- Antoine Desgodetz
-
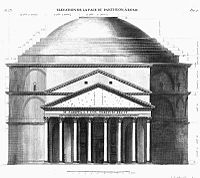
Antoine Babuty Desgodetz's (1653-1728) publication Les edifices antiques de Rome dessinés et mesurés très exactement (Paris 1682) provided detailed engravings of the monuments and antiquities of Rome to serve French artists and architects. Desgodetz had been sent to Rome in an official capacity, part of French architectural and artistic policy,[1] and the engravings for his publication were supervised by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, according to Desgodetz' introduction (Haskell and Penny 1981: 37) The young architect with a copy of Les edifices antiques de Rome could determine the precise proportions of many Roman structures, such as the portico of the Pantheon, or the Temple of Vesta, Tivoli, that were considered the best models, a practice that had the effect of standardizing the details of academic architecture in France. His Edifices antiques was reissued in Paris, 1729[2] and again in 1779, when it proved as helpful to Neoclassical architects as it had been to classicizing Late Baroque ones. The young Robert Adam toyed with the idea of producing a revised version of Desgodetz before he hit on the idea of striking into fresh territory with measured engravings of the ruins of Diocletian's palace at Spalatro (Split, Croatia).
Claude Perrault's view that the architectural norms that had formerly been presented as divinely inspired, authoritative and derived from nature, were in fact arbitrary, with a social origin under constraints of individual situations, "employed empirical observation instead of the opinion of authorities. Essential to his proof were the measurements taken by Desgodetz in Rome, clearly indicating the disparity in the proportions of the great monuments themselves."[3]
Les edifices antiques... was reproduced in 1972 (Portland, Oregon : Collegium Graphicum).
Notes
- ^ "The timing of the commissioning of Perrault to translate Vitruvius, the expedition of Desgodetz to Rome, the public humiliation of Bernini, and the subsequent transfer of the Louvre design to Perrault, the publication of the Ordonnance, the attacks of Colbert on the guilds are too consistent to be considered accidental," note Alexander Tzonis and Liane Lefaivre, reviewing Wolfgang Herrmann, The Theory of Claude Perrault (Studies in Architecture, XII), 1974, in Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians 3 October 1976. (on-line text).
- ^ Les édifices antiques de Rome dessinés et mesurés très exactement sur les lieux par feu M. Desgodez, architecte du roi. Nouvelle Edition (Paris: Claude-Antoine Jombert) 1729.
- ^ Alexander Tzonis and Liane Lefaivre 1976. (on-line text).
References
- Haskell, Francis, and Nicholas Penny, 1981. Taste and the Antique: The Lure of Classical Sculpture 1500-1900 (Yale University Press).
- Herrmann, Wolfgang, 1958. "Antoine Desgodetz and the Academie Royale d'Architecture," The Art Bulletin 40 pp 23–53.
External links
Categories:- 1653 births
- 1728 deaths
- French architects
- Members of the Académie d'architecture
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.