- Graz
-
For other uses, see Graz (disambiguation).
Graz Country Austria State Styria District Statutory city Mayor Siegfried Nagl (ÖVP) Area 127.56 km2 (49 sq mi) Elevation 353 m (1158 ft) Population 261,540 (1 January 2011)[1] - Density 2,050 /km² (5,310 /sq mi) Time zone CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) Postal codes A-801x, A-802x, A-803x, A-804x, A-805x Area codes +43 316 Website www.graz.at Coordinates: 47°04′13″N 15°26′20″E / 47.07028°N 15.43889°E
City of Graz - Historic Centre and Schloss Eggenberg * UNESCO World Heritage SiteCountry Austria Type Cultural Criteria ii, iv Reference 931bis Region ** Europe and North America Inscription history Inscription 1999 (23rd Session) Extensions 2010 * Name as inscribed on World Heritage List
** Region as classified by UNESCOGraz (German pronunciation: [ˈɡʁaːts]; Slovene: Gradec, Hungarian: Grác) is the second-largest city in Austria after Vienna and the capital of the federal state of Styria. On 1 April 2010 it had a population of 291,890 (of which 258,605 had principal residence status).[2]
Graz has a long tradition as a student city: its six universities have more than 44,000 students. Its "Old Town" is one of the best-preserved city centres in Central Europe.
Politically and culturally, Graz was for centuries more important for Slovenes than Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia, and still remains influential.[3]
In 1999, Graz was added to the UNESCO list of World Cultural Heritage Sites, and the site was extended in 2010 by Schloss Eggenberg. Graz was sole Cultural Capital of Europe for 2003 and got the title of a City of Culinary Delights in 2008.
Contents
Geography
Graz is situated on the Mur River in the southeast of Austria. It is about 200 km (120 mi) southwest of Vienna. The nearest larger urban center is Maribor in Slovenia which is about 50 km (31 mi) away. Graz is the capital and largest city in Styria, a green and heavily forested area.
Climate
Due to its position southeast of the Alps, Graz is shielded from the prevailing westerly winds that bring weather fronts in from the North Atlantic to northwestern and central Europe. The weather in Graz is thus influenced by the Mediterranean, and it has more hours of sunshine per year than Vienna or Salzburg and also less wind or rain. Graz lies in a basin that is only open to the south, causing the climate to be warmer than would be expected at that latitude. Plants are found in Graz that normally grow much further south. However, this milder, less windy climate is detrimental to the air quality in Graz as it makes the city prone to smog in winter. The exhaust fumes of the around 120,000 cars driven into Graz every weekday by people living in the surrounding areas, together with the car journeys made by the inhabitants of Graz itself, are the most significant source of air pollution.
- average temperatures: Graz Airport 8.7 °C (48 °F) / Karl-Franzens University 9.4 °C (49 °F)
- average rainfall: 818 mm with on average 92 days of rain (Karl Franzens University)
- average hours of sunshine: 1,890 (Karl Franzens University)
Neighbouring municipalities
The following towns and villages border Graz:
- to the North: Gratkorn, Stattegg, Weinitzen
- to the East: Kainbach bei Graz, Hart bei Graz, Raaba
- to the South: Gössendorf, Feldkirchen bei Graz, Seiersberg
- to the West: Attendorf, Thal, Judendorf-Straßengel
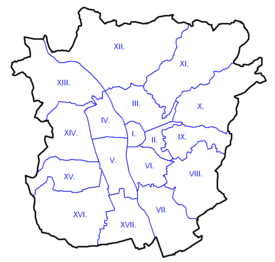
Districts
Graz is divided into 17 districts:
I. Innere Stadt (3,302)
II. St. Leonhard (12,377)
III. Geidorf (19,119)
IV. Lend (22,369)
V. Gries (22,658)
VI. Jakomini (25,808)
VII. Liebenau (11,556)
VIII. St. Peter (12,809)
IX. Waltendorf (10,782)X. Ries (5,789)
XI. Mariatrost (7,403)
XII. Andritz (16,316)
XIII. Gösting (9,227)
XIV. Eggenberg (16,467)
XV. Wetzelsdorf (12,225)
XVI. Straßgang (12,212)
XVII. Puntigam (6,248)Population development
Historical populations Year Pop. ±% 1900 168,808 — 1951 226,476 +34.2% 1961 237,080 +4.7% 1971 249,089 +5.1% 1981 243,166 −2.4% 1991 237,810 −2.2% 2001 226,244 −4.9% 2006 250,099 +10.5% 2008 252,852 +1.1% The more recent population figures do not give the whole picture as only people with principal residence status are counted and people with secondary residence status are not. Most of the people with secondary residence status in Graz are students. At the end of 2006 there were 37,624 people with secondary residence status in Graz.[4][5]
The population (with principal residence status) in the agglomeration was about 320,000 at the end of 2006.
