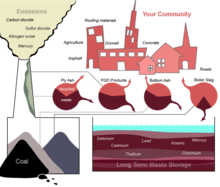
- Coal combustion products
-
Coal combustion products (CCPs) (also called coal combustion wastes (CCW)) are categorized in four groups, each based on physical and chemical forms derived from coal combustion methods and emission controls:
-
- Fly ash is captured after coal combustion by filters (bag houses), electrostatic precipitators and other air pollution control devices. It comprises 60 percent of all coal combustion waste (labeled here as coal combustion products). is most commonly used as a high-performance substitute for portland cement or as clinker for portland cement production. Cements blended with fly ash are becoming more common. Building material applications range from grouts and masonry products to cellular concrete and roofing tiles. Many asphaltic concrete pavements contain fly ash. Geotechnical applications include soil stabilization, road base, structural fill, embankments and mine reclamation. Fly ash also serves as filler in wood and plastic products, paints and metal castings.
-
- Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) materials are produced by chemical “scrubber” emission control systems that remove sulfur and oxides from power plant flue gas streams. FGD comprises 24 percent of all coal combustion waste. Residues vary, but the most common are FGD gypsum (or “synthetic” gypsum) and spray dryer absorbents. FGD gypsum is used in almost thirty percent of the gypsum panel products manufactured in the U.S. It is also used in agricultural applications to treat undesirable soil conditions and to improve crop performance. Other FGD materials are used in mining and land reclamation activities.
-
- Bottom ash and boiler slag can be used as a raw feed for manufacturing portland cement clinker, as well as for skid control on icy roads. The two materials comprise 12 and 4 percent of coal combustion waste respectively. These materials are also suitable for geotechnical applications such as structural fills and land reclamation. The physical characteristics of bottom ash and boiler slag lend themselves as replacements for aggregate in flowable fill and in concrete masonry products. Boiler slag is also used for roofing granules and as blasting grit.
-
- The majority of CCPs are landfilled, placed in mine shafts or stored on site at coal fired power plants. About 43 percent of CCPs were recycled for "beneficial uses," in 2008, according to the American Coal Ash Association. [1] . The chief benefit of recycling is to stabilize the environmental harmful components of the CCPs such as arsenic, beryllium, boron, cadmium, chromium, chromium VI, cobalt, lead, manganese, mercury, molybdenum,selenium, strontium, thallium, and vanadium, along with dioxins and PAH compounds. [2][3]
References
- ^ http://www.acaa-usa.org
- ^ Managing Coal Combustion Residues in Mines, Committee on Mine Placement of Coal Combustion Wastes, National Research Council of the National Academies, 2006
- ^ Human and Ecological Risk Assessment of Coal Combustion Wastes, RTI, Research Triangle Park, August 6, 2007, prepared for the US Environmental Protection Agency
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.