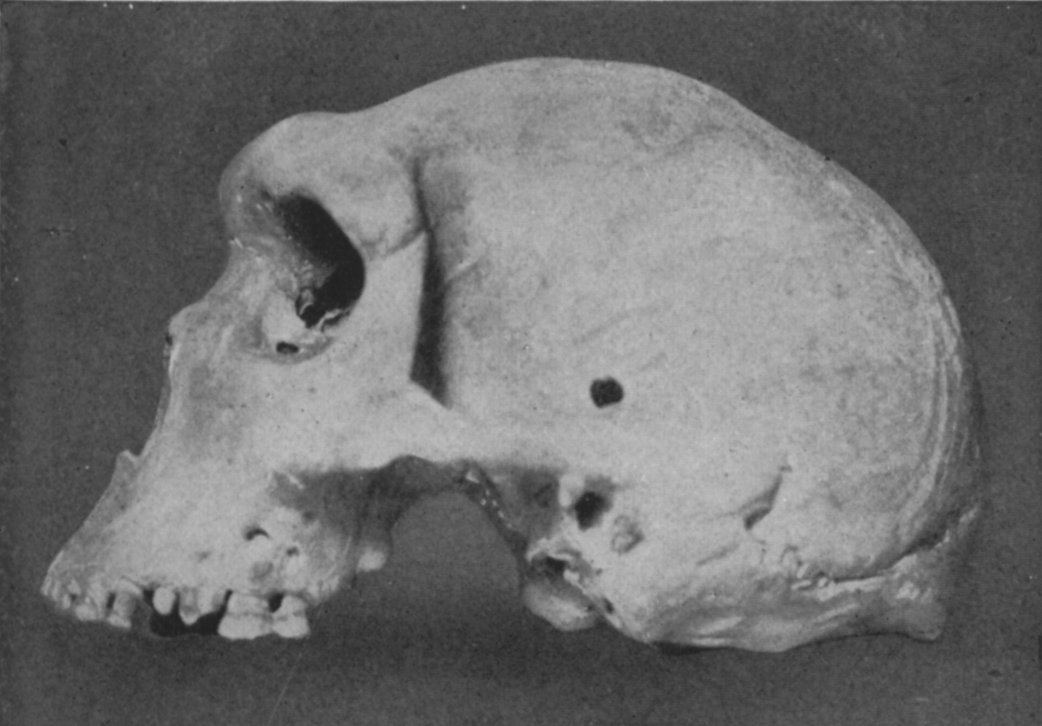
- Kabwe skull
catalog number = Broken Hill 1
common name = Kabwe cranium or Broken Hill man
species = "Homo rhodesiensis " or "Homo heidelbergensis "
age =
place discovered =Kabwe ,Zambia
date discovered = 1921
discovered by = Tom ZwiglaarKabwe skull or Kabwe cranium, or Broken Hill 1 is a
hominin fossil that was frequently classified as belonging to "Homo rhodesiensis ". Thecranium was found in aniron andzinc mine in Broken HillNorthern Rhodesia (nowKabwe ,Zambia ) in 1921 by Tom Zwiglaar, a Swiss miner. In addition to the cranium, an upperjaw from another individual, asacrum , atibia , and twofemur fragments were also found. The skull was dubbed Rhodesian Man at the time of the find, but is now commonly referred to as the Broken Hill Skull or the Kabwe Cranium. The association between the bones is unclear, but the tibia and femur fossils are usually associated with the skull. Rhodesian Man is dated to be between 125,000 and 300,000 years old. Cranial capacity of the Broken Hill skull has been estimated at 1,100 cm³ [The Evolution of Homo Erectus: Comparative Anatomical Studies of an Extinct Human SpeciesBy G. Philip RightmirePublished by Cambridge University Press, 1993ISBN 0521449987, 9780521449984 [http://books.google.com/books?id=edFD6el38mAC&dq=Ndutu+hominid&source=gbs_summary_s&cad=0] ] , which, when coupled with the more recent dating, makes any direct link to older skulls unlikely and negates the 1.75 to 2.5 million year earlier erroneous dating. Bada & al (1974) published direct date of 110 ka for this specimen measured byaspartic acid racemisation . [Concordance of Collagen-Based Radiocarbon and Aspartic-Acid Racemization Agesby 1. Jeffrey L. Bada 2. Roy A. Schroeder 3. Reiner Protsch 4. Rainer BergerPNAS abstract URL [http://www.pnas.org/content/71/3/914.abstract] ] [Amino Acid Racemization Dating of Fossil Bones [http://arjournals.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.ea.13.050185.001325] ] The destruction of the paleoanthropological site, mined to deep filed now with water pit, make layered dating completely impossible.The skull is from an extremely robust individual, and has the comparatively largest brow-ridges of any known hominid remains. It was described as having a broad face similar to "Homo neanderthalensis" (ie. large nose and thick protruding brow ridges), and has been interpreted as an "African Neanderthal". However, when regarding the skulls extreme robustness, recent research has pointed to several features intermediate between modern "
Homo sapiens " and Neanderthal. Most current experts believe Rhodesian Man to be within the group of "Homo heidelbergensis " though other designations such as "Archaic Homo sapiens" and "Homo sapiens rhodesiensis" have also been proposed. According toTim White , it is probable that Rhodesian Man was the ancestor of "Homo sapiens idaltu " (Herto Man), which would be itself at the origin of "Homo sapiens sapiens ". No direct linkage of the species can so far be determined.References
Literature
*cite journal|author=Woodward, Arthur Smith|year=1921|title=A New Cave Man from Rhodesia, South Africa|journal=Nature|volume=108|pages=371–372|doi=10.1038/108371a0
*cite journal|author=Singer Robert R. and J. Wymer|year=1968|title=Archaeological Investigation at the Saldanha Skull Site in South Africa|journal=The South African Archaeological Bulletin|volume=23 (3)|pages=63–73|doi=10.2307/3888485
* [http://www.waspress.co.uk/journals/beforefarming/journal_20022/abstracts/papers/20022_03_s.pdf Bone tools from Broken Hill (Kabwe) cave, Zambia, and their evolutionary significance]ee also
*
List of fossil sites "(with link directory)"
* List of hominina (hominid) fossils "(with images)"
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.