- February 4, 1998 Afghanistan earthquake
Earthquake
title=February 4, 1998 Afghanistan earthquake
date=February 4 1998 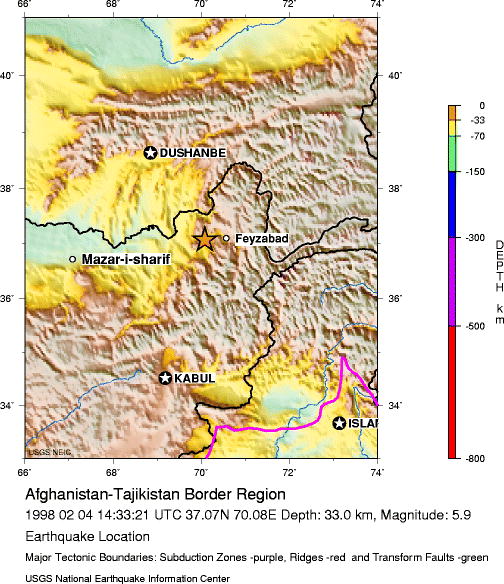
magnitude = 6.1 Mw
depth=convert|33|km|mi|0
location=coord|37.07|N|70.08|E
countries affected = AFG
casualties = Approximately 4000 dead, 10,000 injured and 15,000 homeless.February 4, 1998 Afghanistan earthquake occurred in northern
Afghanistan in the Afghanistan-Tajikistan border region. [http://neic.usgs.gov/neis/eq_depot/1998/eq_980204/ Magnitude 5.9 Afghanistan-Tajikistan Border Region 1998 February 04 14:33:21 UTC] "National Earthquake Information Center "] [http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/february/4/newsid_2534000/2534279.stm 1998: 4,000 feared dead in Afghan earthquake] "BBC News "] Theepicenter of theearthquake was located at Rostaq in theTakhar Province near Afghan-Tajikistan border. Themagnitude of the quake was 6.1 on theRichter scale [http://www.afghanmagazine.com/april98/articles/quake.html Aid Relief Efforts Made by Afghans in America for Earthquake Victims] "Afghanmagazine.com"] [http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/rwb.nsf/db900sid/OCHA-64DCCQ?OpenDocument Afghanistan - Earthquake OCHA Situation Report No. 7] "ReliefWeb "] [http://edition.cnn.com/WORLD/asiapcf/9805/31/afghan.quake/chrono.quakes.html Chronology of earthquakes in the 1990s] "CNN "] [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9804EED6143EF934A15751C1A9659C8B63&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=all Powerful Earthquake in Iran Kills Thousands] "The New York Times "] cite book
author= John Wright
title= The New York Times Almanac 2002
publisher= Routledge
location=
year=
pages= p743
isbn= 1579583482
oclc=
doi=] and it lasted approximately 8 minutes and 7 seconds.Aftershock s continued for the next seven days. The earthquake was also felt atTashkent andDushanbe .Cause
Afghanistan is situated on a major plate boundary.cite book
author= Peter Webber, Neil Punnett
title= Physical Geography and People
publisher= Nelson Thornes
location=
year= 1999
pages= p14
isbn= 0748743030
oclc=
doi=] The location of the country is on the boundary where twotectonic plate s, the Iranian Plate and theEurasian Plate , meet.cite book
author= Neil Punnett, Alison Rae, David Wood, Peter Richardson, John Edwards
title= The New Wider World
publisher= Nelson Thornes
location=
year= 2003
pages= p272
isbn= 0748773762
oclc=
doi=] To the south of Afghanistan, theIndian Plate moves northwards and to the north theEurasian Plate moves south-eastwards. The collision resulting from the movement of the plates has been under way for 50 million years. Due to this, Afghanistan is vulnerable to earthquakes. Both the Iranian Plate and the Eurasian Plate consists ofcontinental crust , which can neither sink nor be destroyed. As a result, the rocks between the two plates are forced upwards to form mountains. The constant movement of the Iranian Plate results in an increase in pressure. The earthquake on February 4, 1998 was caused by this increase in pressure.
=Casualties and daA spokesman for the
United Islamic Front for the Salvation of Afghanistan , which controlled certain area, told theAfghan Islamic Press that they removed more than 3,500 bodies. According to the estimates by theTaliban government inKabul , which ruled theIslamic Emirate of Afghanistan at that time, 3,230 people died in the earthquake.Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) later put the death toll at 4,000. The anti-Taliban Afghan Embassy inDushanbe asserted that approximately 15,000 people became homelesscite book
author= Ahmed Rashid
title= Taliban: Islam, Oil and the New Great Game in Central Asia
publisher= I.B.Tauris
location=
year= 2002
pages= p230
isbn= 1860648304
oclc=
doi=] and dozens of villages were destroyed. Nearly 15,000 houses were destroyed primarily due to thelandslide s triggered by the quake. Approximately 10,000 people were injured and 6,725 livestock were killed in the earthquake.Relief efforts
The Takhar Province was a remote area and
road transport andtelecommunication was poor. So it took three days for the news of the earthquake to reach Kabul. OnFebruary 7 , reports of the quake began to reach the capital city. But relief work was hampered and delayed because of bad weather likefog ,low cloud andsnowfall s, blocked mountain tracks (due to snowfall and landslide) and the civil war. Reports indicated that survivors were living without shelter in subzero temperature and many were starving. Several villagers were making their way down the mountain tracks along with their herds of goats.The
International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement sent a team fromDushanbe to the affected region for relief efforts. The first international relief team reached the affected area on February 7 and the firstUnited Nations (UN) team arrived there on February 10. A convoy of theInternational Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) reached the site onFebruary 14 with 4,800 blankets, 800quilt s, 10 rolls of plastic sheeting and approximately 200 tents. Eleven days after the event, onFebruary 16 , helicopters were able to drop supplies to three isolated villages. TheEuropean Union (EU) offered £1.3m of relief aid including blankets, medical equipment, water and tents. The Taliban ruled Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan offered 100 tonnes each of rice and wheat, and approximately £40,000 to the affected region.ee also
*
May 30, 1998 Afghanistan earthquake References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
