitted as a gunboat with armament consisting of a 30 pound rifled gun on the foredeck and six 32 pound smoothbores on the main deck. Curlew participated in the expedition to Port Royal, S.C. under the command of Acting Lieutenant P.G. Watmough. When her machinery proved to be inadequate she was towed to New York by the transport Baltic arriving on 21 November 1861 to be returned to her owners before the sixty day trial period expired.[5]
Curlew was chartered by the Quartermaster's Department in October 1862 and voyaged as far as New Orleans under Captain H.N. Parrish.[6]
In the panic over the commerce raider CSS Tacony, Curlew was again chartered in June 1863 for use as a gunboat, this time by the Navy Department.[7] She was returned in October of that year.
Final voyage
Back in commercial service the Curlew inaugurated a freight service between New York and Baltimore. She cleared Baltimore, Md. on 5 November 1863 and proceeded down the Bay for New York with a full cargo. Near midnight on a dark, cloudy night she collided with the northbound steamer Louisiana near Point Lookout, Maryland hitting the Louisiana near midships on the port side. Curlew sank but Captain Parrish and the crew rowed to safety at Point Lookout. Louisiana suffered damage and was towed to Baltimore.[8]
Notes on tonnage
Curlew was listed in the Custom House Register in Providence at 343 49/95 tons burden. The register dimensions shown in the box also result in that number when entered in the contemporary tonnage equation. The New York Marine Register and the succeeding American Lloyds Register both show 380 tons. The Navy appears to quote 380 tons from those registers. In February 1862 the registration was changed to New York and the tonnage remeasured at 557 83/95.[2]
Other vessels
A ferryboat Curlew of 392 tons, which was built in 1853, was purchased by the Quartermaster's Department for use during the Civil War.
References
- ^ "American Lloyd's Register of American and Foreign Shipping", 1861.
- ^ a b c "Ship Registers & Enrollments of Providence, R.I.", Survey of Federal Archives, 1941.
- ^ "Loss of a Providence Propeller". The Repository. 18 May 1859.
- ^ "Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion", Series II - Vol. 1, p. 69.
- ^ "Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion", Series I - Vol. 12, p. 354.
- ^ "News from Key West". New York Times: p. 1. 12 Jan 1863.
- ^ "The Pirates and the Navy". New York Times: p. 8. 16 June 1863.
- ^ "The Collision between the Steamers". Baltimore Sun: p. 1. 9 November 1863.
Categories:- Steamships of the United States
- Merchant ships of the United States
- 1856 ships
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
