- Type I hypersensitivity
Infobox_Disease
Name = Type I hypersensitivity
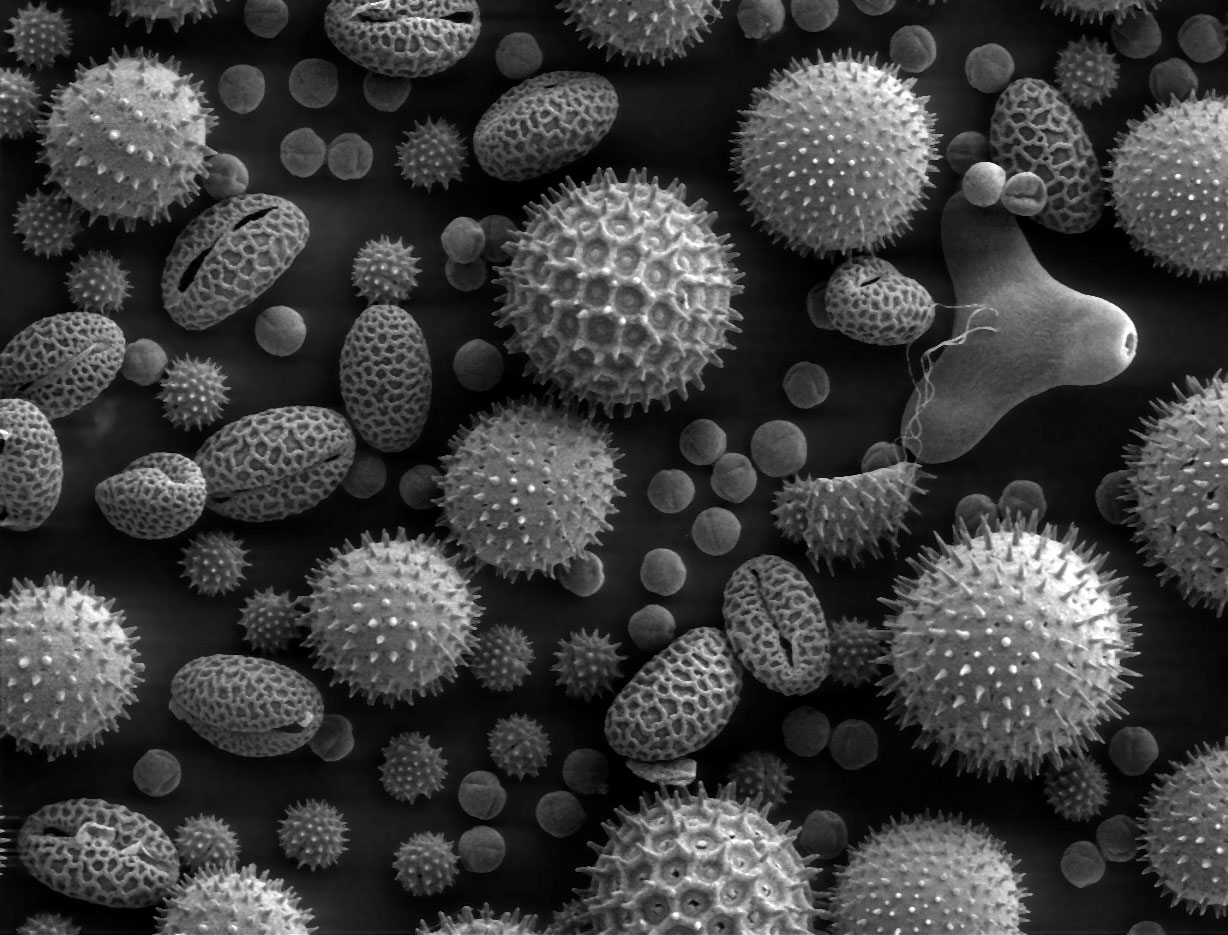
Caption = SEM of miscellaneous plant pollens. Pollens are very common allergens.
DiseasesDB =
ICD10 =
ICD9 =
ICDO =
OMIM =
MedlinePlus =
eMedicineSubj =
eMedicineTopic =
MeshID = D006969Type I hypersensitivity (or immediate hypersensitivity) is an allergic reaction provoked by reexposure to a specific type of
antigen referred to as anallergen . [eMedicine|med|1101]Exposure may be by
ingestion ,inhalation , injection, or direct contact.Pathophysiology
The difference between a normal immune response and a type I hypersensitive response is that plasma cells secrete
IgE . This class of antibodies binds to Fc receptors on the surface of tissue mast cells and blood basophils.cite web |url=http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit5/hypersensitivity/type1/type1.html |title=The Adaptive Immune System: Type I Immediate Hypersensitivity |format= |work= |accessdate=2008-09-22] Mast cells and basophils coated by IgE are "sensitized." Later exposure to the same allergen, cross-links the bound IgE on sensitized cells resulting indegranulation and the secretion of pharmacologically active mediators such as histamine,leukotriene , andprostaglandin that act on the surrounding tissues. The principal effects of these products arevasodilation and smooth-muscle contraction.The reaction may be either local or systemic. Symptoms vary from mild irritation to sudden death from anaphylactic shock.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment usually involves
epinephrine ,antihistamines , andcorticosteroid s. If the entire body gets involved, then anaphylaxis can take place; an acute, systemic reaction that can prove fatal.Examples
Some examples:
*Allergicasthma
*Allergicconjunctivitis
*Allergic rhinitis ("hay fever")
*Anaphylaxis
*Angioedema
*Urticaria (hives)
*Eosinophilia
*Penicillin
*Cephalosporin References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