History
The oldest settlement on the ground of the modern city of Graz dates back to the Copper Age. However, there is no historical continuity of a settlement before the Middle Ages.
The name of the city, Graz (see the Slavic settlement Grad), and some archaeological finds point to the erection of a small castle by Alpine Slavic people[citation needed], which in time became a heavily defended fortification. In literary Slovene, gradec literally means "small castle", which is etymologically a hypocoristic derivative of Proto-West-South Slavic *gradьcъ, itself by means of liquid metathesis descending from Common Slavic *gardьcъ, by Slavic third palatalisation from Proto-Slavic *gardiku (cf. Ancient Greek toponym Γαρδίκι) originally denoting "small town, settlement". The name thus follows the common South Slavic pattern for naming settlements as grad. The German name 'Graz' was first used in 1128,[6] and during this time dukes under Babenberg rule made the town into an important commercial center. Later Graz came under the rule of the Habsburgs, and in 1281 gained special privileges from King Rudolph I.
In the 14th century Graz became the city of residence of the Inner Austrian line of the Habsburgs. The royalty lived in the Schloßberg castle and from there ruled Styria, Carinthia, and parts of today's Italy and Slovenia (Carniola, Gorizia and Gradisca). In the 16th century, the city's design and planning were primarily controlled by Italian Renaissance architects and artists. One of the most famous buildings built in this style is the Landhaus, designed by Domenico dell'Allio, and used by the local rulers as a governmental headquarters.
The astronomer Johannes Kepler lived in Graz for a short period. There, he worked as a math teacher, but found time to study astronomy. He left Graz to go to Prague when Lutherans were banned from the city.
Karl-Franzens Universität, also called the University of Graz, is the city's oldest university, founded in 1585 by Archduke Charles II. For most of its existence it was controlled by the Catholic church, and was closed in 1782 by Joseph II in an attempt to gain state control over educational institutions. Joseph II transformed it into a lyceum where civil servants and medical personnel were trained. In 1827 it was re-instituted as a university by Emperor Franz I, thus gaining the name 'Karl-Franzens Universität,' meaning 'Charles-Francis University.' Over 30,000 students currently study at this university.
Nikola Tesla studied electrical engineering at the Polytechnic in Graz in 1875. Nobel Laureate Otto Loewi taught at the University of Graz from 1909 until 1938. Johannes Kepler was a professor of mathematics at the University of Graz. Erwin Schrödinger was briefly chancellor of the University of Graz in 1936.
Adolf Hitler was given a warm welcome when he visited in 1938, the year Austria was annexed by Nazi Germany. The thriving Jewish community was destroyed by the Nazis, and their grand synagogue was burnt. A small group of Graz Jews returned despite everything after the war. In 2000, on the anniversary of the Reichskristallnacht, Graz city council presented the Jewish community with a new synagogue as a gesture of reconciliation. Hitler promised the people of Graz 1,000 years of prosperity and an end to mass unemployment: only seven years later the Graz resistance surrendered the city to Soviet troops, sparing Graz any further destruction. By then about 16% of buildings had been destroyed by Allied bombing - luckily the Old Town was not seriously hit.
Graz lies in Styria, or Steiermark in German. Mark is an old German word indicating a large area of land used as a defensive border, in which the peasantry are taught how to organize and fight in the case of an invasion. With a strategic location at the head of the open and fertile Mur valley, Graz was often assaulted (unsuccessfully), e.g. by the Hungarians under Matthias Corvinus in 1481, and by the Ottoman Turks in 1529 and 1532. Apart from the Riegersburg, the Schloßberg was the only fortification in the region that never fell to the Ottoman Turks. Graz is home to the region's provincial armory, which is the world's largest historical collection of Baroque weaponry. It has been preserved since 1551, and displays over 30,000 items.
