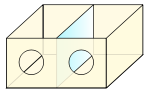
- Mirror box
-
 A diagrammatic explanation of the mirror box. The patient places the good limb into one side of the box (in this case the right hand) and the amputated limb into the other side. Due to the mirror, the patient sees a reflection of the good hand where the missing limb would be (indicated in lower contrast). The patient thus receives artificial visual feedback that the "resurrected" limb is now moving when they move the good hand. See text for more details.
A diagrammatic explanation of the mirror box. The patient places the good limb into one side of the box (in this case the right hand) and the amputated limb into the other side. Due to the mirror, the patient sees a reflection of the good hand where the missing limb would be (indicated in lower contrast). The patient thus receives artificial visual feedback that the "resurrected" limb is now moving when they move the good hand. See text for more details.
A mirror box is a box with two mirrors in the center (one facing each way), invented by Vilayanur S. Ramachandran to help alleviate phantom limb pain, in which patients feel they still have a limb after having it amputated.
Based on the observation that phantom limb patients were much more likely to report paralyzed and painful phantoms if the actual limb had been paralyzed prior to amputation (for example, due to a brachial plexus avulsion), Ramachandran and Rogers-Ramachandran proposed the "learned paralysis" hypothesis of painful phantom limbs (Ramachandran & Blakeslee 1998). Their hypothesis was that every time the patient attempted to move the paralyzed limb, they received sensory feedback (through vision and proprioception) that the limb did not move. This feedback stamped itself into the brain circuitry through a process of Hebbian learning, so that, even when the limb was no longer present, the brain had learned that the limb (and subsequent phantom) was paralyzed. Often a phantom limb is painful because it is felt to be stuck in an uncomfortable or unnatural position, and the patient feels they cannot move it.
To retrain the brain, and thereby eliminate the learned paralysis, Ramachandran and Rogers-Ramachandran (Ramachandran, Rogers-Ramachandran & Cobb 1995) created the mirror box. The patient places the good limb into one side, and the stump into the other. The patient then looks into the mirror on the side with good limb and makes "mirror symmetric" movements, as a symphony conductor might, or as we do when we clap our hands. Because the subject is seeing the reflected image of the good hand moving, it appears as if the phantom limb is also moving. Through the use of this artificial visual feedback it becomes possible for the patient to "move" the phantom limb, and to unclench it from potentially painful positions. The use of the mirror box has also been used in the rehabilitation of hemiparesis, or paralysis one side of the body, due to stroke (Altschuler et al. 1999) and to rehabilition of spatial neglect (Ramachandran et al. 1999).
Although the use of mirror therapy has been shown to be effective in some cases there is still no widely accepted theory of how it works. In a 2010 study of phantom limb pain, Martin Diers and his colleagues found that "In a randomized controlled trial that used graded motor imagery...and mirror training, patients with complex regional pain syndrome or phantom limb pain showed a decrease in pain as well as an improvement in function post-treatment and at the 6-month follow-up. And it was shown that the order of treatment mattered." This study found that mirrored imagery produced no significant cortical activity in patients with phantom limb pain and concluded that "The optimal method to alter pain and brain representation, and the brain mechanisms underlying the effects [of] mirror training or motor imagery, are still unclear." (Diers et al. 2010)
Contents
Is mirror therapy effective?
A number of small scale research studies have shown encouraging results, however there is no current consensus as to the effectiveness of mirror therapy. Recent reviews of the published research literature by Mosely(Moseley et al. 2008) and Ezendam (Ezendam et al 2009) concluded that much of the evidence supporting mirror therapy is anecdotal or comes from studies that had weak methodological quality. In 2011 a large scale review of the literature on mirror therapy by Rothgangel (Rothgangel et al. 2011) summarized the current research as follows.
