- Water opossum
-
Yapok[1] 
Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Infraclass: Marsupialia Order: Didelphimorphia Family: Didelphidae Subfamily: Didelphinae Genus: Chironectes
Illiger, 1811Species: C. minimus Binomial name Chironectes minimus
(Zimmermann, 1780)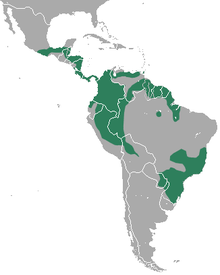
Water Opossum range The water opossum (Chironectes minimus), also locally known as the yapok, is a marsupial of the family Didelphidae. It is the only member of its genus, Chironectes. This semiaquatic creature is found in and near the freshwater streams and lakes in Mexico, Central and South America to Argentina, and is the most aquatic living marsupial (the lutrine opossum also has aquatic habits). It is also the only living marsupial in which both sexes have a pouch. The thylacine, commonly referred to as the Tasmanian tiger, also exhibited this trait, but is now believed to be extinct.
The animal lives in bankside burrows, emerging after dusk to swim and search for fish, crustaceans and other aquatic animals, which it eats on the bank.
Contents
Origin of the name
The local name for the water opossum, "yapok", probably comes from the name of the Oyapok River in French Guyana.
The yapok of Central and South America is superbly adapted to a life in water. It has long webbed toes on its hindfeet, water-repellant fur, and a pouch that closes during dives. It hunts its aquatic prey of fish, frogs, crustaceans, and rests in a riverbank den by day.
True opossums are unique to North America alone. The word "opossum" was taken from the native Algonquian word for the animal. Though the yapok, as well as other marsupials in South America and Australia are called "possums", most are not closely related to the Virginia opossum, and only derive their name by a generally similar shape and appearance.
Physical appearance
The yapok is a small opossum, 27-32.5 cm long, with a 36–40 cm long tail. The fur is in a marbled grey and black pattern while the muzzle, eyestripe, and crown are all black. A light band runs across the forehead anterior to the ears, which are rounded and naked. There are sensory facial bristles in tufts above each eye as well as whiskers. The animal's tail, furred and black at the base, is yellow or white at its end. The hindfeet of the yapok are webbed, while the forefeet ("hands") are not. The forefeet can be used to feel for and grab prey as the yapok swims, propelled by its tail and webbed back feet.
Aquatic adaptations
The water opossum has several adaptations for its watery lifestyle. It has short, dense fur which is water-repellent. The broad hindfeet are webbed and are used for propulsion through water, moving with alternate strokes. They are symmetrical as well, which distributes force equally along both borders of the webbing; this increases the efficiency of the water opossum's movement through the water. The yapok's long tail also aids in swimming.
Being a marsupial and at the same time an aquatic animal, the water opossum has evolved a way to protect its young while swimming. A strong ring of muscle makes the pouch (which opens to the rear) watertight, so the young remain dry, even when the mother is totally immersed in water. The male also has a pouch (although not as watertight as the female's), where he places his genitalia before swimming. This is thought to prevent it from becoming tangled in aquatic vegetation and is probably helpful in streamlining the animal as well.
Reproduction
Yapoks mate in December and a litter of 1-5 young is born 27 weeks later in the nest. By 22 days the offspring are beginning to show some fur, and by 40 days or so their eyes are open, their bodies protruding from the mother's pouch. At 48 days of age, the young opossums detach from the nipples but still nurse and sleep with the mother.
Fossil record
The water opossum seems to have a history dating as far back as to the Pliocene epoch.
Holocene subfossil fragments of Chironectes have been discovered in São Paulo, Brazil. Also, there are fossil specimens from the late Pleistocene-Recent cave deposits in Minas Gerais, Brazil as well as from the late Pliocene in Entre Ríos Province, Argentina.
Subspecies
- Chironectes minimus argyrodytes
- Chironectes minimus langsdorffi
- Chironectes minimus minimus
- Chironectes minimus panamensis
References
- ^ Groves, C. (2005). Wilson, D. E., & Reeder, D. M, eds. ed. Mammal Species of the World (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. OCLC 62265494. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. http://www.bucknell.edu/msw3/browse.asp?id=10400031.
- ^ Cuarón, A. D., Emmons, L., Helgen, K., Reid, F., Lew, D., Patterson, B., Delgado, C. & Solari, S. (2008). Chironectes minimus. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Downloaded on 28 December 2008. Database entry includes justification for why this species is of least concern
- Gardner, Alfred L. (16 November 2005). "Order Didelphimorphia (pp. 3-18)". In Wilson, Don E., and Reeder, DeeAnn M., eds. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2 vols. (2142 pp.). pp. 4-5. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.bucknell.edu/msw3/browse.asp?id=10400032.
External links
- Kalafut, Molly (2007). "Genus Chironectes, "Yapok" or "Water Opossum"". Know Your STO. http://www.knowyoursto.com/didelphidae/chironectes.html. Retrieved March 2010.
- Gorog, A (1999). "Chironectes minimus". Animal Diversity Web. http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Chironectes_minimus.html. Retrieved March 2010.
Categories:- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Opossums
- Mammals of Argentina
- Mammals of Belize
- Mammals of Bolivia
- Mammals of Brazil
- Mammals of Colombia
- Mammals of Costa Rica
- Mammals of Ecuador
- Mammals of El Salvador
- Mammals of French Guiana
- Mammals of Guatemala
- Mammals of Guyana
- Mammals of Honduras
- Mammals of Mexico
- Mammals of Nicaragua
- Mammals of Panama
- Mammals of Paraguay
- Mammals of Peru
- Mammals of Suriname
- Mammals of Venezuela
- Mammals of Central America
- Mammals of South America
- Monotypic mammal genera
- Animals described in 1780
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

