- Mail submission agent
-
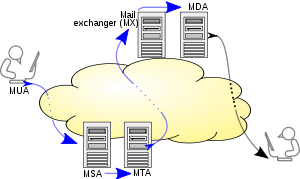
A mail submission agent (MSA) is a computer program or software agent that receives electronic mail messages from a mail user agent (MUA) and cooperates with a mail transfer agent (MTA) for delivery of the mail. It uses a variant of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), as specified in RFC 6409.
Many MTAs perform the function of an MSA as well, but there are also programs that are specially designed as MSAs without full MTA functionality. Historically in Internet mail, both MTA and MSA functions use port number 25. The MTA accepts locally-destined mail from other domains, and an MSA accepts submitted mail from local users.
Contents
Benefits
Separation of the MTA and MSA functions produces several benefits:
One benefit is that an MSA, since it is interacting directly with the author's MUA, can correct minor errors in a message's format (such as a missing Date, Message-ID, To fields, or an address with a missing domain name) and/or immediately report an error to the author so that it can be corrected before it is sent to any of the recipients. An MTA accepting a message from another site cannot reliably make those kinds of corrections, and any error reports generated by such an MTA will reach the author (if at all) only after he has already sent the message.
One more benefit is that with a dedicated port number, 587, it is always possible for users to connect to their domain to submit new mail. Many Internet service providers and enterprise or institutional networks restrict the ability to connect to remote MTAs on port 25. Availability of a Mail Submission Agent on port 587 enables nomadic users to continue to send mail via their preferred submission servers even from within others' networks. Using a specific submission server is a requirement when sender policies or signing practices are enforced.
Another benefit is that separating the MTA and MSA functions makes it easier for an MTA to deny relaying, that is to refuse any mail that is not addressed to a recipient at a domain that is served locally. By contrast, an MSA must generally accept mail for any recipient on the Internet, though it only accepts such mail from authors who are authorized to use that MSA and who have established their identity to the MSA via authentication. In times when both mail submission and acceptance of incoming mail were usually accomplished using the same protocol and the same server, the ability to send mail to arbitrary destinations without authentication allowed spammers to use MTAs as a means of distributing spam (since a single message transaction can request that an MTA relay a message to a large number of recipients), and also made it more difficult to trace a message to its origin.
Yet another benefit is that MSAs and MTAs can have different policies for filtering of spam. Most MSAs require authentication in the form of a username and password provided by the author. Any messages received by such an MSA are therefore traceable to an author who has a direct relationship with the MSA, and who can be held accountable for his actions. This allows the MSA to have either no spam filtering, or more permissive spam filtering than an MTA that exists for the purpose of accepting incoming email from other domains. It is difficult to establish trust in mail sent between arbitrary domains, because there is generally no direct relationship between those domains via which trust, or even identity, can be established. In the absence of such trust, an MTA must generally rely on heuristics and third-party reputation services to distinguish spam from legitimate traffic, and both of these mechanisms have a history of being error-prone.[1][2] The separation of MSA and MTA therefore avoids the use of unreliable spam recognition mechanisms during mail submission, and increases the probability for legitimate mail to be delivered successfully.
Protocol
Mandatory Authentication
Main article: SMTP AuthenticationRFC 6409 requires that clients are authorized and authenticated to use the mail submission service, e.g., as described in SMTP-AUTH (ESMTPA), or by other means such as RADIUS, public key certificates, or (the mostly obsolete) POP before SMTP.
Policy enforcement
The MSA must check that the submitted mail is syntactically valid and conforms to the relevant site policies. RFC 6409 contains some optional features:
- Enforce submission rights guarantees that the envelope sender address is valid and authorized with the used authentication. This in essence complies with the SPF model specified in RFC 4408.
- May add sender permits to add a Sender address header field if the envelope sender address does not match any author address in the "From" header field. This roughly complies with the Sender ID model specified in RFC 4406 - ignoring the tricky case of Resent-From header fields not covered in RFC 6409.
See also
- E-mail authentication
- SMTP AUTH
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- List of mail servers
- Comparison of mail servers
- Smart host
- E-mail agent (infrastructure) (MxA)
- Mail delivery agent (MDA)
- Mail transfer agent (MTA)
- Mail user agent (MUA)
References
- C. Hutzler, D. Crocker, P. Resnick, E. Allman, T. Finch, Email Submission Operations: Access and Accountability Requirements, RFC 5068, November 2007.
- R. Gellens, J. Klensin, Message Submission for Mail, RFC 6409, April 2006. (obsoleted RFC4409, RFC 2476)
- J. Klensin, ed. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. RFC 2821, April 2001.
- "SMTP is not secure". Kasoft Central. http://kasoft.freeyellow.com/Central/smtpbad.html. Retrieved 2008-06-14.
- ^ Amir Herzberg (19 May 2009). "DNS-based email sender authentication mechanisms: A critical review". Computers & Security (ScienceDirect). doi:10.1016/j.cose.2009.05.002.
- ^ Jeremy Blosser and David Josephsen (November, 2004). "Scalable Centralized Bayesian Spam Mitigation with Bogofilter". Proceedings of LISA '04: Eighteenth Systems Administration Conference. USENIX. http://www.usenix.org/event/lisa04/tech/blosser/blosser_html/. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
Categories:- Email agents
- Email authentication
- Internet mail protocols
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.