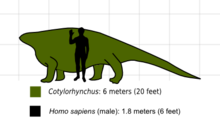
- Cotylorhynchus
-
Cotylorhynchus
Temporal range: Early to Mid-Permian
C. romeri fossil Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Synapsida Order: Pelycosauria Suborder: Caseasauria Family: Caseidae Genus: Cotylorhynchus Species - C. bransoni
- C. hancocki
- C. romeri
Cotylorhynchus was a very large mammal-like reptile (more accurately synapsid) that lived in the southern part of what is now North America during the Early Permian period and persisted until the late-Mid Permian (about 265 mya). Cotylorhynchus are the most well known of the synapsid clade Caseidae and are in the order Pelycosauria.
The Cotylorhynchus were the largest pelycosaurs, the largest terrestrial vertebrates of their time, as well as the terrestrial vertebrates up to that time. They were herbivores, and because of their enormous size they probably did not fear any of the carnivores.
Contents
Description
Cotylorhynchus was a massively built animal with a disproportionately small head and a huge barrel-shaped body. They could grow to lengths of up to 20 feet and could achieve weights of up to 2 tons. Their skeletal features included a massive scapulocoracoid, humeri with large flared ends, stout forearm bones and broad, robust hands that had large claws. Certain features of their hands indicate that they had to dig considerably to obtain their food supply and also they may have used these features to dig burrows for shelter or safety. Their digits were believed to have a considerable range of motion and large retractor processes on the ventral surfaces of the unguals allowed them to flex their claws with powerful motions. Also, the articulatory surfaces of their phalanges were oblique to the bone's long axis rather than perpendicular to it. This allowed for much more surface area for the flexor muscles.
Their skulls are distinctive in the presence of large temporal openings and very large nostril openings, which could have been utilized for better breathing or may have housed some sort of sensory or moisture conserving organ. Also they featured large pineal openings and a snout or upper jaw that overhangs the row of teeth to form a projecting rostrum. Rounded deep pits and possibly large depressions were present on the outer surface of the skull. Their teeth were very similar to those of iguanas with posterior marginal teeth that bore a longitudinal row of cusps.
Discovery
Cotylorhynchus were considered a part of the first wave of amniote diversity. There have been three species of Cotylorhynchus discovered: C. hancocki, C. romeri and C. bransoni. C. hancocki is believed to be a descendent of the slightly smaller C. romeri. Various skeletal parts of C. romeri have been found around central Oklahoma in parts of Cleveland County. Parts of C. hancocki have been found in northern Texas in Hardeman and Knox counties. C. bransoni specimens have been uncovered in Kingfisher and Blaine Counties of central-northwest Oklahoma.
See also
- List of synapsids
References
- Stovall, JW et al. The Postcranial Skeleton of the Giant Permian Pelycosaur
-
- Cotylorhynchus romeri.
Categories:- Caseasaurs
- Prehistoric synapsids of North America
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.