- Shaft mining
-
Shaft mining or shaft sinking refers to the method of excavating a vertical or near-vertical tunnel from the top down, where there is initially no access to the bottom.[1] When the top of the excavation is the ground surface, it is referred to as a shaft or portal; when the top of the excavation is underground, it is called a winze.
Contents
Off-shaft access
The mine shaft is used to gain access to an underground mining facility. Horizontal workings off the shaft are called drifts, galleries or levels. These extend from the central shaft toward the ore body. The point of contact between these levels and the shaft itself is known as the inset, shaft station or plat.
Surface facilities
On the surface above the shaft stands a building known as the headframe (or winding tower, poppet head or pit head). Depending on the type of hoist used the top of the headframe will either house a hoist motor or a sheave wheel (with the hoist motor mounted on the ground). The headframe will also contain bins for storing ore being transferred to the processing facility. If the shaft is used for mine ventilaton a plenum or casing, is incorporated into the headframe to ensure the proper flow of air into and out of the mine.
Shaft lining
In North and South America, smaller shafts are designed to be rectangular with timber supports. Larger shafts are round and are concrete lined.[2]
Shaft compartments
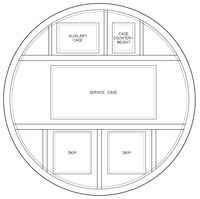
A mine shaft is frequently split into multiple compartments. The largest compartment is typically used for the mine cage, a conveyance used for moving workers and supplies below the surface. It functions in a similar manner to an elevator, with the largest often double-deck.
The second compartment is used for one or more skips, used to hoist ore to the surface. Smaller mining operations use a skip mounted underneath the cage, rather than a separate device, while some large mines have separate shafts for the cage and skips. The third compartment is used for an emergency exit; it may house an auxiliary cage or a system of ladders. An additional compartment houses mine services such as high voltage cables and pipes for transfer of water, compressed air or diesel fuel.
A second reason to divide the shaft is for ventilation. One or more of the compartments discussed above may be used for air intake, while others may be used for exhaust.
See also
- Underground mining (hard rock)
- Drift mining
- Raise borer
- Salt-concrete
- Headframe
References
External links
Mining techniques Surface Sub-surface Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.