From the earlier part of the 15th century Graz was the residence of the younger branch of the Habsburgs, which succeeded to the imperial throne in 1619 in the person of Emperor Ferdinand II, who moved the capital to Vienna. New fortifications were built on the Schlossberg at the end of the 16th century. Napoleon's army occupied Graz in 1797. In 1809 the city withstood another assault by the French army. During this attack, the commanding officer in the fortress was ordered to defend it with about 900 men against Napoleon's army of about 3,000. He successfully defended the Schloßberg against eight attacks, but they were forced to give up after the Grande Armée occupied Vienna and the Emperor ordered to surrender. Following the defeat of Austria by Napoleonic forces at the Battle of Wagram in 1809, the fortifications were demolished using explosives, as stipulated in the Peace of Schönbrunn of the same year. The belltower and the civic clock tower, often used as the symbol of Graz, were spared after the people of Graz paid a ransom for their preservation.[6]
Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria had 20,000 Protestant books burned in the square of what is now a mental hospital, and succeeded in returning Styria to the authority of the Holy See. Archduke Franz Ferdinand was born in Graz, in what is now the Stadtmuseum (city museum).
Slovenes and Graz
The name of Graz is undoubtedly of Slovene origin and the city was Slovene for a short period. Politically, culturally, scientifically and religiously, Graz was an important centre for all Slovenes, especially from the establishment of the University of Graz in 1586 until the establishment of University of Ljubljana in 1919. In 1574, the first Slovene Catholic book was published in Graz, and in 1592, Hyeronimus Megiser published in Graz the first multilingual dictionary that included Slovene.[3]
Styrian Slovenes did not feel Graz a German city, but their own, a place to study while living at their relatives' homes and to fulfill one's career ambitions. Student associations in Graz were a forge of Slovenehood and Slovene students in Graz were more nationally aware than some others. This led to fierce anti-Slovene efforts of German nationalists in Graz before and during World War II.[3]
Nowadays, the city is cosmopolitan and quite fond of Slovenes. Many Slovenian Styrians study there. Slovenes are among professors at the Institute for Jazz in Graz. Numerous Slovenes have found employment there, while being formally unemployed in Slovenia. For Slovene culture, Graz remains permanently important due to its university and the Universalmuseum Joanneum archives containing numerous documents from the Slovenian Styria.[3]
Main sights
In the last few years some strikingly modern new public buildings have been erected in the city. The most famous include the Kunsthaus (house of modern art) designed by Peter Cook and Colin Fournier, a museum constructed right next to the river Mur, and the "Murinsel" (island in the Mur), an island made of steel, situated in the river. It was designed by the American architect Vito Acconci and contains a café, an open-air theatre and a playground.
Old town
 Grazer Schloßberg (Castle mountain) with clock tower
Grazer Schloßberg (Castle mountain) with clock tower
The old town was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1999[6] due to the harmonious co-existence of typical buildings from different epochs and in different architectural styles. Situated in a cultural borderland between Central Europe, Italy and the Balkan States, Graz absorbed various influences from the neighbouring regions and thus received its exceptional townscape. Today the old town consists of over 1000 buildings, their age ranging from Gothic to Contemporary.
The most important sights in the old town are:
- Rathaus (Town Hall).
- Schloßberg, hill dominating the old town (475 m (1,558.40 ft) high), site of demolished fortress, with views over Graz.
- Uhrturm clocktower, symbol of Graz, on the top of Schloßberg.
- Neue Galerie . Museum of art.
- Schloßbergbahn, a funicular railway up the Schloßberg.
- The Landhaus, the building where the federal state parliament of Styria resides, a palace in Lombardic style. It is one of the most important examples of Renaissance architecture in Austria and was built by the Italian architect Domenico dell'Allio between 1557 and 1565.
- The Landeszeughaus, armoury, the largest of its kind in the world.
- The Opernhaus, the principal venue for opera, ballet, and operetta performances. It is the 2nd largest opera house in Austria.
- The Schauspielhaus, the principal theatre for productions of plays.
