- Allan Kardec
Infobox Person
name = Allan Kardec
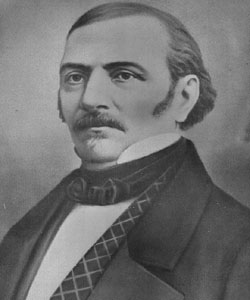
image_size = 250px
birth_name = Hippolyte Léon Denizard Rivail
birth_date = birth date|1804|10|3
birth_place =Lyon ,France
death_date = death date and age|1869|3|31|1804|10|3
death_place =Paris ,France
known_for = Allan Kardec was a pseudonym of the French teacher and educator Hippolyte Léon Denizard Rivail, who is known today as the systematizer ofSpiritism Allan Kardec was a pseudonym of the French teacher and educator Hippolyte Léon Denizard Rivail (
Lyon ,October 3 ,1804 –Paris ,March 31 ,1869 ), who is known today as the systematizer ofSpiritism .Rivail was born in
Lyon ,France , in 1804. Rivail was a disciple and collaborator ofJohann Heinrich Pestalozzi , and a teacher in courses inmathematics ,physics ,chemistry ,astronomy ,physiology ,comparative anatomy and French in Paris. For one of his research papers, he was inducted in 1831 into theRoyal Academy of Arras Fact|date=February 2007. He organized and taught free courses for the underprivileged.On February 1832 he married
Amélie Gabrielle Boudet .He was already in his early fifties when he became interested in the wildly popular phenomenon of
spirit-tapping . At the time, strange phenomena attributed to the action of spirits were reported in many different places, most notably in the U.S. and France, attracting the attention of high society. The first such phenomena were at best frivolous and entertaining, featuring objects that moved or "tapped" under what was said to be spirit control. In some cases, this was alleged to be a type of communication: the supposed spirits answered questions by controlling the movements of objects so as to pick out letters to form words, or simply indicate "yes" or "no."At the time,
Franz Mesmer 's theory ofanimal magnetism was popular in the upper reaches of society. When confronted with the phenomena described, some researchers, including Rivail, pointed out that animal magnetism might explain them. Rivail, however, after personally seeing a demonstration, quickly dismissed the animal-magnetism hypothesis as being insufficient to completely explain all the facts observed (see Chapters VIII and XIV in theThe Book on Mediums ). Rivail was determined to understand exactly what was causing the physical effects popularly attributed to spirits.As a teacher with some scientific background (he had never attended a university), Rivail decided to do his own research. Not being a medium himself, he compiled a list of questions and began working with mediums and channelers to pose them to spirits. Soon the quality of the allegedly communication with spirits appeared to improve.
Rivail used the name "Allan Kardec" allegedly after a spirit identified as Zefiro, whom he had been communicating with, told him about a previous incarnation of his as a
Druid by that name. Rivail liked the name and decided to use it to keep his Spiritists writings separate from his work, basically books for high school students.In
April 18 1857 Rivail (signing himself "Allan Kardec") published his first book on Spiritism, The Spirits' Book, comprising a series of 1,019 questions exploring matters concerning the nature of spirits, thespirit world , and the relations between the spirit world and the materialworld . This was followed by a series of other books, likeThe Book on Mediums andThe Gospel According to Spiritism , and by a periodical, the "Revue Spirite", which Kardec published until his death.Allan Kardec coined the word "spiritism" and followed modern scientific methods in its study, which was recognized among others by
Camille Flammarion , a famous French astronomer and author, who said "spiritism is not a religion but a science". Allan Kardec's eulogy on April 2, 1869, in "Death and Its Mystery - After Death. Manifestations and Apparitions of the Dead; The Soul After Death" Translated by Latrobe Carroll (1923, T. Fisher Unwin, Ltd. London: Adelphi Terrace.), online version at [http://www.survivalafterdeath.org/articles/flammarion/manifestations.htm Manifestations of the Dead in Spiritistic Experiments] ]Having died due to
aneurysm , Kardec is buried at the Cimetière du Père Lachaise. The eulogy was delivered byCamille Flammarion . Allan Kardec's eulogy on April 2, 1869, in "Death and Its Mystery - After Death. Manifestations and Apparitions of the Dead; The Soul After Death" Translated by Latrobe Carroll (1923, T. Fisher Unwin, Ltd. London: Adelphi Terrace.), online version at [http://www.survivalafterdeath.org/articles/flammarion/manifestations.htm Manifestations of the Dead in Spiritistic Experiments] ]Visitors from all over the world, especially from
Brazil where his doctrine has millions of followers, come bringing flowers to his tombstone, which is reputed to be one of the most flowered at the Cimetière. The body of his wifeAmélie Gabrielle Boudet is also buried there. At the top part of his burial chamber is written a sentence that became a sort of spiritist's motto: "Naitre, mourir, renaitre encore et progresse sans cesse, telle est la loi".References
ee also
*
Spiritism
*"The Spirits' Book"
*"The Book on Mediums "
*"The Gospel According to Spiritism "
*"Heaven and Hell"
*"The Genesis According to Spiritism "External links
* [http://pt.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allan_kardec Main Allan Kardec article, in Portuguese]
* [http://www.allan-kardec.org/ Allan Kardec Educational Society]
* [http://www.allan-kardec.com/ ALLAN KARDEC: spiritisme, spiritism...]
* [http://www.spiritwritings.com/kardec.html Allan Kardec Biographic Information]
* [http://www.spiritwritings.com/kardecspiritstoc.html The Spirits' Book] by Allan Kardec
** [http://www.allankardec.com/Allan_Kardec/Le_livre_des_esprits/lesp_us.pdf Le Livre des Esprits] (PDF file)
** [http://www.geae.inf.br/en/books/codification/mb.pdf The Book on Mediums] by Allan Kardec (PDF file)
** [http://www.sgny.org/main/Books/ESE.pdf The Gospel According to Spiritism] by Allan Kardec (PDF file)
*Domínio Público author|id=183|name=Allan Kardec
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
