- Madang languages
-
Madang Madang–Adelbert Range Geographic
distribution:New Guinea Linguistic classification: Trans–New Guinea - Madang
Subdivisions: Southern Adelbert Range–KowanRai Coast–KalamCroisilles linkage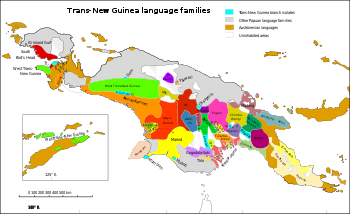
Madang languagesThe Madang or Madang–Adelbert Range languages are the largest family of Trans–New Guinea languages (TNG) in the classification of Malcolm Ross. William Foley concurs that it is "highly likely" that the Madang languages are part of TNG. The family is named after Madang Province and the Adelbert Range.
Contents
History
Sidney Herbert Ray identified the Rai Coast family in 1919. In 1951 these were linked with the Mabuso languages by Arthur Capell to create his Madang family. John Z'graggen (1971, 1975) expanded Madang to languages of the Adelbert Range and renamed the family Madang–Adelbert Range, and Wurm (1975)[1] adopted this as a branch of his Trans–New Guinea phylum. For the most part, Ross's (2005) Madang family includes the same languages as Z'graggen Madang–Adelbert Range, but the internal classification is different in several respects, such as the dissolution of the Brahman branch.
Internal classification
In the outline of the Ross (2000) classification below,[1] those nodes in bold are clearly valid families, consisting of closely related languages. The branches not in bold are likely subject to further revision.
- Southern Adelbert Range–Kowan
- Kowan family
- Southern Adelbert Range
- Rai Coast–Kalam
- Rai Coast family
- Kalam family (perhaps part of Rai Coast)
- Croisilles linkage (Northern Adelbert Range; few branches retain traditional membership)
- Dimir–Malas (Isumrud): Dimir, Malas
- Kaukombar: Bargam (Mugil), Mala (Pay), Miani (Tani), Maia (Pila, Saki)
- Kumil: Brem (Bunabun), Bepour, Mauwake (Ulingan), Moere, Musar
- Tibor–Omosa
- Omosan: Pal (Abasakur), Kobol (Koguman)
- Tiboran: Kowaki, Mawak, Pamosu (Hinihon), Wanambre
- Amaimon isolate
- Numugen–Mabuso
- Numugen family
- Mabuso family
External links
- The Madang–Adelbert Range languages in Ethnologue, showing Z'graggen's classification as set out by Wurm
Notes
- ^ Summarized in Pawley et al. (2005)
References
- Ross, Malcolm (2005). "Pronouns as a preliminary diagnostic for grouping Papuan languages". In Andrew Pawley, Robert Attenborough, Robin Hide, Jack Golson, eds. Papuan pasts: cultural, linguistic and biological histories of Papuan-speaking peoples. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 15–66. ISBN 0858835622. OCLC 67292782.
- Pawley, Ross, & Osmond, 2005. Papuan languages and the Trans New Guinea phylum. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 38–51.
Categories:- Languages of Papua New Guinea
- Madang languages
- Papuan language stubs
- Papua New Guinea stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
