- Carnotaurus
Taxobox
name = "Carnotaurus"
fossil_range =Late Cretaceous
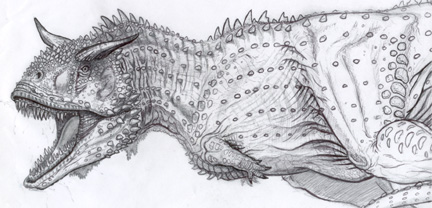
image_width = 200px
image_caption = Restoration of "Carnotaurus sastrei".
regnum =Animal ia
phylum = Chordata
classis = Sauropsida
superordo =Dinosaur ia
ordo =Saurischia
subordo =Theropoda
familia =Abelisauridae
subfamilia =Carnotaurinae
tribus =Carnotaurini
genus = "Carnotaurus"
genus_authority = Bonaparte, 1985
subdivision_ranks =Species
subdivision ="C. sastrei" Bonaparte, 1985 (type)"Carnotaurus" (pronEng|ˌkɑrnoʊˈtɔrəs KAHR-noh-TAWR-us; meaning "meat-bull", referring to its distinct bull-like horns (
Latin "carne" = flesh + Greek "tauros" = bull) was a large predatorydinosaur , with horns vaguely resembling a bull's."Carnotaurus" lived in
Patagonia , Argentina during theMaastrichtian stage of theLate Cretaceous , and was discovered byJosé F. Bonaparte , who has uncovered many otherSouth America n dinosaurs.Bonaparte (1985). "A horned Cretaceous carnosaur from Patagonia." "National Geographic Research", 1: 149-151.]Description
"Carnotaurus" was a medium-sized theropod, about 9.0 m (30 ft) in length, 3 m tall at the hips, and weighing about 1,600 kg (1.76 tons). The most distinctive features of "Carnotaurus" are the two thick horns above the
eye s, and the extremely reduced forelimbs with fourfinger s.Bonaparte, Novas, and Coria (1990). "Carnotaurus sastrei" Bonaparte, the horned, lightly built carnosaur from the Middle Cretaceous of Patagonia." "Contributions in Science (Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County)", 416: 41 pp.] It is also characterized by its unusually long neck (compared to other theropods), and its small head with box-shaped jaws. It had a smallskull , a thick chest, and a thintail . The eyes of "Carnotaurus" faced forward, which is unusual in a dinosaur, and may indicatebinocular vision anddepth perception .There is a rather puzzling contrast between "Carnotaurus"’ deep, robust-looking skull and its shallow, slender lower jaw. So far no-one has worked out what this might imply about its methods of feeding. cite book | author= Paul, G.S. | title=Predatory Dinosaurs of the World | date=1988 | isbn=0-671-61946-2 ]
A single nearly complete skeleton has been described including impressions of
skin along almost the entire right side, that show "Carnotaurus" lackedfeather s, unlike the more advancedcoelurosaur iantheropod s ("see also"feathered dinosaurs ). Instead, the skin is lined with rows of bumps, which become larger toward the spine.The
type species "Carnotaurus sastrei" is the only knownspecies . Its closest relatives include "Aucasaurus " (Argentina), "Majungasaurus " (Madagascar), and "Rajasaurus " (India). Together, these dinosaurs form thesubfamily Carnotaurinae in the familyAbelisauridae . Among the carnotaurines, "Carnotaurus" is most closely related to "Aucasaurus", and together these two genera form the tribeCarnotaurini .In popular culture
Since the mid-1990s, "Carnotaurus" has been featured occasionally in the popular media. One of its earliest prominent roles in fiction was the 1995 sequel to "
Jurassic Park ",Michael Crichton 's "The Lost World". In the novel, "Carnotaurus" was portrayed as having the (completely fictional) ability to change its colour to blend into the background, like achameleon or acuttlefish .cite book | last =Crichton | first =Michael | authorlink =Michael Crichton
title =The Lost World | publisher =Ballantine Books | date =September 1995 | location = | pages =416 pp. | url = | doi =ISBN 0-679-41946-2 | id = ] While it did not appear in the 1997 film adaptation of the novel, "Carnotaurus" subsequently appeared in numerous tie-ins to the "Jurassic Park" franchise, including several video games. Another prominent movie role for "Carnotaurus" came with the 2000 Walt Disney animated film "Dinosaur", which featured two "Carnotaurus" attacking a large herd of herbivorous dinosaurs. The "Carnotaurus" in the film were much larger than the real life animal, scaled up to proportions more closely resembling the giant theropod "Tyrannosaurus ". In reality, "Carnotaurus" was even smaller than "Iguanodon ", the main dinosaur featured in the Disney picture.Cite visual|director=Eric Leighton & Ralph Zondag|producer=|crew=| title=Dinosaur|url=http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0130623/|date=2000-05-19 |medium=motion picture|distributor=Walt Disney Pictures|location=USA] Currently, "Carnotaurus" can be seen as a regular protagonist in the "4KidsTV "anime , "Dinosaur King ".Bibliography
* Bonaparte (1991). "The Gondwanian theropod families Abelisauridae and Noasauridae." "Historical Biology. An International Journal of Paleobiology", 5: 1-25.
* Lamanna, Martinez, and Smith (2002). "A definitive abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the early Late Cretaceous of Patagonia." "Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology", 22: 58–69.References
External links
* [http://www.mdp.edu.ar/rectorado/secretarias/investigacion/nexos/16/16carnosaurio.htm The bite of "Carnotaurus"] at Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata. [in Spanish]
* Gerardo V. Mazzetta, Adrián P. Cisilino & R. Ernesto Blanco. [http://www.apaleontologica.org.ar/contenido/Ameg41408.php Mandible stress distribution during the bite in "Carnotaurus sastrei" Bonaparte, 1985 (Theropoda: Abelisauridae)] . (2004) "Ameghiniana 41": 605-617. Buenos Aires.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
