Conquests of Sargon of Akkad
- Conquests of Sargon of Akkad
-
| Conquests of Sargon of Akkad |
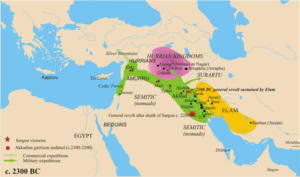
Sargon of Akkad's conquests. |
| Date |
c. 2340-2284 BCE |
| Location |
Mesopotamia |
| Result |
Akkadian victory |
|
| Belligerents |
| Akkad |
Sumerian provinces |
| Commanders and leaders |
| Sargon the Great |
Various |
| Strength |
| A standing army of 5,400 men |
various |
| Casualties and losses |
| no reliable estimates |
no reliable estimates |
Sargon of Akkad was the first ruler to carve out an empire by conquest. Establishing a power base in his own city at Akkad, he then conquered the powerful city of Uruk, seizing hegemony over all the other city-states of Sumer. He came to control the rest of Mesopotamia as far as Ebla in Syria, creating an empire covering roughly the area of modern-day Iraq. His campaigns may well have extended as far as Cyprus and Anatolia. Although later sources credit him with around a 54 year reign, actual dated documents have been found for only four different year-names in his reign. The year-names describe campaigns waged against Elam, Mari, and Simurrum (a Hurrian region).
One inscription tells that he won 34 battles; another suggests that he had a standing army, recording that "5,400 soldiers eat bread before him each day". Sargon's infantry probably used bronze weapons and composite bows, and he would have also possessed four-wheeled chariots pulled by asses. This army could cope with siege warfare, since records tell of Sargon destroying the walls of the cities he captured. Sargon died about 2284 BCE and his empire survived for more than 125 more years. Later Mesopotamians regarded him as the founder of the region's tradition of expansion by military conquest as exemplified by Assyrian Empire, the Babylonian Empire, and the Persian Empire.
References
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Sargon of Akkad — You may be looking for the Assyrian kings Sargon I (r. 1920 – 1881 BC) or Sargon II (r. 722 – 705 BC). Sargon of Akkad, also known as Sargon the Great (Akkadian Šarru kinu , cuneiform ŠAR.RU.KI.IN cuneiform|????, meaning the true king or the king … Wikipedia
Sargon II — died 705 B.C., king of Assyria 722 705. * * * died 705 BC Assyrian king (r. 721–705 BC). He continued the empire building work of his presumed father, Tiglath pileser III. One of his aims was to prove the might of the Assyrian god Ashur by… … Universalium
Steppe, the — ▪ geographical area, Eurasia Introduction belt of grassland that extends some 5,000 miles (8,000 kilometres) from Hungary in the west through Ukraine and Central Asia to Manchuria in the east. Mountain ranges interrupt the steppe, dividing it… … Universalium
List of wars before 1000 — *Prehistoric warfare *Mythological wars **Battle of Zhuolu about 2500 BC **Kurukshetra War, based on warfare in the Kuru kingdom of ancient India, ca. 1200 900 BC **Trojan War, based on events of ca. 1200 BC *ca. 2530 BC Battle of Magh Ithe in… … Wikipedia
Mesopotamia, history of — ▪ historical region, Asia Introduction history of the region in southwestern Asia where the world s earliest civilization developed. The name comes from a Greek word meaning “between rivers,” referring to the land between the Tigris and… … Universalium
MESOPOTAMIA — The original article in the first edition of the Encyclopaedia Judaica traced Mesopotamian history to its earliest beginnings and provided a detailed survey of Mesopotamian literature and institutions. With the availability of such tools as J.… … Encyclopedia of Judaism
Military history of the Neo-Assyrian Empire — Assyrian Army Participant in Assyrian wars of conquest … Wikipedia
Babylonia — • Includes geography, history, and biblical references Catholic Encyclopedia. Kevin Knight. 2006. Babylonia Babylonia † … Catholic encyclopedia
Syria — This article is about the modern state of Syria. For other uses, see Syria (disambiguation). Syrian Arab Republic الجمهورية العربية السورية Al Jumhūriyyah al ʿArabiyyah as Sūriyyah … Wikipedia
art and architecture, Mesopotamian — Introduction the art and architecture of the ancient Mesopotamian civilizations. The name Mesopotamia has been used with varying connotations by ancient writers. If, for convenience, it is to be considered synonymous with the modern… … Universalium