- Dom (cathedral), a rare monument of Gothic architecture. Once, there were many frescos on the outer walls; today, only a few remain, like the Landplagenbild ("picture of plagues") painted in 1485, presumably by Thomas von Villach. The three plagues it depicts are locusts, pestilence and the invasion of the Turks, all of them striking the town in 1480. It features the oldest painted view of Graz.
- Mausoleum of Emperor Ferdinand II next to the cathedral, the most important building of Mannerism in Graz. It includes both the grave where Ferdinand II and his wife are buried, and a church dedicated to St Catherine of Alexandria.
- Burg (castle complex), with Gothic double staircase, built between 1438 and 1453 by Emperor Frederick III because the old castle on the Schloßberg was too small and uncomfortable. The Burg remained the residence of the Inner Austrian Court until 1619. Today, it serves as residence of the government of Styria.
- Gemaltes Haus ("painted house"), in Herrengasse 3. It is completely covered with frescos (painted in 1742 by Johann Mayer).
- Kunsthaus (museum of modern art).
- Murinsel, an artificial island in the Mur.
- Buildings, courtyards (e. g. Early Renaissance courtyard of the Former House of Teutonic Knights in Sporgasse 22) and roofscape of the old town.
Outside the Old Town
- Schloss Eggenberg a Baroque palace on the western edge of Graz with State rooms and museum. In 2010 it was added to the existing World Heritage site of the historic centre of Graz.
- Basilika Mariatrost a late Baroque church, on the eastern edge of Graz.
- The Herz Jesu Kirche is the largest church in Graz with the third highest spire in Austria, built in Gothic Revival style.
- Calvary Hill in the Gösting area of Graz with a 17th century calvary and church.
- The LKH-Universitätsklinikum, is the biggest hospital of Graz and one of the biggest hospitals in Austria. It is the largest Jugendstil building complex in Austria and was built between 1904 and 1912. It is run by the state and one of the most renowned hospitals in Austria and Central Europe.
- Best viewpoints for vistas of the city are Ruine Gösting, hilltop castle ruins on northwestern edge of city, and Plabutsch/Fürstenstand, behind Schloss Eggenberg with a hilltop restaurant and viewing tower.
Greater Graz area
- Österreichisches Freilichtmuseum Stübing, an open-air museum containing old farmhouses/farm buildings from all over Austria reassembled in historic setting.
- Lurgrotte, the most extensive cave system in Austria.
- Lipizzanergestüt Piber, Lipizzaner stud at Piber where the famous horses are bred.
- The Steirische Weinstraße is a wine-growing region south of Graz, also known as the "Styrian Tuscany".
- Thermenregion, spa region east of Graz.
- Riegersburg, a mighty fortress that was never taken. It was a bastion against Turkish invasions
Culture
During 2003 Graz held the title of "European Capital of Culture" and is (as of 2011) one of the UNESCO "Cities of Design."
Museums
The most important museums in Graz are:
- Schloss Eggenberg (Graz) with Alte Galerie (paintings and sculptures from the Romanesque to the end of the Baroque period), Coin Collection, Lapidarium (Roman stonework collection),Archeological Museum (featuring the Cult Wagon of Strettweg) a special exhibitions area and the 90,000 m2 romantic landscape gardens.
- Museum im Palais museum of Styrian cultural history from the Middle Ages to the present
- Neue Galerie visual arts from the 19th and 20th centuries.
- Natural History Museum exhibition of botany, mineralogy and zoology.
- Stadtmuseum Graz city museum.
- Grazer Kunsthaus exhibition hall of contemporary art.
- Forum Stadtpark museum of contemporary art.
- Camera Austria museum of contemporary photography.
- Landeszeughaus medieval armory comprising 32,000 pieces of armour and weaponry, largest of its kind in the world.
- Volkskundemuseum museum of folk culture and lore.
- Diözesanmuseum museum of the Roman Catholic Church.
- Künstlerhaus exhibition hall of contemporary visual arts.
- Literaturhaus museum of contemporary German literature.
- Museum der Wahrnehmung museum of the senses, samadhi bath.
- Kindermuseum Frida&Fred museum for children.
- Tramwaymuseum 40 historic trams, the oldest dating from 1873.
- Kriminalmuseum museum of criminology.
- Luftfahrtmuseum (Graz airport) aviation museum.
- Hanns Schell Collection key and lock museum, largest of its kind in the world.
