- Croconate blue
-
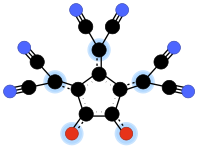
Croconate blue or 1,2,3-tris(dicyanomethylene)croconate is a divalent anion with chemical formula C14N6O2−
2 or ((N≡C-)2C=)3(C5O2)2−. It is one of the pseudo-oxocarbon anions, as it can be described as a derivative of the croconate oxocarbon anion C5O2−
5 through the replacement of three oxygen atoms by dicyanomethylene groups =C(-C≡N)2. The term Croconate Blue as a dye name specifically refers to the dipotassium salt K2C14N6O2.Contents
History and synthesis
The anion was syntesized and characterized by A. Fatiadi in 1978, together with croconate violet. He obtained the corresponding acid, croconate acid blue C14H2N6O2 by treating croconic acid C5H2O5 with malononitrile in water solution at 80–90 °C.[1][2]
Properties
Croconate acid blue
Croconate acid blue is strongly acidic (pK1 ≈ 1). It crystallizes from water as a purple sesquihydrate C14H2N6O2·1.5H2O and gives a red solution in acetone or ethanol, but deep blue in water. It hydrolizes slowly in water to give croconic acid violet. Extended heating in water produces deep green plates, apparently a polymer.[2] Croconate acid blue retains the aromatic character and some other properties of the croconate anion.[3]
Croconate blue dianion
Unlike croconate violet, the croconate blue dianion is not planar; the three dicyanomethylene groups are twisted by about 30 degrees from the ring plane.
The dipotassium salt is obtained from the acid by treatment with potassium methoxide from water as a green-blue trihydrate, that slowly loses water converting to the dihydrate. The water solutions have an intense blue color. It quickly converts to croconate violet when treated with potassium hydroxide. It is a weak semiconductor with conductivity 10−7 Ω−1 cm−1 at room temperature.[2]
The bis(tetramethylammonium) salt ((CH3)4)2C14N6O2 is green-blue and crystallizes as the dihydrate.[2]
See also
- 2-(dicyanomethylene)croconate
- Croconate violet, 1,3-bis(dicyanomethylene)croconate
- 1,2-bis(dicyanomethylene)squarate
- 1,3-bis(dicyanomethylene)squarate
References
- ^ Alexander J. Fatiadi (1978), Synthesis of 1,3-(dicyanomethylene)croconate salts. New bond-delocalized dianion, "Croconate Violet". Journal of the American Chemical Society, volume 100 issue 8, pages 2586–2587. doi:10.1021/ja00476a073
- ^ a b c d Alexander J. Fatiadi (1980), Pseudooxocarbons. Synthesis of 1,2,3-tris(dicyanomethylene)croconate salts. A new bond-delocalized dianion, croconate blue. Journal of Organic Chemistry volume 45, pages 1338-1339. doi:10.1021/jo01295a044
- ^ Lawrence M. Doane, Alexander J. Fatiadi (1981) Electrochemical Oxidation of Croconate Salts; Evidence of the Chemical Equivalence of the Carbonyl Oxygen Atom and the Dicyanomethylene Group doi:10.1002/anie.198206351
Categories:- Dyes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.