- PRR D6
Infobox Locomotive
name = PRR D6
powertype = Steam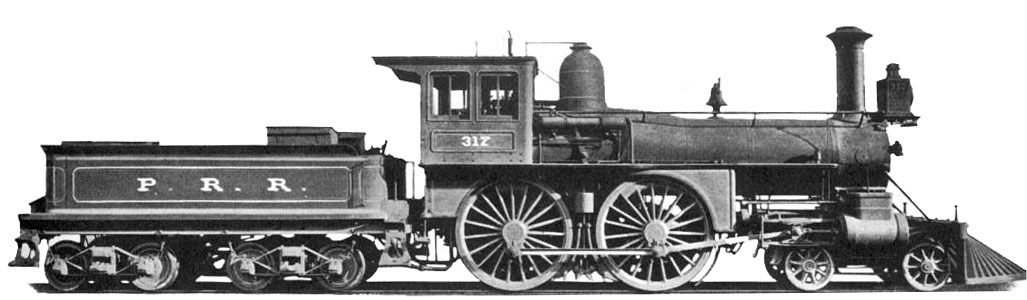
caption = PRR D6 #317 in its builders' portrait
whytetype = 4-4-0
uicclass = 2'B
designer =Theodore N. Ely
builddate = 1881–1883
builder = PRR Altoona Works
totalproduction = 19
gauge = RailGauge|ussg
leadingsize = convert|33|in|m|2|abbr=oncite web
title = D16 Diagram
url = http://prr.railfan.net/diagrams/PRRdiagrams.html?diag=d6.gif&sel=ste&sz=sm&fr=
work = PRR.Railfan.net
author = Pennsylvania Railroad
accessdate = 2007-12-31]
driversize = convert|78|in|m|2|abbr=on
wheelbase = convert|22|ft|8.5|in|m|2|abbr=on
length = convert|58|ft|0.3|in|m|2|abbr=on
height = convert|15|ft|0|in|m|2|abbr=on
axleload = convert|32900|lb|kg|abbr=on
weightondrivers = convert|58800|lb|kg|abbr=on
weight = convert|96700|lb|kg|abbr=on
locotenderweight = convert|153000|lb|kg|abbr=on
fueltype = Soft coal
fuelc
convert|12000|lb|kg|abbr=on
waterc
convert|2400|USgal|L|abbr=on
boilerpressure = convert|140|psi|bar|abbr=on
firearea = convert|34.76|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on
tubearea = convert|1085|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on
fireboxarea = convert|155|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on
totalsurface = convert|1240|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on
cylinders = 2
cylindersize = convert|18|in|mm|abbr=on bore × convert|24|in|mm|abbr=on stroke
valvegear = Stephenson
tractiveeffort = convert|11170|lb|kN|2|abbr=on (D6)
convert|12800|lb|kN|2|abbr=on (D6a)
factorofadhesion = 5.3 (D6) 4.6 (D6a)Class D6 (formerly Class K, pre-1895) on the
Pennsylvania Railroad was a class of4-4-0 steam locomotive .cite book
title = Pennsy Power: Steam and Electric Locomotives of the Pennsylvania Railroad, 1900–1957
author = Staufer, Alvin F. and Pennypacker, Bert
publisher = Staufer
year = 1962
id = LOC 62-20878] Nineteen were built by the PRR's Altoona Works between 1881–1883. They were equipped with convert|78|in|m|2|abbr=on drivers.cite web
title = PRR Steam Roster
url = http://www.northeast.railfan.net/prr_steam2.html
work = Northeast Rails
accessdate = 2007-12-31] Seven were later converted to convert|72|in|m|2|abbr=on drivers and classified D6a.The D6 is notable as one of the first American 4-4-0s to place the firebox above, rather than between, the locomotive's frames. [cite book
title = Modern Engineering Practice
author = Gunsaulus, Frank W. (ed.)
year = 1906
publisher = American School of Correspondence] This added about 8 inches to the possible width of the firebox, enabling a larger, easier to fire and more powerful locomotive; the maximum fire grate area increased to about convert|35|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on from the previous maximum of about convert|18|sqft|m2|2|abbr=on. [cite journal
title = Mechanical Stokers for Locomotives
journal = Cassier's Magazine
volume = XXXII
issue = 1
year = 1907
month = May
pages = p. 75
publisher = Cassier Magazine
location = New York]The innovation was not wholly new, having been first seen on the
Philadelphia and Reading Railroad 's 1859 "Vera Cruz", designed byJames Milholland of that road and built in their own shops; the Reading used this design until the invention of theWootten firebox in 1877. [cite book
title = Report of the Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual Convention of the American Railway Master Mechanics' Association in Convention at Tremont Temple, Boston, Mass., June 15th, 16th and 18th, 1886
date = 1886
publisher = Aldine
location =Cincinnati, Ohio ] It was subsequently adopted by theBaldwin Locomotive Works in 1881 for six locomotives constructed for theCentral of New Jersey ; these were followed by the Pennsylvania Railroad locomotives, which garnered more attention for this design feature, in addition to having larger drivers than most previous 4-4-0s.References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
