- Estonian Swedes
-
Estonian Swedes 
Flag of Noarootsi parish, based on Swedish and Estonian flags Regions with significant populations  Estonia
Estonia211–1,000 [1]  Sweden
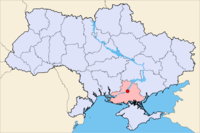
Sweden26,000  Ukraine
Ukraine108 Languages Religion Lutheran
The Estonian Swedes, Estonia-Swedes, or Coastal Swedes (Swedish: estlandssvenskar, "Estonia Swedes", colloquially aibofolke, "Island People", Estonian: rannarootslased, i.e. "Coastal Swedes" or eestirootslased) are a Swedish-speaking linguistic minority traditionally residing in the coastal areas and islands of what is now western and northern Estonia. The beginning of the continuous settlement of Estonian Swedes in these areas (known as Aiboland) dates back to the 13th and 14th centuries, when their Swedish-speaking ancestors arrived in Estonia from what is now Sweden and Finland. Almost all of Estonia's Swedish-speaking minority fled to Sweden during World War II, and only the descendants of a few individuals who opted to stay are permanently resident in Estonia today.
Contents
History
Early history
The Swedish speaking population in Estonia persisted for about 650 years. The first written mention of the Swedish population in Estonia comes from 1294, in the laws of the town of Haapsalu. Further early mentions of Swedes in Estonia came in 1341 and 1345 (when an Estonian monastery in Padise sold "the Laoküla Estate" and Suur-Pakri Island to a group of Swedes). During the 13th through 15th centuries, large numbers of Swedes arrived in coastal Estonia from Finland, which was under Swedish control (and would remain so for hundreds of years), often settling on Church-owned land. The first documented record of the island of Ruhnu (Swedish: Runö), and of its Swedish population, is also a 1341 letter sent by the Bishop of Courland which confirmed the islanders' right to reside and manage their property in accordance with Swedish law.
Swedish Estonia
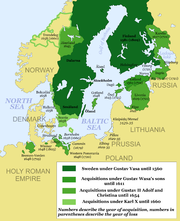 The Swedish Empire in 1658, including the Dominion of Swedish Estonia and the Dominion of Swedish Livonia (now southern Estonia).
The Swedish Empire in 1658, including the Dominion of Swedish Estonia and the Dominion of Swedish Livonia (now southern Estonia).
In 1561, Sweden established the Dominion of Swedish Estonia, which it would hold until 1710 (formally until 1721, when the territory was ceded to Russia under the Treaty of Nystad). The Estonia-Swedes prospered during this period. Swedish, along with German and Estonian, was one of the official languages.
Russian rule
After the Teutonic Order lost much of its power in the 16th century and the Dominion of Swedish Estonia was lost to Russia following the Great Northern War (1700–1721), conditions worsened for Swedes in Estonia: the lands they had settled were often confiscated from the Church and given to local nobility, and taxes increased. This situation remained the same during Russian rule, and the Estonian Swedes' suffering continued as, for example, the Agrarian reforms which liberated the land of Estonian serfs in 1816, did not apply to Estonian (mostly non-serf) Swedes.
Forced emigrations
At certain times during Russian Estonia period, groups of Estonian Swedes were forced to leave Estonia for other parts of the Russian Empire. Most notably, Empress Catherine II of Russia forced the 1,000 Swedes of Hiiumaa (Swedish: Dagö), to move to Ukraine in 1781, where they established the community of Gammalsvenskby.
Conditions improve
The Estonian Swedes' positions improved during the 1850s and 1860s, due to further agrarian reforms, but discrimination remained during the rest of the period of Tsarist rule in Estonia. After the First World War and the Russian Revolution, the independent Republic of Estonia was created in 1918. The constitution of independent Estonia granted the ethnic minority groups the control over their language of education, the right to form institutions for their national and social rights, the right to use their native language in official capacities where they formed majorities of the population, and the choice of nationality. Swedes, Baltic Germans, Russians, and Jews all had ministers in the new national government. Svenska Folkförbundet, a Swedish political organization, was formed. In 1925, a new law giving more cultural autonomy was passed, although the Russians and Swedes in Estonia did not take advantage of these new freedoms, mainly for economic reasons.
World War II
In 1939, the Soviet Union forced Estonia to sign a treaty concerning military bases. Many of the islands upon which Estonian Swedes lived were confiscated, bases were built on them, and their inhabitants were forced to leave their homes. A year later, Estonia was occupied by, and annexed into, the Soviet Union, and their voice in government was lost. Estonian Swedish men were conscripted into the Red Army and, during the German occupation, into the German armed forces. Most of the remaining Estonian Swedes fled to Sweden prior to the second invasion of Estonia by the Soviet army in 1944. On June 8 1945, there were 6,554 Estonian Swedes and 21,815 ethnic Estonian refugees in Sweden.[2]
Today
Today, small groups of remaining Estonian Swedes are regrouping and re-establishing their heritage, by studying Swedish language and culture. They are led by the Estonian Swedish Council, which is backed by the Estonian government. In 2000, Swedes were the 21st largest ethnic group in Estonia, numbering only 300.[3] There are however many Estonian Swedes and descendants of Estonian Swedes residing in Sweden.
