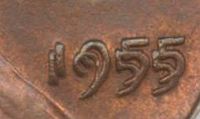- Doubled die
-
"Double die" redirects here. For the urological test, see double dye.

Numismatics Terminology
 Portal
PortalCurrency Circulating currencies
Community currenciesAncient currencies Medieval currencies
Modern currencies-
Africa, The Americas,
Europe, Asia, Oceania
Production -
Mint, Designers
Exonumia Doubled die is a term in numismatics used to refer to doubling in the design elements of a coin. Doubled dies can appear as an outline of the design or in extreme cases, having legends and dates appear twice in an overlapping fashion.
Doubled die error coins can fetch significant prices when they are noticeable to the naked eye or occur in a popular coin series. One example of this is the 1955 doubled die Lincoln Wheat cent.
Note that the proper terminology for this occurrence includes the letter 'd' at the end of the first word, hence "doubled die". The term "double die" without the first word ending in 'd' is not proper numismatic terminology.
Contents
Classes of Doubled Dies
Doubled dies are created when the hub imprints an additional, misaligned image onto a die. There are many ways this misalignment of images can occur, which have been classified into eight accepted classes.
Class 1, Rotated
A class I doubled die results when the die receives an additional hubbing that is misaligned in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction.
Class 2, Distorted
A class 2 doubled die results when the hub's design moves toward the rim between hubbings.
Class 3, Design
A class 3 doubled die results when a hub bearing a different design stamps a die bearing another design.
Class 4, Offset
A class 4 doubled die results when the die receives an additional hubbing that is misaligned in an offset direction.
Class 5, Pivoted
A class 5 doubled die results when the die receives an additional hubbing that was misaligned via rotation with a pivot point near the rim.
Class 6, Distended
A class 6 doubled die results when the die receives an additional hubbing from a hub that was distended.
Class 7, Modified
A class 7 doubled die results when the hub is modified between the die's hubbings (e.g., a design element was chiseled off).
Class 8, Tilted
A class 8 doubled die results when a die and/or hub is tilted during a hubbing.
United States Coinage
To first learn where doubled dies are formed, one must first know how dies in the United States Mint are created. Before 1997, a die was made by hubs that contained the raised design elements that were intended to appear on the coin. The blank dies were heated (to soften them) and then were pressed against the hubs to transfer the design from the hub to the striking die. In every case, one impression was not enough to transfer the design elements from the hub to the die, so multiple impressions were required to transfer enough of the design. For this reason, after the first impression was made, the die was reheated and prepared for a second impression. The mint workers would use guides to align the hub and the working die perfectly to prevent overlapping, or a doubled die. It is when mint workers failed to align dies properly during this process that doubled dies were produced. In many instances three to four impressions were required, which could but rarely led to tripled and quadrupled dies.
Modern coining methods have vastly reduced the frequency of these varieties due to the use of a single squeeze hubbing method during die creation, but doubled dies in modern United States coinage are still occurring. With the new die making process, implemented after 1996, dies only required one impression of the hub to transfer all of the design from the hub to the die. But it has been discovered that the pressure created is so great, that some dies tend to slightly rotate during this process.
Modern doubled dies in American coinage are being discovered mainly in Lincoln cents. The 2004 Peace Reverse Nickel shows doubling in the date, motto, designer initials and eyelid of Thomas Jefferson. The 2005 Bison Reverse Nickel, shows slight doubling in the word "Liberty" and in other devices of the coin.
See also
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.