"For stroke there is a moderate quality of evidence that MT [Mirror Therapy] as an additional intervention improves recovery of arm function, and a low quality of evidence regarding lower limb function and pain after stroke. The quality of evidence in patients with complex regional pain syndrome and phantom limb pain is also low. Firm conclusions could not be drawn. Little is known about which patients are likely to benefit most from MT, and how MT should preferably be applied. Future studies with clear descriptions of intervention protocols should focus on standardized outcome measures and systematically register adverse effects."(Rothgangel et al. 2011)
See also
References
- Altschuler, E. L.; Wisdom, S. B.; Stone, L.; Foster, C.; Galasko, D.; Llewellyn, D. M.; Ramachandran, V.S. (1999), "Rehabilitation of hemiparesis after stroke with a mirror.", Lancet (353(9169)): 2035–2036
- Karl, A; Mühlnickel, W; Kurth, R; Flor, H (2004), "Neuroelectric source imaging of steady-state movement-related cortical potentials in human upper extremity amputees with and without phantom limb pain", Pain 110 (1–2): 90–102, doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.03.013, PMID 15275756
- Flor, H.; Diers, M.; Christmann, C.; Koeppe, C. (2006), "Mirror illusions of phantom hand movements. Brain activity mapped by fMRI", NeuroImage 31: S159
- Ramachandran, VS; Altschuler, EL; Stone, L; Al-Aboudi, M; Schwartz, E; Siva, N (1999), "Can mirrors alleviate visual hemineglect?", Medical Hypotheses 52 (4): 303–305, doi:10.1054/mehy.1997.0651, PMID 10465667
- Ramachandran, V. S.; Rogers-Ramachandran, D. C.; Cobb, S. (1995), "Touching the phantom", Nature (377): 489–490
- Ramachandran, V. S.; Rogers-Ramachandran, D. C. (1996), "Synaesthesia in phantom limbs induced with mirrors", Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (263(1369)): 377–386, http://psy.ucsd.edu/chip/pdf/Synsth_Phant_Lmb_P_Roy_Soc.pdf
- Ramachandran, V. S.; Blakeslee, S. (1998), Phantoms in the brain: Probing the mysteries of the human mind, William Morrow & Company, ISBN 0-688-15247-3
- Ramachandran, V. S.; Hirstein, W. (1998), "The perception of phantom limbs: The D.O. Hebb lecture", Brain 9 (121): 1603–1630, http://psy.ucsd.edu/chip/pdf/Percpt_Phantom_Limbs_Brain.pdf
- Diers, M; Christmann, C; Koeppe, C; Ruf, M; Flor, H (2010), "Mirrored, imagined, and executed movements differentially activate sensorimotor cortex in amputees with and without phantom limb pain", PAIN 149 (2): 296–304, doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.020, PMID 20359825, http://krieger.jhu.edu/bin/y/h/Diers%20et%20al._2010.pdf
- Moseley, GL; Gallace, A; Spence, C (2008), "Is mirror therapy all it is cracked up to be? Current evidence and future directions", PAIN 138 (1): 7–10, doi:10.1016/j.pain.2008.06.026, PMID 18621484, http://www.psych.uncc.edu/pagoolka/pain2008.pdf
- Ezendam, D.; Bongers, RM.; Jannink, MJ. (2009), "Systematic review of the effectiveness of mirror therapy in upper extremity function", Disability Rehabilitation 20 (May): 1–15
- Ezendam, Daniëlle; Bongers, Raoul M.; Jannink, Michiel J. A. (2009), "Systematic review of the effectiveness of mirror therapy in upper extremity function", Disability Rehabilitation 20 (May): 1–15, doi:10.3109/09638280902887768
- Rothgangel, AS; Braun, SM; Beurskens, AJ; Seitz, RJ; Wade, DT (2011), "The clinical aspects of mirror therapy in rehabilitation: a systematic review of the literature", International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 34 (March): 1–13, doi:10.1097/MRR.0b013e3283441e98, PMID 21326041
External links
- V.S. Ramachandran's website
- WNYC - Radio Lab: Where Am I? (May 5, 2006) downloadable segment of radio program looks at historical examples and a present-day case of phantom limbs
- Ramachandran's Reith Lecture on Phantom Limbs
- Mirror box therapy web site
- The Itch a The New Yorker article that discusses mirror therapy and its current, and possible future, uses.
- Mirror therapy aiding US amputees
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.