- Darboux integral
-
In real analysis, a branch of mathematics, the Darboux integral or Darboux sum is one possible definition of the integral of a function. Darboux integrals are equivalent to Riemann integrals, meaning that a function is Darboux-integrable if and only if it is Riemann-integrable, and the values of the two integrals, if they exist, are equal. Darboux integrals have the advantage of being simpler to define than Riemann integrals. Darboux integrals are named after their discoverer, Gaston Darboux.
Definition
A partition of an interval [a,b] is a finite sequence of values xi such that
Each interval [xi−1,xi] is called a subinterval of the partition. Let ƒ:[a,b]→R be a bounded function, and let
be a partition of [a,b]. Let
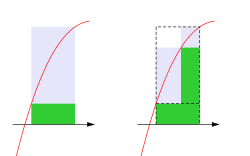
The upper Darboux sum of ƒ with respect to P is
The lower Darboux sum of ƒ with respect to P is
The upper Darboux integral of ƒ is
The lower Darboux integral of ƒ is
If Uƒ = Lƒ, then we say that ƒ is Darboux-integrable and set
the common value of the upper and lower Darboux integrals.
Facts about the Darboux integral
A refinement of the partition
is a partition
such that for every i with
there is an integer r(i) such that
In other words, to make a refinement, cut the subintervals into smaller pieces and do not remove any existing cuts. If
is a refinement of
then
and
If P1, P2 are two partitions of the same interval (one need not be a refinement of the other), then
 .
.
It follows that
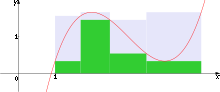
Riemann sums always lie between the corresponding lower and upper Darboux sums. Formally, if
and
together make a tagged partition
(as in the definition of the Riemann integral), and if the Riemann sum of ƒ corresponding to P and T is R, then
From the previous fact, Riemann integrals are at least as strong as Darboux integrals: If the Darboux integral exists, then the upper and lower Darboux sums corresponding to a sufficiently fine partition will be close to the value of the integral, so any Riemann sum over the same partition will also be close to the value of the integral. It is not hard to see that there is a tagged partition that comes arbitrarily close to the value of the upper Darboux integral or lower Darboux integral, and consequently, if the Riemann integral exists, then the Darboux integral must exist as well.
See also
Integrals Methods Riemann integral · Lebesgue integral · Burkill integral · Bochner integral · Daniell integral · Darboux integral · Henstock–Kurzweil integral · Haar integral · Hellinger integral · Kolmogorov integral · Lebesgue–Stieltjes integral · Pettis integral · Pfeffer integral · Riemann–Stieltjes integral · Regulated integralImproper Integrals Stochastic integrals Categories:- Definitions of mathematical integration
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



![\begin{align}
M_i = \sup_{x\in[x_{i-1},x_{i}]} f(x) , \\
m_i = \inf_{x\in[x_{i-1},x_{i}]} f(x) .
\end{align}](6/85684dcca6470d3d3ce51b90a1792f67.png)


![U_f = \inf\{U_{f,P} \colon P \text{ is a partition of } [a,b]\} . \,\!](7/af7030989dec193d783acbbfb17241df.png)
![L_f = \sup\{L_{f,P} \colon P \text{ is a partition of } [a,b]\} . \,\!](9/e997dab8d1d70293d4de410601192360.png)