- Compañía Minera San Esteban Primera
-
Compañía Minera
San Esteban PrimeraType Private Industry Metal & Gold Copper Genre Mining Founded 1957 Founder(s) Jorge Kemeny Letay Headquarters Santiago, Chile Number of locations Copiapó Revenue estimated US$20 million Total assets Frozen by Court Order as of 2010 Website Unknown
Compañía Minera San Esteban Primera (San Esteban Primera Mining Company) is a Chilean mining company, dedicated to the production of copper and gold concentrates.[1] San Esteban's headquarters are located in Providencia, Santiago Metropolitan Region.[1]San Esteban also owns the San José Mine in Copiapó, Chile, where 33 miners were trapped underground for 69 days after a mining accident on August 5, 2010.
Contents
Background
 Satellite image of the San José mine and its surroundings
Satellite image of the San José mine and its surroundings See also: Mining in Chile
See also: Mining in ChileChile has a long tradition in mining, which developed during the 20th century and made the country the world's top producer of copper.[2] Since 2000, an average of 34 people have died every year in mining accidents in Chile, with a high of 43 in 2008, according to a review of data collected by the state regulatory agency Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería de Chile (abbreviated Sernageomin).[3]
The Compañía Minera San Esteban Primera (CMSE) is notorious in the mineral-rich region and, according to an official with the Chilean Safety Association, eight workers have died the company's mines in the 12 years to 2010.[4][5][6] Between 2004 and 2010, the company received 42 fines for breaching safety regulations.[4] The San Jose Mine was shut down in 2007 when relatives of a miner who had died in an accident sued company executives, but was reopened in 2008[7][4] despite failing to comply with all regulations. The matter is still under investigation according to mining committee Senator Baldo Prokurica.[8] Due to budget constraints, there were only three inspectors for the Atacama Region's 884 mines.[4]
CMSE had ignored warnings and worker-initiated lawsuits concerning unsafe working conditions in its mines. CMSE's management operates "without listening to the voice of the workers when they say that there is danger or risk," said Javier Castillo, secretary of the trade union that represents miners and a former miner at the San José mine. "Nobody listens to us. Then they say we're right. If they would have believed the workers, we would not be lamenting this now," said Gerardo Núñez, head of the union at a nearby Candelaria Norte mine.[9]
Chilean copper mine workers are among the highest-paid miners in South America.[10] Although the accident itself has put into question mine safety in Chile, serious accidents in large mines are rare, particularly in those owned by the state copper mining company, Codelco, or by multinational companies.[2] However, smaller mines such as the one at San José have generally lower safety standards.[2] Mine workers at this mine were paid around 20% higher wages than at other Chilean mines, due to its poor safety record.[11]
History
The San José Mine is located 45 kilometers northwest of Copiapó. It began operations in 1889.[12] In 1957, Jorge Kemeny Letay, a Hungarian immigrant founded the San Esteban Mining Company (Spanish: Compañía Minera San Esteban).[12]
San Jose Mine
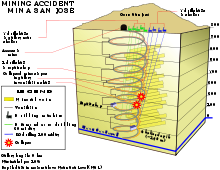
The San José Mine (Spanish: Mina San José) is a small copper-gold mine located near Copiapó, Atacama Region, Chile.[12] The mine is mostly known for its 2010 collapse which trapped 33 miners 700 metres (2,300 ft) underground.[13] Its workings are reached by a long sloping roadway with many spiral turns (a diagram shows ten turns), not by a vertical mineshaft.
According to Terra, the mine's annual sales surpassed 20 million dollars.[12]
Between 2003 and 2010, several mining accidents occurred in the mine, causing at least three deaths.[12] In 2007, a geologist was killed in the mine, and led to its closure. It was reopened in May 2008 by SERNAGEOMIN – Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (National Geology and Mining Service). In July 2010, miner Gino Cortés lost one of his legs in an accident.[12]
2010 accident
Main article: 2010 Copiapó mining accidentCompañía Minera San Esteban advised national authorities on 5 August 2010 that a collapse had occurred at 14:00 local time, and rescue efforts began the next day. The National Emergencies Office of Chile that day issued a list of 33 trapped and possibly deceased miners, that included Franklin Lobos, a retired footballer, and Carlos Mamani, a Bolivian national. 17 days later on August 22 the miners were found to be alive, but trapped. It was not until 69 days after the collapse on October 13, 2010, that the first miner, Florencio Ávalos, was rescued.[13] All 33 were eventually rescued.
