- Land grid array
-
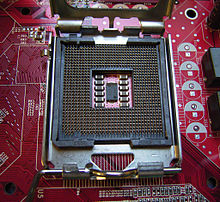
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board.
Contents
Use in microprocessors
LGA is used as a physical interface for microprocessors of the Intel Pentium 4 (Prescott), Intel Xeon, Intel Core 2, Intel Core (Bloomfield and Lynnfield) and AMD Opteron families. Unlike the pin grid array (PGA) interface found on most AMD and older Intel processors, there are no pins on the chip; in place of the pins are pads of bare gold-plated copper that touch protruding pins on the microprocessor's placeholder on the motherboard.
While LGA sockets have been in use as early as 1996 by the MIPS R10000 and HP PA-8000 processors, the interface did not gain widespread use until Intel introduced their LGA platform, starting with the 5x0 and 6x0 sequence Pentium 4 (Prescott) in 2004. All Pentium D and Core 2 desktop processors currently use an LGA socket. As of Q1 2006, Intel switched the Xeon server platform to LGA, starting with the 5000-series models. AMD introduced their server LGA platform starting with the 2000-series Opteron in Q2 2006. AMD offers the Athlon 64 FX-74 on socket 1207FX through ASUS's L1N64-SLI WS motherboards. It is the only desktop LGA solution currently in the market for AMD.
The most common Intel desktop LGA socket is dubbed LGA 775 (Socket T), while the server variant is dubbed LGA 771 (Socket J). However, the new Intel Core i7 and i7 Extreme families uses the LGA 1366 (Socket B) socket. As of September 2009, the new Core i5 700 series and the Core i7 800 series — codenamed Lynnfield — use LGA 1156 (Socket H). The LGA setup provides higher pin densities, allowing more power contacts and thus a more stable power supply to the chip. LGA packaging also has a tertiary benefit of placing pins onto the motherboard; if a pin breaks, the motherboard is often cheaper to replace than the CPU chip (as compared to a PGA chip/socket setup).
The AMD server LGA socket is designated Socket F (LGA 1207). Like Intel, AMD decided to use LGA sockets for their higher pin densities, as a 1207-pin PGA would simply be too large for most motherboards.
List of microprocessor LGA sockets
AMD
- Socket F (LGA 1207)
- Socket C32 (LGA 1207) (replaces Socket F)
- Socket G34 (LGA 1974)
Intel
- LGA 775 (Socket T)
- LGA 771 (Socket J)
- LGA 1366 (Socket B)
- LGA 1356 (Socket B2)
- LGA 1156 (Socket H)
- LGA 1155 (Socket H2)
- LGA 2011 (Socket R)
See also
- Chip carrier
- Dual in-line package (DIP)
- Pin grid array (PGA)
- Ball grid array (BGA)
References
External links
Categories:- Chip carriers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.