- OAuth
-
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open standard for authorization. It allows users to share their private resources (e.g., photos, videos, contact lists) stored on one site with another site without having to hand out their credentials, typically username and password.
OAuth allows users to hand out tokens instead of credentials to their data hosted by a given service provider. Each token grants access to a specific site (e.g., a video editing site) for specific resources (e.g., just videos from a specific album) and for a defined duration (e.g., the next 2 hours). This allows a user to grant a third party site access to their information stored with another service provider, without sharing their access permissions or the full extent of their data.
OAuth is a service that is complementary to, but distinct from, OpenID.
Contents
History
OAuth began in November 2006, during which Blaine Cook was developing the Twitter OpenID implementation. Meanwhile, Ma.gnolia needed a solution to allow its members with OpenIDs to authorize Dashboard Widgets to access their service. Cook, Chris Messina and Larry Halff from Ma.gnolia met with David Recordon to discuss using OpenID with the Twitter and Ma.gnolia APIs to delegate authentication. They concluded that there were no open standards for API access delegation.
The OAuth discussion group was created in April 2007, for the small group of implementers to write the draft proposal for an open protocol. DeWitt Clinton from Google learned of the OAuth project, and expressed his interest in supporting the effort. In July 2007 the team drafted an initial specification. Eran Hammer-Lahav joined and coordinated the many OAuth contributions, creating a more formal specification. On October 3, 2007, the OAuth Core 1.0 final draft was released.
At the 73rd Internet Engineering Task Force meeting in Minneapolis in November of 2008, an OAuth BOF was held to discuss bringing the protocol into the IETF for further standardization work. The event was well attended and there was wide support for formally chartering an OAuth working group within the IETF.
The OAuth 1.0 Protocol was published as RFC 5849, an informational Request for Comments, in April 2010.
Since August 31, 2010, all third party Twitter applications have been required to use OAuth.[1]
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0 is the next evolution of the OAuth protocol and is not backward compatible with OAuth 1.0. OAuth 2.0 focuses on client developer simplicity while providing specific authorization flows for web applications, desktop applications, mobile phones, and living room devices. The specification is being developed[2] within the IETF OAuth WG and is expected to be finalized by the end of 2010 according to Eran Hammer-Lahav.[3]
Facebook's new Graph API only supports OAuth 2.0 and is the largest implementation of the emerging standard.[4] As of 2011, both Google[5] and Microsoft[6] had added OAuth 2.0 experimental support to their APIs.
Security
On April 23, 2009, a session fixation security flaw in the 1.0 protocol was announced. It affects the OAuth authorization flow (also known as "3-legged OAuth") in OAuth Core 1.0 Section 6.[7] Version 1.0a of the OAuth Core protocol was issued to address this issue.[8]
There is a debate over security concerns of OAuth.[9][10]
Uses
OAuth can be potentially used as an authorizing mechanism to consume secured (i.e., authenticated) RSS/ATOM feeds. Consumption of RSS/ATOM feeds that requires authentication has always been an issue. For example; an RSS feed from a secured Google Sites can not be consumed using Google Reader. 3-Legged OAuth can be used to authorize Google Reader to the RSS feed from that Google Site.
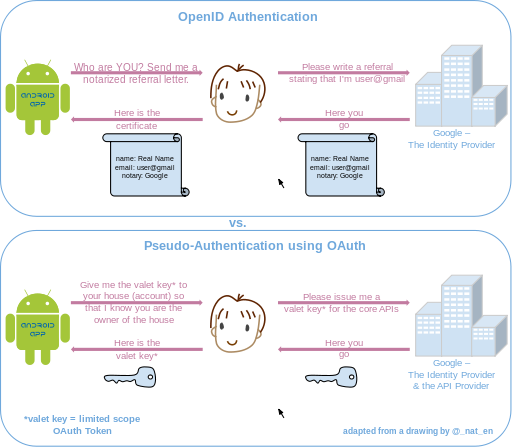
OpenID vs. pseudo-authentication using OAuth
The following drawing highlights the differences between using OpenID vs. OAuth for authentication. Note that with OpenID, the process starts by the application asking the user for their identity (typically a openid URI), whereas in the case of OAuth, the application directly requests a limited access OAuth Token (valet key) to access the APIs (enter the house) on user's behalf. If the user can grant that access, the application can retrieve the unique identifier for establishing the profile (identity) using the APIs.
See also
- OpenID
- DataPortability
- BrowserID
References
- ^ Chris Crum (2010-08-31). "Twitter Apps Go OAuth Today ". WebProNews.com. http://www.webpronews.com/topnews/2010/08/31/twitter-apps-go-oauth-today. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Protocol". 2011-02-16. http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-v2 .
- ^ Eran Hammer-Lavah (2010-05-15). "Introducing OAuth 2.0". http://hueniverse.com/2010/05/introducing-oauth-2-0/. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ "Authentication - Facebook Developers". developers.facebook.com. http://developers.facebook.com/docs/authentication/.
- ^ "Making auth easier: OAuth 2.0 for Google APIs". googlecode.blogspot.com. 2011-03-14. http://googlecode.blogspot.com/2011/03/making-auth-easier-oauth-20-for-google.html.
- ^ Dare Obasanjo (2011-05-04). "Announcing Support for OAuth 2.0". windowsteamblog.com. http://windowsteamblog.com/windows_live/b/developer/archive/2011/05/04/announcing-support-for-oauth-2-0.aspx.
- ^ "OAuth Security Advisory: 2009.1". 2009-04-23. http://oauth.net/advisories/2009-1. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- ^ http://oauth.net/core/1.0a
- ^ {{Cite web | title = Is OAuth 2.0 Bad for the Web? | accessdate = 2010-09-21 | date = 2010-09-20 | url = http://www.infoq.com/news/2010/09/oauth2-bad-for-web }}
- ^ "an unwarranted bashing of Twitter’s oAuth". 2011-08-03. http://benlog.com/articles/2010/09/02/an-unwarranted-bashing-of-twitters-oauth/. Retrieved 2011-08-03.
External links
- RFC5849 at the IETF
- OAuth.net
- OAuth WG at the IETF
- OAuth Code Library Support on Google Groups
- OAuth Beginner's Guide and Resource Center on Hueniverse
- Google OAuth & Federated Login Research
- Yahoo! OAuth Quick Start Guide
- How-to: Real-time Linux system monitoring on Twitter using OAuth and perl
- OAuth Checklist
- OAuth Toolkit May Help Secure APIs
- LIVE Demo of OAuth with Google, Yahoo
Categories:- Cloud standards
- Internet protocols
- 2007 introductions
- Computer access control
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.