- Core Based Statistical Area
-
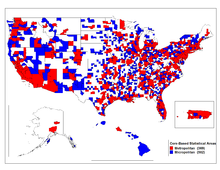 An enlargeable map of the Core Based Statistical Areas of the United States. The 363 MSAs are shown in red and the 577 μSAs are shown in blue.
An enlargeable map of the Core Based Statistical Areas of the United States. The 363 MSAs are shown in red and the 577 μSAs are shown in blue.
A Core Based Statistical Area (CBSA) is a U.S. geographic area defined by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) based around an urban center of at least 10,000 people and adjacent areas that are socioeconomically tied to the urban center by commuting. Areas defined on the basis of these standards applied to Census 2000 data were announced by OMB in June 2003. These standards are used to replace the definitions of metropolitan areas that were defined in 1990. The OMB expects to define new CBSAs based on the 2010 census in 2013.[1]
The term "CBSA" refers collectively to both metropolitan statistical areas and micropolitan areas. Micropolitan areas are based around Census Bureau-defined urban clusters of at least 10,000 and fewer than 50,000 people. The map on the right shows the metropolitan areas (in red) and micropolitan areas (in blue) for the CBSAs for the United States and Puerto Rico.
The basic definition of metropolitan areas has had slight changes made to it as well.[when?] A metropolitan area, as it did in 1990, requires a Census Bureau-defined urbanized area of at least 50,000 people. A metropolitan statistical area containing an urbanized area of at least 2.5 million people can be subdivided into two or more "metropolitan divisions," provided specified criteria are met. Metropolitan divisions are conceptually similar to the primary metropolitan statistical areas (PMSAs) defined under previous standards.
By a similar token, there are now definitions for "Combined Statistical Areas" (CSA). These areas can be formed when adjoining CBSAs meet particular standards to become new areas. It does not matter which kind of areas they are; any combination of metro and micro areas may be used to form a CSA.
Unlike past years, the traditional listings of metropolitan areas list New England regions as county-based areas. In the past, these were referred to by the Census as "NECMA"'s (New England County Metropolitan Areas) and were separate from the normal census counts for the areas, which used cities and towns as their basis. They have essentially swapped places now, with the city and town areas (or NECTAs for New England City and Town Areas) being the separate listings.
Despite there not being much change in the basic definition, 49 new metropolitan areas were formed[when?] as a result of the new rules for them. Over 550 other areas were classified as micropolitan. All told, the present rules have defined 935 CBSAs in the U.S. and Puerto Rico. 11 of the CBSAs have metropolitan divisions, 29 in total. In comparison, the definition of metropolitan areas in 1999, the last year areas were formed based on the 1990 rules for them, there were 284 metropolitan areas, with 19 of the areas providing 76 primary metropolitan areas (the equivalent of divisions); almost three times the number of areas overall are now recognized by the OMB.
See also
- Demographics of the United States
- Table of United States Combined Statistical Areas (CSA)
- Table of United States Core Based Statistical Areas (CBSA)
- Table of United States Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA)
- Table of United States Micropolitan Statistical Areas (µSA)
- Table of United States primary census statistical areas (PCSA)
- List of United States urban areas
References
- ^ Office of Management and Budget, 2010 Standards for Delineating Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas, 75 Federal Register 37246, Monday, June 28, 2010
External links
Categories:- Demographics of the United States
- United States Census Bureau geography
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