- Austrian Sculpture Park seven hectares of contemporary sculpture
- Botanical Garden of Graz three architecturally interesting glass houses plus gardens
Architecture
- Tallest buildings
There are currently 228 buildings in Graz that are classified as high-rise: the floor of at least one room is 22 metres above ground level. Such buildings have to adhere to much more stringent fire safety regulations because the ladders of the majority of fire appliances used by Graz Fire Brigade cannot reach higher than 22 metres.
Name or Address Completion Usage Height (m) floors 1. Herz-Jesu-Kirche 1887 church 109 2. Elisabeth Hochhaus 1964 residential 75 25 3. Kärntner Straße 212, Liebenauer Hauptstraße 309 1968 and 1955 residential 69 21 4. Franziskanerkirche 1240 church 69 5. Telekom Austria Tower 1960s office 65 15 6. Basilica Mariatrost 1724 church 61 7. Hafnerriegel 1960 residential 61 19 8. St. Peter Pfarrweg, Kindermanngasse, Hanuschgasse 1970s residential 55 17 9. Vinzenz Muchitschstraße, Ungergasse, Kärntner Straße 216, Eggenberger Gürtel 1970s residential 52 16 There are some new high-rise buildings in the pipeline; the only ones that currently (June 2009) seem certain to be built are a 15-storey office block opposite the "Stadthalle" on the southern edge of the city centre and a 21-storey officeblock next to the motorway leading from the Graz Ost Interchange (road) into town.
Transportation
An extensive public transportation network makes Graz an easy city to navigate without a car. The city has a comprehensive bus network, complementing the Graz tram network consisting of six lines, two of which run from the main train station (Hauptbahnhof) to the old town before branching out. Furthermore, there are seven night-time bus routes, although these run only at weekends and on evenings preceding public holidays. The tram is also called "Bim".
From the main train station (Graz Hauptbahnhof), regional trains link to most of Styria. Direct trains also run to most major cities nearby including Vienna, Salzburg, Innsbruck, Maribor and Ljubljana in Slovenia, Zagreb in Croatia, Prague in the Czech Republic, Budapest in Hungary and Zürich in Switzerland. Trains for Vienna leave every hour.
Graz Airport is about 10 kilometres south of the city centre and has a railway station within walking distance (east of the airport). The main hubs Graz Airport is connected with Frankfurt and Munich in Germany and Vienna. Main cities connected to Graz Airport are London (Ryanair) and Berlin (Airberlin).
Health
In Graz there are seven hospitals, several private hospitals and sanatoriums, as well as 44 pharmacies.
The LKH-Universitätsklinikum Graz is one of the hospitals that can provide maximum care, with 1556 beds and 7190 employees. It covers the east of the city. In the west of the city there is the LKH Graz-West in Eggenberg with 280 beds and about 500 employees, the Landesnervenklinik Sigmund Freud (LSF) in Straßgang with 880 beds and 1,100 employees, as well as the Unfallkrankenhaus der AUVA in Eggenberg with 180 beds and a total of 444 employees.
Furthermore there is the gereatric hospital Albert-Schweitzer-Klinik in the west of the city with 304 beds, the Krankenhaus der Barmherzigen Brüder I in Lend with 225 beds, the Krankenhaus der Barmherzigen Brüder II in Eggenberg with 260 beds and the Krankenhaus der Elisabethinen in Gries with 182 beds.
There are several private clinics as well: the Privatklinik Kastanienhof, the Privatklinik Leech, the Privatklinik der Kreuzschwestern, the Sanatorium St. Leonhard, the Sanatorium Hansa and the Privatklinik Graz-Ragnitz.
EMS in Graz is provided solely by the Austrian Red Cross. Perpetually two emergency doctor's cars (NEF - Notarzteinsatzfahrzeug), two NAWs (Notarztwagen - ambulances staffed with a doctor in addition to regular personnel) and about 30 RTWs (Rettungswagen - regular ambulances) are on standby. Furthermore, several non-emergency ambulances (KTW - Krankentransportwagen) and a Mobile Intensive Care Unit (MICU) are operated by the Red Cross in order to organise transportation of non-emergency patients to and between hospitals. In addition to the Red Cross the Arbeiter-Samariter-Bund Österreichs (Labor-Samaritan-Alliance), the Malteser Hospitaldienst Austria (the Austrian organisation of the Order of Malta Ambulance Corps) and the Grünes Kreuz (Green Cross) operate various non-emergency ambulances (KTW) for non-emergency patient transportation. In addition to the land-ambulances there's also the C12 air ambulance helicopter stationed at Graz airport, which is also staffed with an emergency doctor in addition to regular personnel.
