- Dühring's rule
-
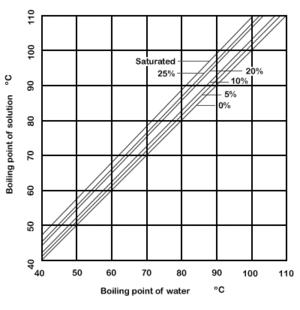
Dühring's rule states that a linear relationship exists between the temperatures at which two solutions exert the same vapor pressure.[1][2] The rule is often used to compare a pure liquid and a solution at a given concentration.
Dühring's plot is a graphical representation of such a relationship, typically with the pure liquid's boiling point along the x-axis and the mixture's boiling point along the y-axis; each line of the graph represents a constant concentration.
See also
References
- ^ a b Earle, Richard L.; Earle, M. D. (2004). "Evaporation". Unit Operations in Food Processing. The New Zealand Institute of Food Science & Technology (Inc.). http://www.nzifst.org.nz/unitoperations/evaporation4.htm. Retrieved March 15, 2009.
- ^ Price, R. M. (2003). "Evaporation". RMP Lecture Notes. Christian Brothers University. http://www.cbu.edu/~rprice/lectures/evap1.html. Retrieved March 15, 2009.
Categories:- Chemical engineering
- Chemical properties
- Solutions
- Thermodynamics stubs
- Chemistry stubs
- Engineering stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.