Areas of population and demographics
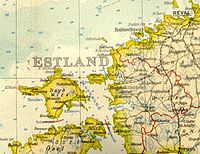 An older Swedish map of the West Estonian archipelago, in which the Estonian Swedish population was concentrated.
An older Swedish map of the West Estonian archipelago, in which the Estonian Swedish population was concentrated.
Population figures during the early centuries of Swedish settlement are not available. At the end of the Teutonic period, there were probably around 1,000 Estonian Swedish families, with some 1,500 Swedes in the capital Tallinn (Swedish: Reval), giving a total population of roughly 5-7 thousand, some 2-3% of the population of what is now Estonia at the time.
The 1897 Russian Census gives a total Swedish population of 5,768 or 1,39 % in the Governorate of Estonia. The majority of the Swedes lived in the Hapsal district where they formed a minority of 5,6 %.[4]
The 1922 census gives Estonia a total population of 1,107,059[5][6] of which Estonia-Swedes made up only 0.7%, some 7,850 people,[5][7] who made up majorities in some places, such as Ruhnu (Swedish: Runö), Vormsi (Swedish: Ormsö), Riguldi (Swedish: Rickull). It dropped slightly to 7,641 in 1934.[8] By the time of the Second World War, the population was nearly 10,000, and roughly 9,000 of these people fled to Sweden.[citation needed] Towns with large pre-war Swedish populations include Haapsalu (Swedish: Hapsal) and Tallinn (Swedish: Reval).
After World War II the numbers stayed fairly stable: there were 435 Estonian Swedes in 1970, 254 in 1979 and 297 in 1989, when they placed 26th on the list of Estonia's minority groups (before the Second World War, they were third in number, after Russians and Germans). The 2000 census shows a number of 300, placing Swedes at 20th on the list of Estonia's minority groups.[3] However, only 211 of them are Estonian citizens. Since all do not claim their real ethnic background, some have estimated the real number of Estonian Swedes in Estonia to be about 1,000.[9]
In Ukraine
In Ukraine, the village of Gammalsvenskby, founded by Estonian Swedish refugees, had considerable Swedish population until August 1, 1929, when 885 of the villagers fled for Sweden. There are a few hundred people of Estonian Swedish descent in Gammalsvenskby today.
Language
Main article: Swedish dialectsTraditional Swedish Sprachraum, with Estonian dialects marked.
There was not a unified Estonian-Swedish dialect, but several. The Estonian-Swedish dialects are subdivisions of the Eastern varieties of Standard Swedish. Ruhnu had its own dialect, the Vormsi-Noarootsi-Riguldi dialect was spoken on those islands, there was also a Pakri-Vihterpalu variety. The dialect of Hiiumaa is still spoken by a few in Gammalsvenskby (which is called Gammölsvänskbi in the Hiiumaa/Gammmalsvenskby dialect).
References
- ^ Population of Estonia by ethnic nationality, mother tongue and citizenship
- ^ Seppo Zerterberg: Viro, Historia, kansa, kulttuuri. Helsinki: Suomalaisen kirjallisuuden seura, 1995, ISBN 951-717-806-9 (Finnish)
- ^ a b (in Estonian and English) (PDF) 2000. Aasta rahva ja eluruumide loendus (Population and Housing Census). 2. Statistikaamet (Statistical Office of Estonia). 2001. ISBN 9985-74-202-8. http://www.stat.ee/dokumendid/26495. Retrieved 2009-09-23.
- ^ Russian Imperial Census 1897
- ^ a b Riigi Statistika Keskbüroo (1924) (in Estonian) (PDF). 1922 a. üldrahvalugemise andmed. Vihk II. Üleriikline kokkuvõte. Tabelid. http://dspace.utlib.ee/dspace/bitstream/10062/4443/1/rahvalugemineyleriikl.pdf. Retrieved 2009-09-15.
- ^ "Population in counties and towns, 1922". Statistics Estonia. 2008-01-12. http://www.stat.ee/26398. Retrieved 2009-09-13.
- ^ "Ethnic minorities in Estonia: past and present". Estonian Institute. 1998-12-26. http://www.einst.ee/factsheets/ethnic_minor/. Retrieved 2009-09-13.
- ^ Riigi Statistika Keskbüroo (1937) (in Estonian) (PDF). Rahvastikuprobleeme Eestis. II Rahvaloenduse tulemusi. Vihk IV. http://dspace.utlib.ee/dspace/bitstream/10062/4440/1/rahvastikuprobleeme.pdf. Retrieved 2009-09-15.
- ^ Estlandssvenskarna i Estland - har upprättat kulturellt självstyre (Swedish)
External links
- Estonian Institute: Estonian Swedes
- Estonian Swedes embrace cultural autonomy rights
- Ethnic Minorities in Estonia
- Gammalsvenskby: the true story of Swedish settlement in Ukraine
- Statistics Estonia: Population by Ethnic Group, Nationality, Mother Tongue, and Citizenship
- Den Andra Stranden -Information project about the Estonian Swedes with history, interactive maps, thousands of pictures, music and personal stories
- Estlandssvenskarna i Estland - har upprättat kulturellt självstyre (In Swedish)
Swedish diaspora Europe Americas Asia & Oceania Categories:- Swedish minorities
- Ethnic groups in Estonia
- Estonian people of Swedish descent
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.