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in AustriaTwin towns and sister cities
Other forms of cooperation and city friendship similar to the twin city programmes:
 Niš, Serbia
Niš, Serbia Banja Luka Bosnia and Herzegovina,
Banja Luka Bosnia and Herzegovina,
Notable people
- Arnold Schwarzenegger, former bodybuilding champion, actor and former governor of California. Born and raised in the farming village Thal, 2 km from Graz. In 2005, the Graz football stadium named after Schwarzenegger was renamed Stadion Graz-Liebenau after controversy over the use of the death penalty in California; now it is called the UPC-Arena.
- Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach, architect of the Baroque period.
- Johann Puch, Slovenian inventor, mechanic and vehicle producer.
- Ludwig Boltzmann, Austrian physicist, Professor of Mathematical Physics at the University of Graz (1869), chair of Experimental Physics at the University of Graz (1876–1890).
- Diane Bernie DeArmond (1961-)Artist, Writer and Philosopher. Born in Newport Beach California resides in Graz.
- Robert Stolz, Austrian composer and conductor.
- Friedrich St. Florian, Austrian-American architect.
- Olga Neuwirth, one of the most important contemporary Austrian composers.
- Nicolaus Harnoncourt, born in Berlin and raised in Graz, a conductor known for his performances of classical works on period instruments.
- Jochen Rindt, the first Austrian Formula One champion raised in Graz by his grandmother.
- Otto Wanz, former professional wrestler who held the AWA World Heavyweight Championship.
- Wolfgang Bauer, Austrian writer.
- Werner Schwab, playwright and visual artist.
- Bernd Brückler, professional ice hockey player
- Thomas Tebbich, decathlete and pole vaulter
- Thomas Vanek, professional hockey player, born in Baden bei Wien, raised in Graz.
- Helmut Marko, former racing driver
- Emanuel Pogatetz, Middlesbrough F.C. defender and captain.
- Markus Schopp, former football midfielder
- August Musger, inventor of the slow motion technique in cinema.
- Karl Böhm, an Austrian conductor.
- Lili Novy, Slovenian poet.
- Otto Loewi Nobel prize-winning physiologist.
- Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke of Austria-Este and heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
- Soo-Young Lee, a clarinetist in the Youtube Symphony Orchestra
- Nikola Tesla studied electrical engineering in Graz.
- Gert Schnider, Abalone-champion
- Baron Roman Ungern von Sternberg, enemy of the Soviet State and dictator of Mongolia in 1921.
- Anton Rintelen, Cabinet Minister and Nazi conspirator.
- Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg, Austrian statesman and early "prime minister" during the Thirty Years' War
- Mick Blue, an actor.
- Manfred Hoeberl, Powerlifter and Strongman.
References
- ^ Statistik Austria - Bevölkerung zu Jahres- und Quartalsanfang, 2011-01-01.
- ^ "Anwesende Bevölkerung nach Wohnsitz und Gechlecht pro Bezirk - Stand 1. April 2010" (in German). Graz: Stadt Graz - Präsidialamt. http://www1.graz.at/Statistik/Bev%C3%B6lkerung/aktuelles_quartal.pdf. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ^ a b c d Granda, Stane (2006). "Gradec in Slovenci" (in Slovene, with a short abstract in English). Traditiones (University of Graz) 35 (2): pp. 99-103. http://isn.zrc-sazu.si/files/file/Traditiones/Traditiones_35_2_Krek_separati/TR352%20099-103%20Granda.pdf. Retrieved 17 December 2010 (via Google Documents; [1]).
