- Acanthothoraci
Taxobox
name = Acanthothoraci
fossil_range =Silurian ? - EarlyDevonian
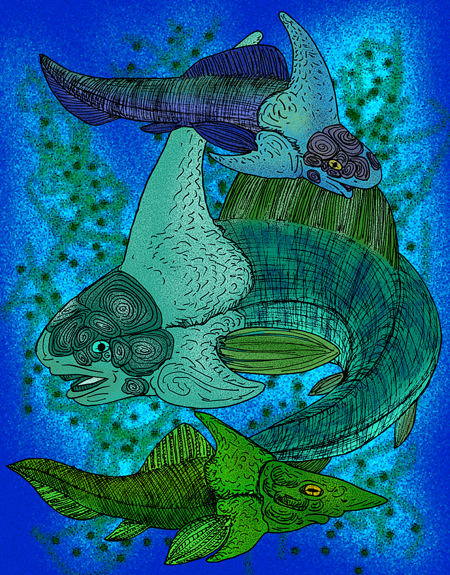
image_caption = "Weejasperaspis gavini", "Murrindalaspis wallacei" & "Brindabellaspis stensioi "
regnum =Animal ia
phylum = Chordata
subphylum = Vertebrata
infraphylum =Gnathostomata
classis =Placodermi
classis_authority = McCoy, 1848
ordo = Acanthothoraci
ordo_authority = Stensiö, 1944
subdivision_ranks = Families
subdivision =Weejasperaspididae †Palaeacanthaspidae †Description
The Acanthothoraci ("Spine Chests") were a group of
chimaera -likeplacoderm s who were closely related to therhenanid placoderms. Superficially, the acanthoracids resembled scaly chimaeras, lightly armoredarthrodire s, or (relatively) heavily armoredptyctodont s. They were distinguished from chimaeras by the presence of large scales and plates, a pair of large spines that emanate from their chests (thus, the order's name), tooth-like beak plates, and the typical bone-enhanced placoderm eyeball. They were distinguished from other placoderms due to differences in the anatomy of their skulls, and due to patterns on the skull plates and thoracic plates that are unique to this order.The acanthothoracids were once thought to be closely related to the rhenanids because of similar arrangements of the plate armor, and that the patterns on the former's plates resemble the patterns of the latter's tubercle mosaics.
Fossil Record
Fossils of the Acanthothoracids are found in various deposits from the Lower Devonian throughout the world. The Palaeacanthaspids are found primarily in Europe and Canada, while the Weejasperaspids have only been found in the Taemas
Wee Jasper reef, in SoutheasternAustralia .While the Acanthothoracids' fossils date back to the Lower Devonian, they are believed to have arose during the
Silurian , and that Silurian Acanthothoracids either lived in environments wholly unconductive to fossilization, or that their fossils have yet to be found.Ecology
From what can be inferred from the mouthplates of fossil specimens, the acanthothoracids were ecologically similar to modern-day
chimaera s, being a clique of shellfish hunters. Competition with their relatives, the ptyctodont placoderms, may have been one of the main reasons for the acanthothoracids' extinction prior to the Mid Devonian extinction event.Relation to Other Placoderms
Most placoderm experts have reached a consensus that Acanthothoracida is the sister group of the rest of
Placodermi , save for, perhaps, "Stensioella " andPseudopetalichthyida . This is the result of a careful reexamination of the various members of the Acanthothoracid familyPalaeacanthaspidae , in that particular species within that family share various anatomical similarities with other placoderm orders, particularly the anatomies of theirbraincase , dermal plate arrangement and bonehistology . As a result, that family is now considered to beparaphyletic due to the similarities its members have to primitive members of other placoderm orders.The family
Weejasperaspididae , on the other hand, is considered to bemonophyletic . Because of the Weejasperaspids' generalized anatomy, and strong similarities with the Palaeacanthaspids, but no overt similarities with any other order, saveBrindabellaspida , they are regarded as either basal placoderms or very close to the basal placoderm.External links
Mikko's Phylogeny Archive [http://www.fmnh.helsinki.fi/users/haaramo/Metazoa/Deuterostoma/Chordata/Placodermi/Acanthothoraci.htm]
References
* Janvier, Philippe. "Early Vertebrates" Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0-19-854047-7
* Long, John A. "The Rise of Fishes: 500 Million Years of Evolution" Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996. ISBN 0-8018-5438-5
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
