- Diophantus (crater)
-
Diophantus (crater) 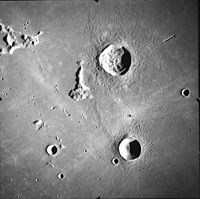
The craters Delisle (above) and Diophantus (below) from Apollo 15. NASA photo.Coordinates 27°36′N 34°18′W / 27.6°N 34.3°WCoordinates: 27°36′N 34°18′W / 27.6°N 34.3°W Diameter 19 km Depth 3.0 km Colongitude 34° at sunrise Eponym Diophantus Diophantus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southwestern part of the Mare Imbrium. It forms a pair with the larger crater Delisle to the north. Diophantus has a wide inner wall and a low central rise. To the north of Diophantus is the sinuous rille designated Rima Diophantus, named after the crater. There is a tiny craterlet near the exterior of the southwest wall.
Contents
Rima Diophantus
This cleft follows a generally east–west path across the Mare Imbrium. It is centered at selenographic coordinates 31.0° N, 32.0° W, and has a maximum diameter of 150 km. Several tiny craters near this rille have been assigned names by the IAU. These are listed in the table below.
Crater Coordinates Diameter Name source Isabel 28°12′N 34°06′W / 28.2°N 34.1°W 1 km Spanish feminine name Louise 28°30′N 34°12′W / 28.5°N 34.2°W 0.8 km French feminine name Samir 28°30′N 34°18′W / 28.5°N 34.3°W 2 km Arabic masculine name Walter1 28°00′N 33°48′W / 28.0°N 33.8°W 1 km German masculine name 1 Not to be confused with the large crater Walther in the southern hemisphere which is misidentified as 'Walter' in some publications Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater mid-point that is closest to Diophantus.
Diophantus Latitude Longitude Diameter B 29.1° N 32.5° W 6 km C 27.3° N 34.7° W 5 km D 26.9° N 36.3° W 4 km The following craters have been renamed by the IAU.
- Diophantus A — See Artsimovich.
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A., (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-81528-2.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 0-936389-27-3.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. http://host.planet4589.org/astro/lunar/. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode 1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 0-304-35469-4.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-33500-0.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 0-913135-17-8.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revision ed.). Dover. ISBN 0-486-20917-2.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-62248-4.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 1-85233-193-3.
External links
- LTO-39B3 Diophantus — L&PI topographic map of crater and vicinity.
- "Featured Image: Dark Streaks in Diophantus Crater". Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. NASA. February 23, 2011. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/multimedia/lroimages/lroc-20110223-dark.html. Retrieved 2011-03-18.
Categories:- LQ11 quadrangle
- Impact craters on the Moon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