- ^ Tautscher, Sonja (7 January 2010). "Graz in Numbers". Graz: Stadt Graz - Magistratsdirektion, Abteilung für Öffentlichkeitsarbeit. http://www.graz.at/cms/ziel/606066/EN/. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ^ "Ein Blick auf die Gemeinde Graz <60101>" (in German). Statistik Austria. http://www.statistik.at/blickgem/blick1/g60101.pdf. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ^ a b c Strobl, Alexander (8 July 2008). "A Short History of the City". Graz: Stadt Graz - Magistratsdirektion, Abteilung für Öffentlichkeitsarbeit.. http://www.graz.at/cms/ziel/606777/EN/. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Twin Towns - Graz Online - English Version". www.graz.at. http://www.graz.at/cms/beitrag/10045157/606819/. Retrieved 2010-01-05.
- ^ Town Twinnings and international relations (from the official city website. Accessed 2008-08-11.)
- ^ "Groningen - Partner Cities". © 2008 Gemeente Groningen, Kreupelstraat 1,9712 HW Groningen. http://www.groningen.nl/functies/pagfunctie.cfm?parameter=1285. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- ^ "Stadt Graz: Sister Cities". http://www.graz.at/cms/beitrag/10099866/606819. Retrieved 2008-12-01.
- ^ (Norwegian)Trondheims offisielle nettsted - Vennskapsbyer
- "Graz: Stadtplanung und Stadtentwicklung (Rechnungshofbericht, 2006) in German" (PDF). 2006. http://www.rechnungshof.gv.at/fileadmin/downloads/Teilberichte/Steiermark/Steiermark_2006_02/Steiermark_2006_02_1.pdf. Retrieved 2008-04-08.
External links
Official websites
- Municipal data for Graz. In: Statistik Austria.
- Graz travel guide from Wikitravel
- City website (German) (English)
- Searchable map of Graz
- Graz Tourism Office
- KulturServerGraz Town's cultural portal
- tramway in Graz
History
- Jews in Graz. Expelled 1439 - returned 1447 - expelled 1496 - returned 1783 - holocaust (from Encyclopaedia Judaica 1971)
Further information
- Various Graz Information Sorted by Categories. Choose from 5 languages.
 Cities and districts (Bezirke) of Styria
Cities and districts (Bezirke) of StyriaCities Graz
Districts Bruck an der Mur • Deutschlandsberg • Feldbach • Fürstenfeld • Graz-Umgebung • Hartberg • Judenburg • Knittelfeld • Leibnitz • Leoben • Liezen • Mürzzuschlag • Murau • Radkersburg • Voitsberg • WeizAdministrative seats of Austrian states 

European Capitals of Culture 1985 Athens · 1986 Florence · 1987 Amsterdam · 1988 West Berlin · 1989 Paris · 1990 Glasgow · 1991 Dublin · 1992 Madrid · 1993 Antwerp · 1994 Lisbon · 1995 Luxembourg City · 1996 Copenhagen · 1997 Thessaloniki · London 1998 Stockholm · 1999 Weimar · 2000 Reykjavík · Bergen · Helsinki · Brussels · Prague · Kraków · Santiago de Compostela · Avignon · Bologna · 2001 Rotterdam · Porto · 2002 Bruges · Salamanca · 2003 Graz · 2004 Genoa · Lille · 2005 Cork · 2006 Patras · 2007 Luxembourg City and Greater Region · Sibiu · 2008 Liverpool · Stavanger · 2009 Linz · Vilnius · 2010 Essen · Istanbul · Pécs · 2011 Turku · Tallinn · 2012 Maribor · Guimarães · 2013 Košice · Marseille · 2014 Umeå · Riga · 2015 Mons · Plzeň · 2016 San Sebastián · Wrocław
World Heritage Sites in Austria East Cultural Landscape of Fertő / Neusiedlersee1 · Cultural Landscape of Wachau · Historic Centre of Vienna · Palace and Gardens of Schönbrunn · Semmering railway2
South Cultural Landscape of Hallstatt-Dachstein Salzkammergut2 · Historic Centre of the City of Graz and Schloss Eggenberg · Semmering railway2
West Cultural Landscape of Hallstatt-Dachstein Salzkammergut2 · Historic Centre of the City of Salzburg · Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps3
1 Shared with Hungary · 2 Shared with other region/s · 3 Shared with France, Germany, Italy, Slovenia and SwitzerlandCategories:- Cities and towns in Styria
- Graz
- World Heritage Sites in Austria
- European Capitals of Culture
- History of Slovenia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.