San Esteban Mining Company is considering bankruptcy.[14] San José is the only mine owned by San Esteban.[14] President of Chile Sebastián Piñera said on October 12 that "the mine will remain closed until security measures that guard the life and dignity of the workers are established."[15]
See also
Further information: Economy of ChileReferences
- ^ a b "Compania Minera San Esteban Primera" (in Spanish). Chile CompanyMine. http://chile.infomine.com/companies/listings/11003/COMPANIA_MINERA_SAN_ESTEBAN_PRIMERA.html. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Celebration before a hard slog". The Economist. 23 August 2010. http://www.economist.com/blogs/americasview/2010/08/chiles_trapped_miners. Retrieved 23 August 2010. (subscription required)
- ^ Jones, Sam (27 August 2010). "Trapped Chilean miners sing national anthem in footage from inside mine". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2010/aug/27/trapped-chilean-miners-video%20©.
- ^ a b c d Govan, Fiona, Aislinn Laing and Nick Allen (26 August 2010). "Families of trapped Chilean miners to sue mining firm". London Daily Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/southamerica/chile/7966590/Families-of-trapped-Chilean-miners-to-sue-mining-firm.html. Retrieved 26 August 2010.
- ^ From collapse to rescue: Inside the Chile mine disaster, Toronto Star, Jennifer Yang, 10 Oct 2010
- ^ "Rescuers struggle to reach trapped miners in Chile". Mining Weekly. Reuters. 6 August 2010. http://www.miningweekly.com/article/rescuers-struggle-to-reach-trapped-miners-in-chile-2010-08-06. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ "Trapped Chile miner's family sues owners and officials". BBC News. 26 August 2010. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-11102478. Retrieved 27 August 2010.
- ^ "New video gives tour of trapped miners' refuge" – Associated Press writers – Bradley Brooks and Peter Prengaman – with Federico Quilodran in Copiapo, Eduardo Gallardo in Santiago, and Michael Warren in Buenos Aires, Argentina, contributing to this report. The Associated Press, (NBC26.com) 28 August 2010 – Copyright 2010.
- ^ Unions Say Mining Becoming More Dangerous in Chile Latin American Herald Tribune, 9 August 2010
- ^ "A worrying precedent". The Economist. 7 September 2006. http://www.economist.com/node/7894761?story_id=7894761. Retrieved 23 August 2010. (subscription required)
- ^ The Media Circus at Chile's San José Mine Spiegel Online, 8 September 2010
- ^ a b c d e f "Derrumbe en la Mina San José" (in Spanish). Terra Perú. http://www.pe.terra.com/shared/pop/noticias/mina-san-jose/mina_san_jose.html. Retrieved October 13, 2010.
- ^ a b Navarrete, Camila (August 6, 2010). "Se confirman las identidades de mineros atrapados en mina San José en Región de Atacama." (in Spanish). Radio Bío Bío. http://www.radiobiobio.cl/2010/08/06/se-confirman-las-identidades-de-mineros-atrapados-en-mina-san-jose-en-region-de-atacama/. Retrieved October 12, 2010.
- ^ a b "Chile: la minera San José podría declararse en quiebra" (in Spanish). Central de Noticias Tucumán. http://cntucuman.com/cnt/2010/08/25/chile-la-minera-san-jose-podria-declararse-en-quiebra/. Retrieved October 13, 2010.
- ^ "Piñera: Mina San José será clausurada hasta que se establezcan normas de seguridad" (in Spanish). Agencia Venezolana de Noticias. http://www.avn.info.ve/node/22692. Retrieved October 13, 2010.
Categories:- Mining stubs
- Mines in Chile
- 2010 Copiapó mining accident
- Copper mines in Chile
- Gold mines in Chile
- Mines in Atacama Region
- Underground mines in Chile
- Copper mining companies
- Companies of Chile
- Mining companies of Chile
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.